Communication method Two-wire, half-duplex transmission
Synchronous method Start stop synchronous system
Transmission line Shielded twisted-pair cable or VCTF
Transmission
code
Computer link ASCII
General-purpose serial
communication
ASCII, Binary
MODBUS RTU Binary
Communicati
on format (to
be set by
system
register)
Note4)
Data length 7 bits / 8 bits
Parity None/Even/Odd
Stop bit 1 bit / 2 bits
Start code STX/No STX
End code CR/CR+LF/None/ETX
No. of connected units
Note2) 5)
Max. 99 units
(Max. 32 units when our C-ENT adapter is connected.)
Communication function
Computer link (master/slave)
Modem initialization
General-purpose serial communication
Modbus RTU (Master/Slave)
PC(PLC) link
Note1) When connecting a commercially available device that has an RS485 interface, please confirm
operation using the actual device. In some cases, the number of units, transmission distance, and
baud rate vary depending on the connected device.
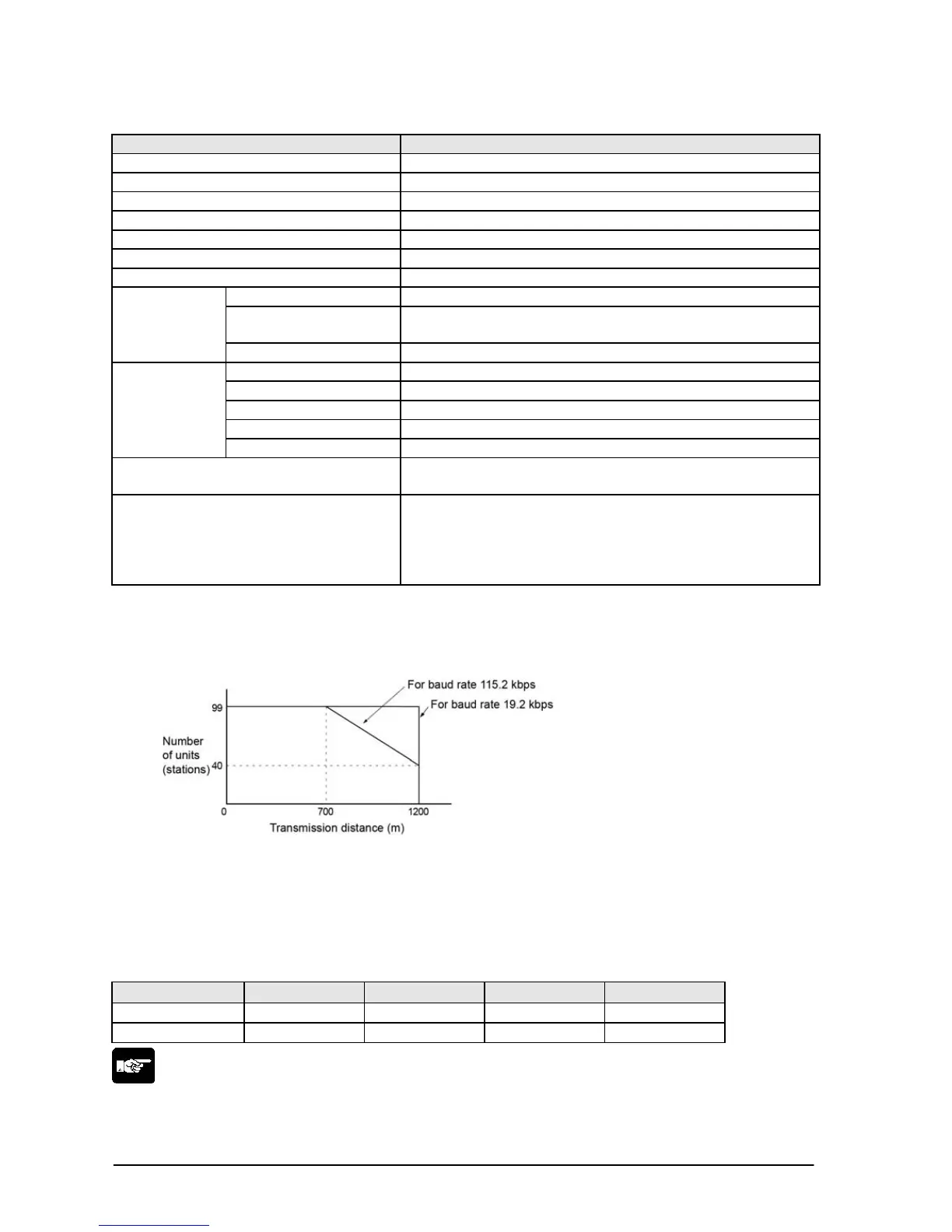
Note2) The values for the transmission distance, baud rate and number of units should be within the
values noted in the graph below.
Note3) The settings of the baud rate switches on the side of the unit and the system register No. 415
should be the same. Only 19200 bps can be specified when the C-NET adapter is connected with
the RS485 interface.
Note4) The start code and end code can be used only in the general-purpose serial communication
mode.
Note5) Unit numbers should be registered by the system register.
Factory default settings
Port type
Baud rate Data length Parity Stop bit
Tool port 9600 bit/s 8 bits Odd 1 bit
COM port 115200 bit/s 8 bits Odd 1 bit
Note:
If the potential difference between the power supplies of RS485 devices exceeds 4 V, the unit may not
communicate as it is the non-isolated type. The large potential difference leads to the damage to the
devices.

 Loading...
Loading...











