Mfr’s value: 1
When F106=2, the function of F137 is valid.
To compensate low-frequency torque controlled
by V/F, output voltage of inverter while
low-frequency should be compensated.
When F137=0, linear compensation is chosen
and it is applied on universal constant-torque
load;
When F137=1, square compensation is chosen
and it is applied on the loads of fan or water
pump;
When F137=2, user-defined multipoint
compensation is chosen and it is applied on the
special loads of spin-drier or centrifuge;
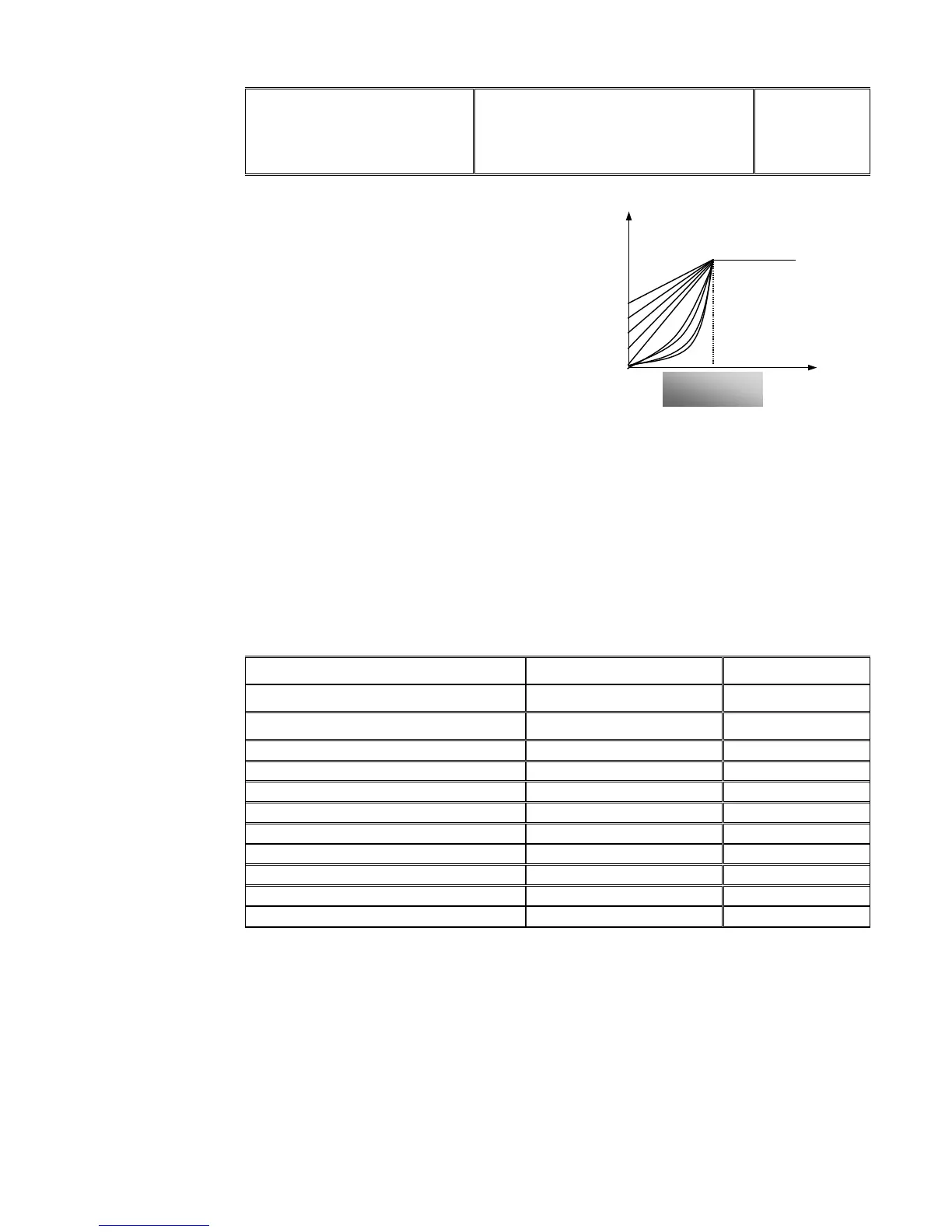
Figure 9-3 Torque Promotion
This parameter should be increased when the load is heavier, and this parameter should be
decreased when the load is lighter.
If the torque is elevated too much, the motor overheats easily, and the current of inverter will be
too high. Please check the motor while elevating the torque.
When F137=3, auto torque compensation is chosen and it can compensate low-frequency
torque automatically, to diminish motor slip, to make rotor rotary speed close to synchro rotary
speed and to restrain motor vibration. Customers should correctly set motor power, rotary
speed, numbers of motor poles, motor rated current and stator resistance. Please refer to the
chapter “Operation process of measuring motor parameters”.
F140 User-defined frequency point F1
Setting range: 0~F142
Mfr’s value: 1.00
F141 User-defined voltage point V1
Setting range: 0~100%
Mfr’s value: 4
F142 User-defined frequency point F2
Setting range: F140~F144
Mfr’s value: 5.00
Multi-stage V/F curves are defined by 12 parameters from F140 to F151.
The setting value of V/F curve is set by motor load characteristic.
Note: V1<V2<V3<V4<V5<V6,F1<F2<F3<F4<F5<F6.As low-frequency, if the setting voltage is too
high, motor will overheat or be damaged. Inverter will be stalling or occur over-current
protection.

 Loading...
Loading...