56 / 92
Siemens Actuators SAX.., SAY.., SAV.., SAL.. for valves CE1P4040en
Building Technologies Functions and control 2018-12-05
4.2 Modulating control
The modulating positioning
signal drives the actuator
steplessly. The positioning
signal range
(DC 0...10 V / DC 4...20 mA,
0...1000 Ω) corresponds in a
linear manner to the positioning
range (fully closed...fully open,
or 0…100% stroke).
The actuator is driven via
connection terminal Y or forced
control Z (page 66). The
required stroke / rotation is
transferred to the valve’s stem /
spindle.
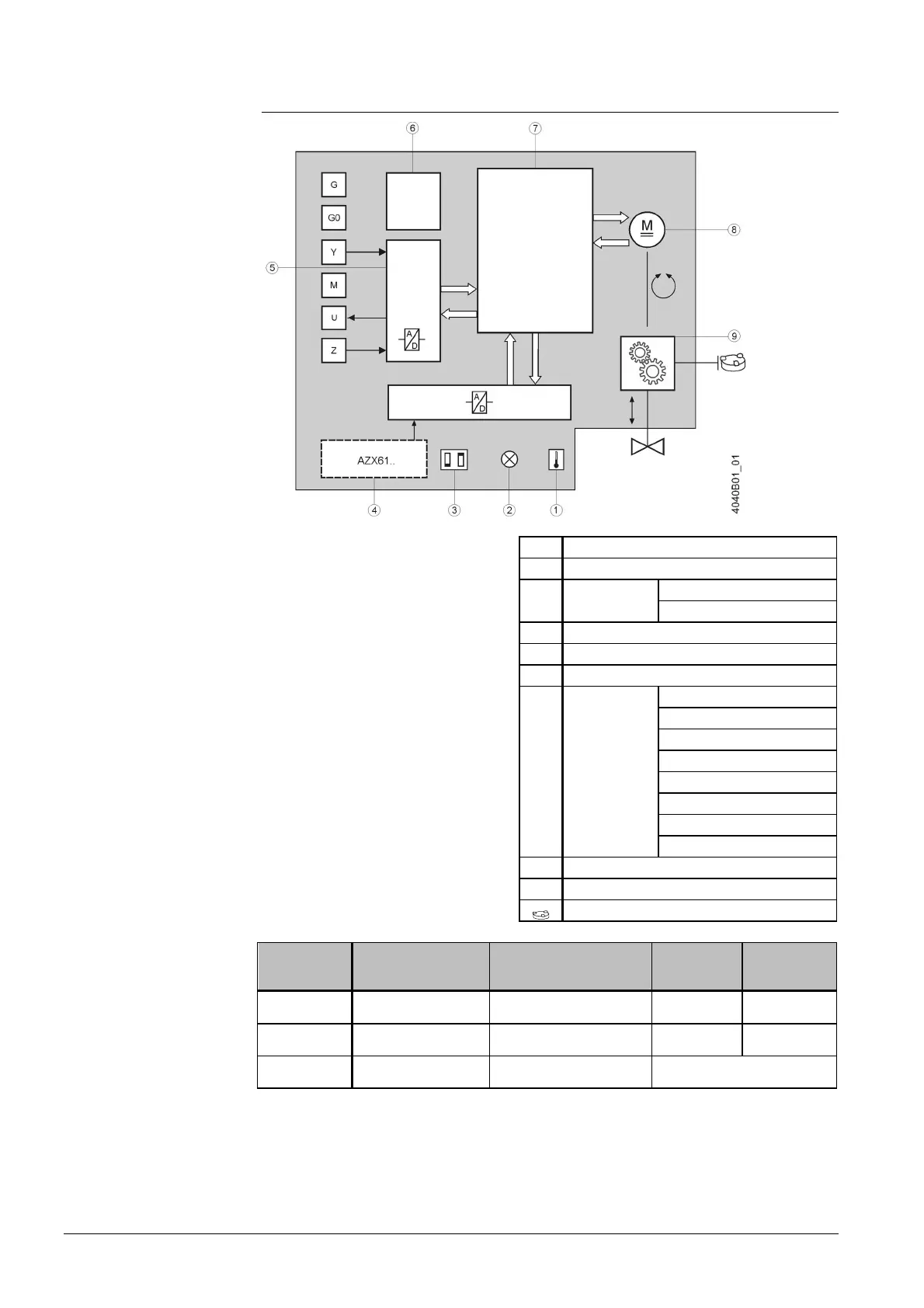
1 Calibration slot
2 LED (2 colors)
3 DIL switches
Changeover of characteristic
Positioning signal
4 Function module
5 A/D conversion
6 Power supply
7
Control
functions
Identification of seat
Position control
Motor control
Detection of foreign bodies
Calibration
Forced control
Characteristics function
Manual adjustment
8 Brushless DC motor
9 Gear train
Manual adjuster
Positioning
signal
Stroke actuator Rotary actuator
Control
path valve
AàAB
Bypass
valve
B à AB
Signal Y, Z
increasing
Actuator’s stem
extends
Actuator’s spindle turns in
clockwise direction
Opening Closing
Signal Y, Z
decreasing
Actuator’s stem
retracts
Actuator’s spindle turns in
counterclockwise direction
Closing Opening
Signal Y, Z
constant
Actuator’s stem
maintains the position
Actuator’s spindle
maintains the position
Maintains the position
· If function module AZX61.1 is used, observe the information given in chapter
"Changeover of acting direction" (page 59).
· Observe the information given in chapter "Acting direction and flow
characteristic" on page 61.
Notes

 Loading...
Loading...











