Cycle and response times
7.2 Cycle time
7.2.3 Different cycle times
Overview
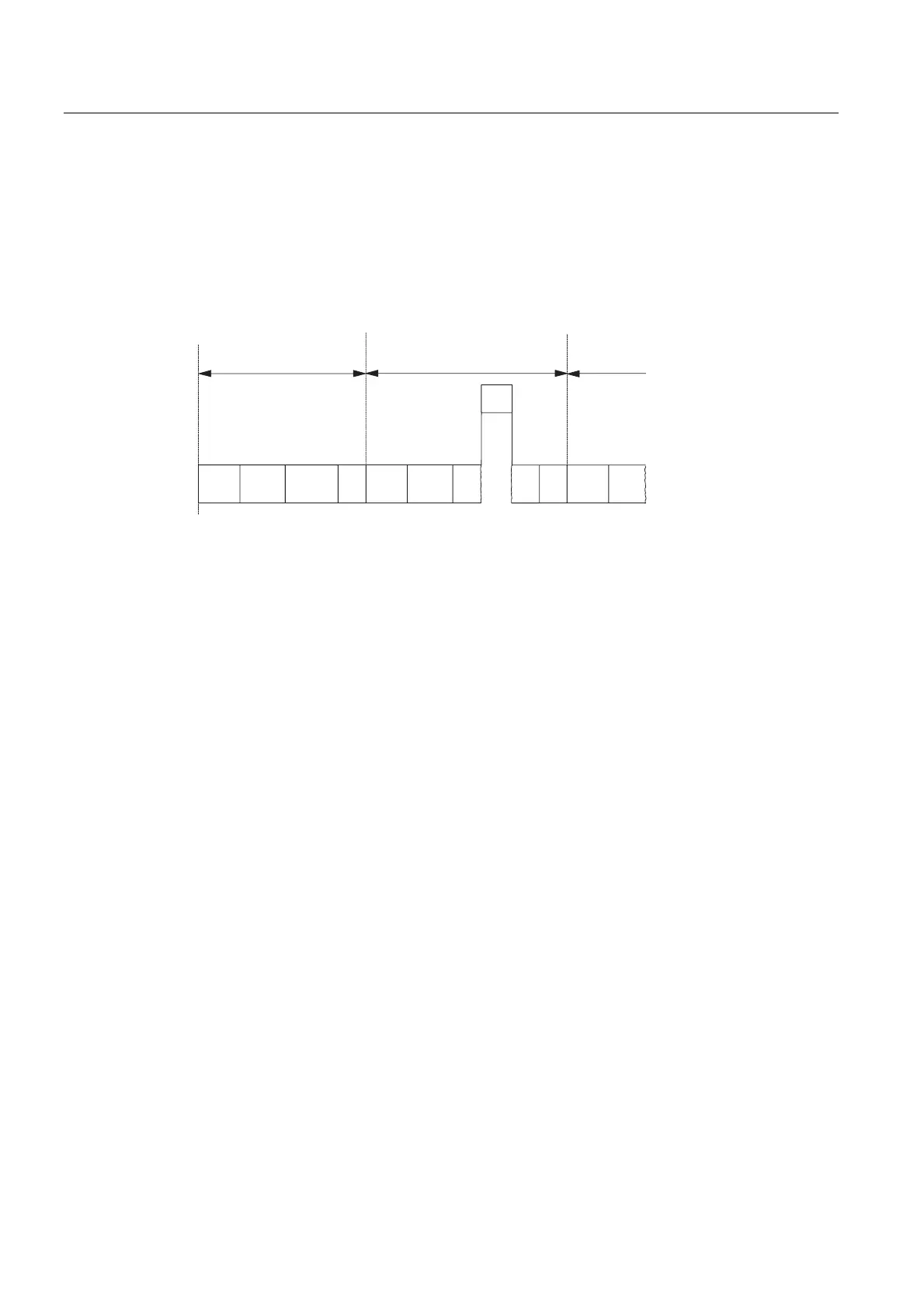
The length of the cycle time (T
cyc
) is not identical in each cycle. The following figure shows
different cycle times, T
cyc1
and T
cyc2
. T
cyc2
is longer than T
cyc1
, because the cyclically scanned
OB 1 is interrupted by a time-of-day interrupt OB (here, OB10).
2%
T
2%
PIO PII
6&&
OB
PIO
PII
-
6&&
OB
7
PIO
3,,
&XUUHQWF\FOH
XSGDWH XSGDWH XSGDWH XSGDWH XSGDWH XSGDWH
1H[WF\FOH
1H[WF\FOH
F\F F\F
Figure 7-2 Different cycle times
Block processing times may fluctuate
Fluctuation of the block processing time (e.g. OB 1) may also be a factor causing cycle time
fluctuation, due to:
• Conditional instructions,
• Conditional block calls,
• Different program paths,
• Loops, etc.
Maximum Cycle Time
In
STEP 7
you can modify the default maximum cycle time. If this time has expired, OB 80 is
called, and in it you can define how you want the CPU to respond to the time error.
The CPU switches to STOP mode if OB80 does not exist in its memory.
S7-300 CPU Data: CPU 315T-2 DP
7-6 Manual, 12/2005, A5E00427933-02

 Loading...
Loading...











