Notes on Configuration
S7-GRAPH for S7 300/400 Programming Sequential Control Systems
14-2 C79000-G7076-C526-01
Enable
operation
Modes
Hydraulics
Pneumatics
Save
,
remove
Conveyor belt
Motor
memory
Coolant
Cell level
Coordination
level
Function or
unit level
General
Utilities
Station n: Save
Turn
Insert
,
weld
Clamp
Centere
Station 1: Insert
Turntable
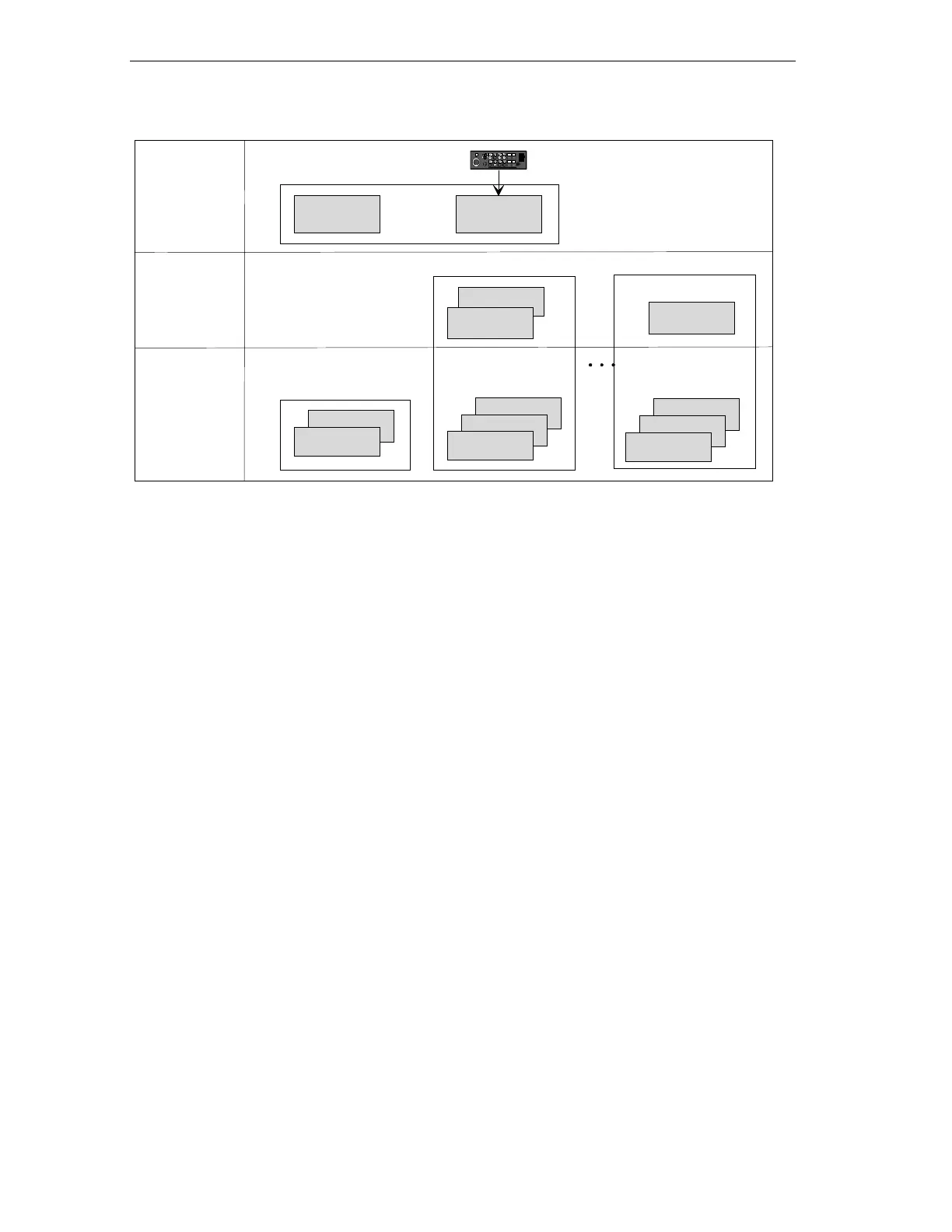
The individual levels have the following significance:
• Cell level
The cell level encompasses functions with a central or wider reaching
significance, for example preparations for enabling operation and modes.
The blocks at the cell level provide signals that are relevant for all blocks of the
coordination and unit level in this cell.
• Coordination level
The coordination level includes various coordination functions, for example for
the automatic mode and retraction following a break in operation. For each
station, at least one sequencer is required for coordination at this level.
• Unit level
The unit level includes functions for activating individual units of equipment, for
example motors and valves. This includes all the lower-level functions, for
example interlocks and supervision conditions independent of the sequencer
and direct manual intervention in the operation of the units.
Specifying the Program Structure and Incorporating the Sequencer
For each sequencer, S7-Graph creates an FB with its instance DB. This S7-Graph
FB must be called in a block (for example OB, FB or FC). Since other programs are
normally required along with the programs created by S7-Graph, it is usually the
best policy to call all the FBs created by F7 Graph in one block (FC or FB) as
shown in the following example.
 Loading...
Loading...











