AMI Trides
Product Description
A-96.250.111 / 211019 11
Measuring
principle
3-electrode amperometry:
The sensor consists of two platinum electrodes and a reference
electrode. A voltage is applied between the measuring electrode
(platinum rod) and the counter electrode (platinum ring) of the tri-
des sensor. The disinfectant in the sample generates a small cur-
rent between the electrodes, which is proportional to the
disinfectant concentration. The reference electrode controls the
voltage and guarantees optimal measuring conditions on the plati-
num sensor.
For optimal sensitivity, a rotor continuously cleans the surfaces of
the platinum electrodes (hydrodynamic cleaning). A Hall-effect sen-
sor measures the rotations of the rotor to detect if there is sufficient
flow.
The signal of amperometric systems depends on flow. The flow cell
with constant head excludes all flow effects if the sample always
overflows into the longer constant head tube.
Temperature compensation is done automatically.
About free
chlorine
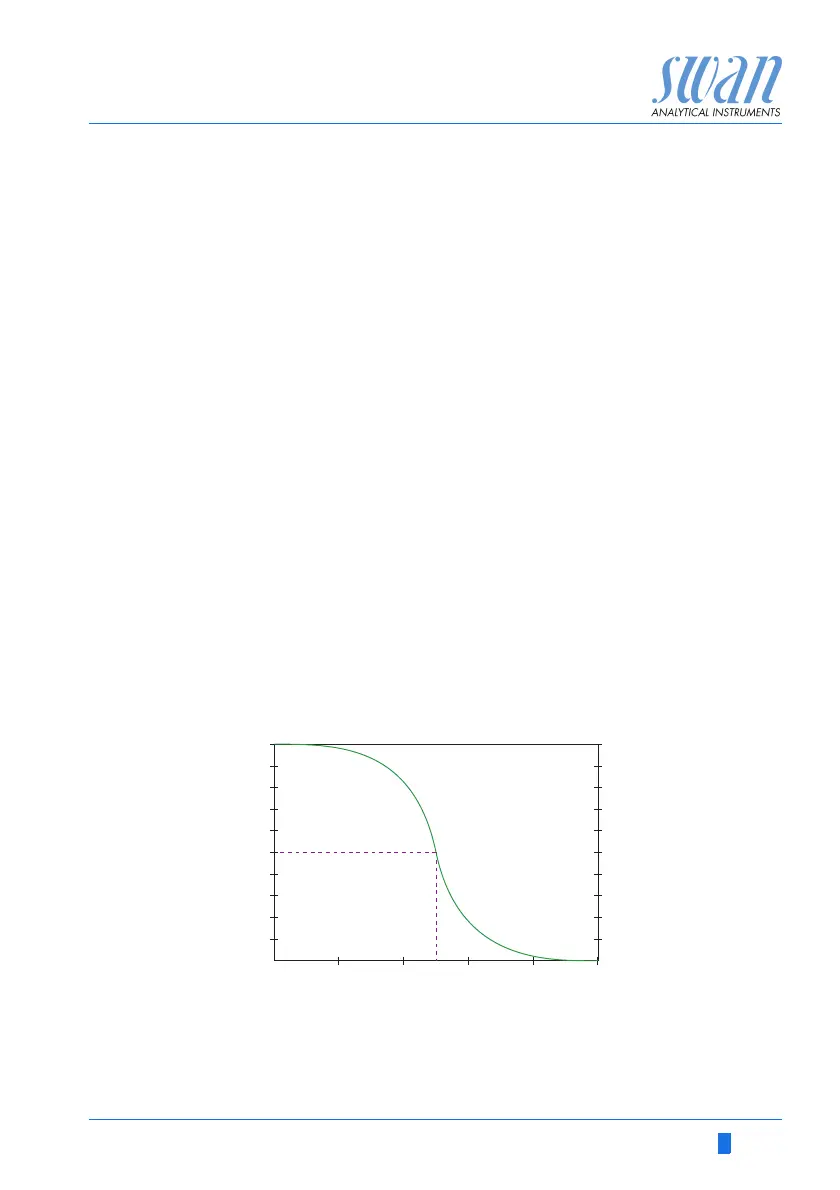
If chlorine is dissolved in water, it decomposes into hypochlorous
acid and hypochlorite. Free chlorine = hypochlorous acid + hypo-
chlorite. The ratio depends on the pH value.
At pH 7: 77% hypochlorous acid, 23% hypochlorite
At pH 8: 25% hypochlorous acid, 75% hypochlorite
The hypochlorous acid is a much better disinfectant than hypochlo-
rite. This means the efficiency of disinfection depends on pH value.
y
1
% HOCL (hypochlorous acid)
y
2
% Disinfection
a
1
, a
2
Sensitivity of electrochemical measurement in %
The DPD test always indicates free chlorine.
100
y
1
a
1
a
2
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
5678 910
pH
0
100
y
2
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
 Loading...
Loading...