88 Appendix B: Theory of Operation
The concept for direct-digital phase-noise measurements is shown in Figure B-2.
Figure B-2: The RF signals are immediately converted to digital samples in order to perform direct-digital phase-noise
measurements.
B.2 Theory
The analog-to-digital converters have 14 bits of precision and maximum sampling rates of
80 MHz. In order to prevent harmonics, spurs, and noise from aliasing into the measured
spectrum, a 30 MHz analog anti-alias filter is employed before the RF signals are sampled. The
heart of the approach is the down converter that immediately follows the sampler. In-phase
samples of each input signal are multiplied by the sine and cosine of a synthesized local oscillator
and low-pass filtered. When the LO frequency is approximately equal to the input frequency, the
output of the filters are in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) base-band samples. The phase difference
between the input signal and the synthesized LO is computed using the arctangent function as
shown in Figure B-3.
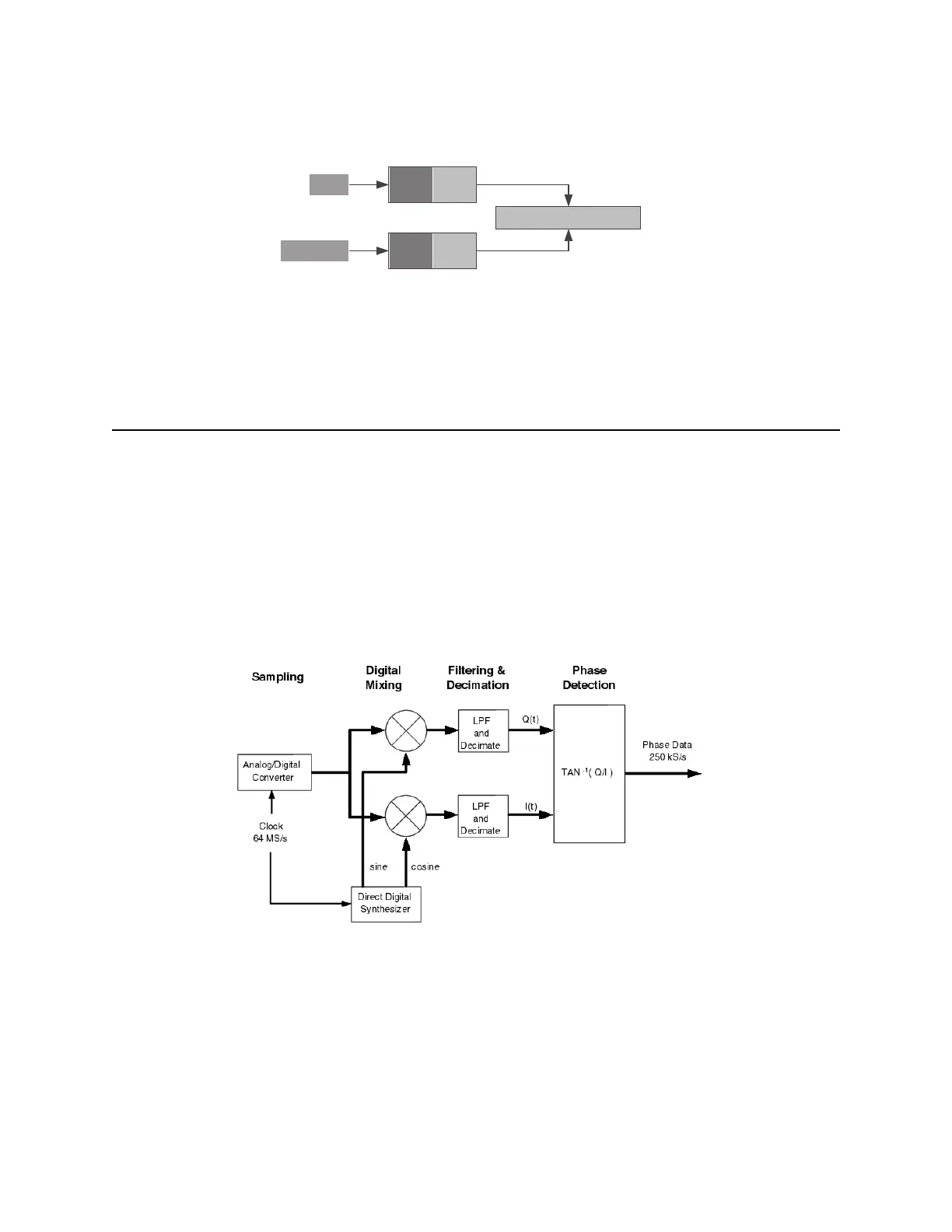
Figure B-3: A local oscillator synthesized from the internal clock down-converts the input to base-band where the
samples are used to compute the phase difference between the LO and the input.
This step is the heart of the direct-digital technique. It is not necessary to down-convert to DC
before computing the phase difference. A small DC offset causes the phase to accumulate nearly
linearly. Although the arctangent function repeats every π radians, it is possible to unwrap the
phase and recover the correct linear function. This should be contrasted with the analog approach.
The double balanced mixer produces a distorted sine function of the phase difference. As the two
inputs approach the in-phase condition, the output of the mixer is insensitive to the phase
difference between the signals, and the distortion makes it impossible to accurately compute the
Analog/Digital
Converter
Analog/Digital
Converter
Input
Reference
Digital Signal Processing

 Loading...
Loading...