© Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
BSSID: MAC address of the SSID
SSID Advertise: Select to broadcast SSID.
4. See section Secure your wireless network to configure wireless security settings.
Additional Wireless Settings
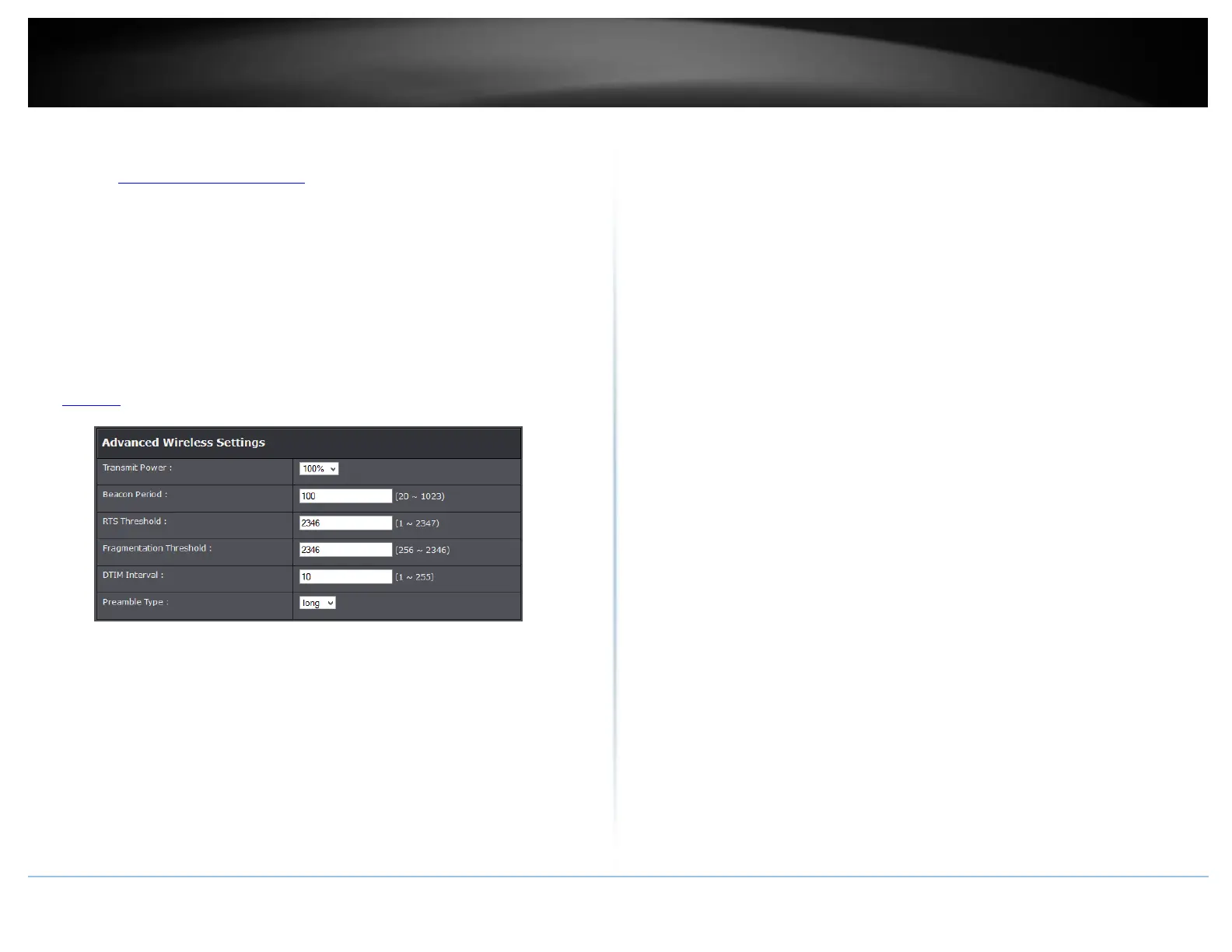
Advanced > Advanced Wireless
These settings are advanced options that can be configured to change advanced
wireless broadcast specifications. It is recommended that these settings remain set to
their default values unless you are knowledgeable about the effects of changing these
values. Changing these settings incorrectly can degrade performance.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page”
on page 23).
2. Click on Advanced, and click on Advanced Wireless. Click Apply to save settings.
Transmit Power: The wireless transmit power can be modified to a lower setting
such as 50%, 25%, and 12% if necessary. Lowering the wireless transmit may help to
better stabilize the wireless connectivity and reduce the effects of wireless
interference in areas where there are several 2.4GHz wireless devices. (Default:
100%)
Beacon Interval: A beacon is a management frame used in wireless networks that
transmitted periodically to announce the presence and provide information about
the router’s wireless network. The interval is the amount time between each
beacon transmission.
Default Value: 100 milliseconds (range: 1-1000)
RTS Threshold: The Request To Send (RTS) function is part of the networking
protocol. A wireless device that needs to send data will send a RTS before sending
the data in question. The destination wireless device will send a response called
Clear to Send (CTS). The RTS Threshold defines the smallest data packet size
allowed to initiate the RTS/CTS function.
Default Value: 2346 (range: 256-2346)
Fragment Threshold: Fragmentation in wireless networks is the process of breaking
down data communications into smaller data packets in order to improve data
efficiency when transferring or receiving data between wireless devices. The
fragmentation threshold defines the maximum size of the data packets that are
broken down.
DTIM Interval: Is the interval of when the access point informs the clients about the
presence of buffered multicast/broadcast data.
Preamble Type: Select long or short preamble.
Wireless bridging using WDS (Wireless Distribution System)
Advanced > Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz) > WDS
Wireless bridging using WDS allows the device to create a wireless bridge with other
WDS supported wireless routers and access points configured in WDS mode to bridge
groups of network devices together wirelessly. Simultaneously, the router will also
function in access point mode allowing wireless client devices such as computers, game
consoles, mobile phones, etc. to connect in order to access network resources from
multiple groups of network devices as well as the Internet.
Note: You can create up to four WDS bridge connections on each wireless band (2.4GHz
and 5GHz). WDS (Wireless Distribution System) is not currently standardized and may
not connect to different model wireless routers or access points, therefore, when using
WDS, it is recommended to use the same model and version for wireless bridging.
By default, your router functions in Access Point mode to allow wireless client devices to
connect and access your network resources and access the Internet.
The diagram below shows your router in Access Point mode and clients connecting to
your router.

 Loading...
Loading...











