RADIATION THEORY
A more detailed discussion of radiological theory can be found in
the Troxler Nuclear Gauge Safety Training Program manual,
provided at the Troxler safety class.
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
All materials consist of chemical elements that can not decompose
by ordinary chemical methods. Some examples are:
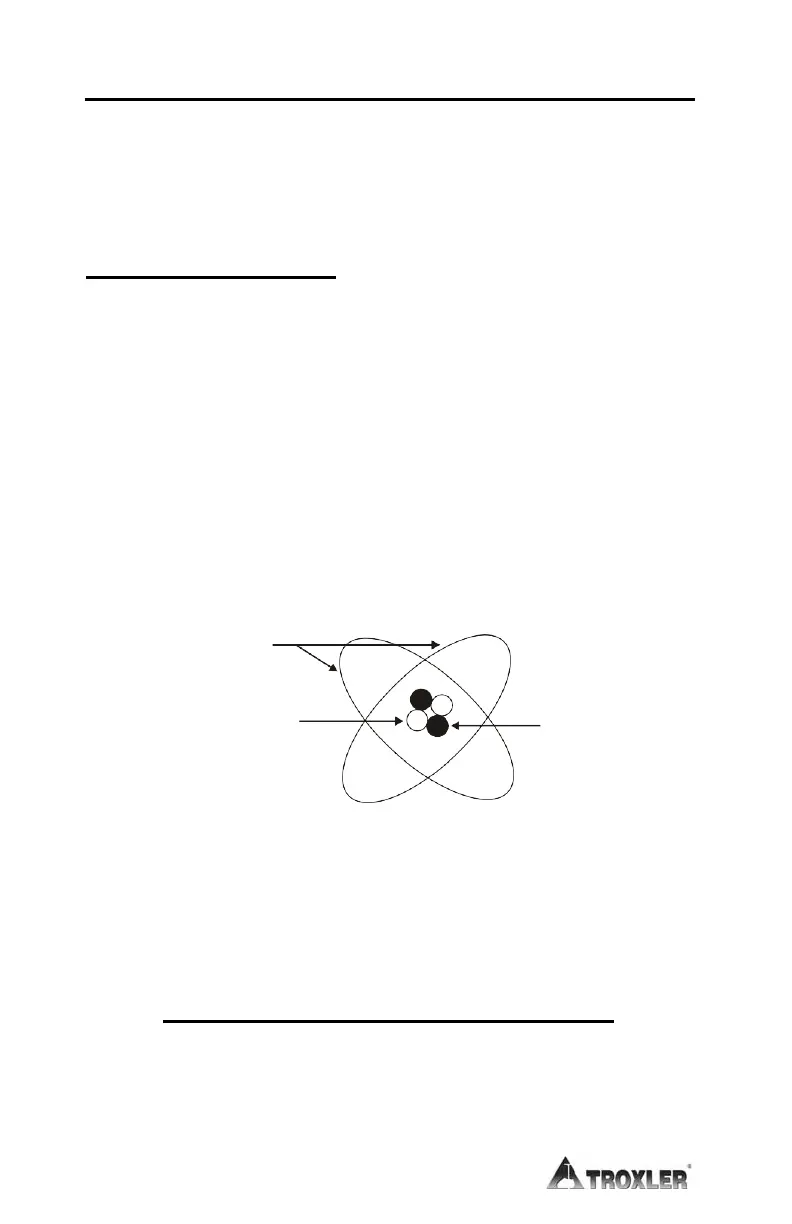
Each element contains an atom with a unique structure. The atom
consists of protons, neutrons, and electrons (Figure A-1). The
protons and neutrons are grouped together in the nucleus. The
electrons orbit the nucleus. An atom is normally electrically neutral
because the positive charge of the protons cancels out the negative
charge of the electrons.
ELECTRONS
NEUTRON
PROTON
Figure A-1. Diagram of an Atom
Protons carry a positive charge and are described as having a mass
of one. Neutrons have no charge and also have a mass of one.
Electrons carry a negative charge and essentially have no mass.
MASS
(ATOMIC WEIGHT SCALE)
CHARGE
Protons 1.0073 +1
Neutrons 1.0087
0
 Loading...
Loading...











