Chapter 1 11
Introduction and Measurement Theory
Fault Location Measurement Theory
Typically, fault location measurement results are expressed in one of four ways:
Format Description
Return Loss
(RL)
The number of dB that the reflected signal is below the
incident signal. Its relationship to the reflection
coefficient (ρ) is described by the following formula:
RL = −20 log ρ.
Reflection
Coefficient (ρ)
The ratio of the reflected voltage wave to the incident
voltage wave.
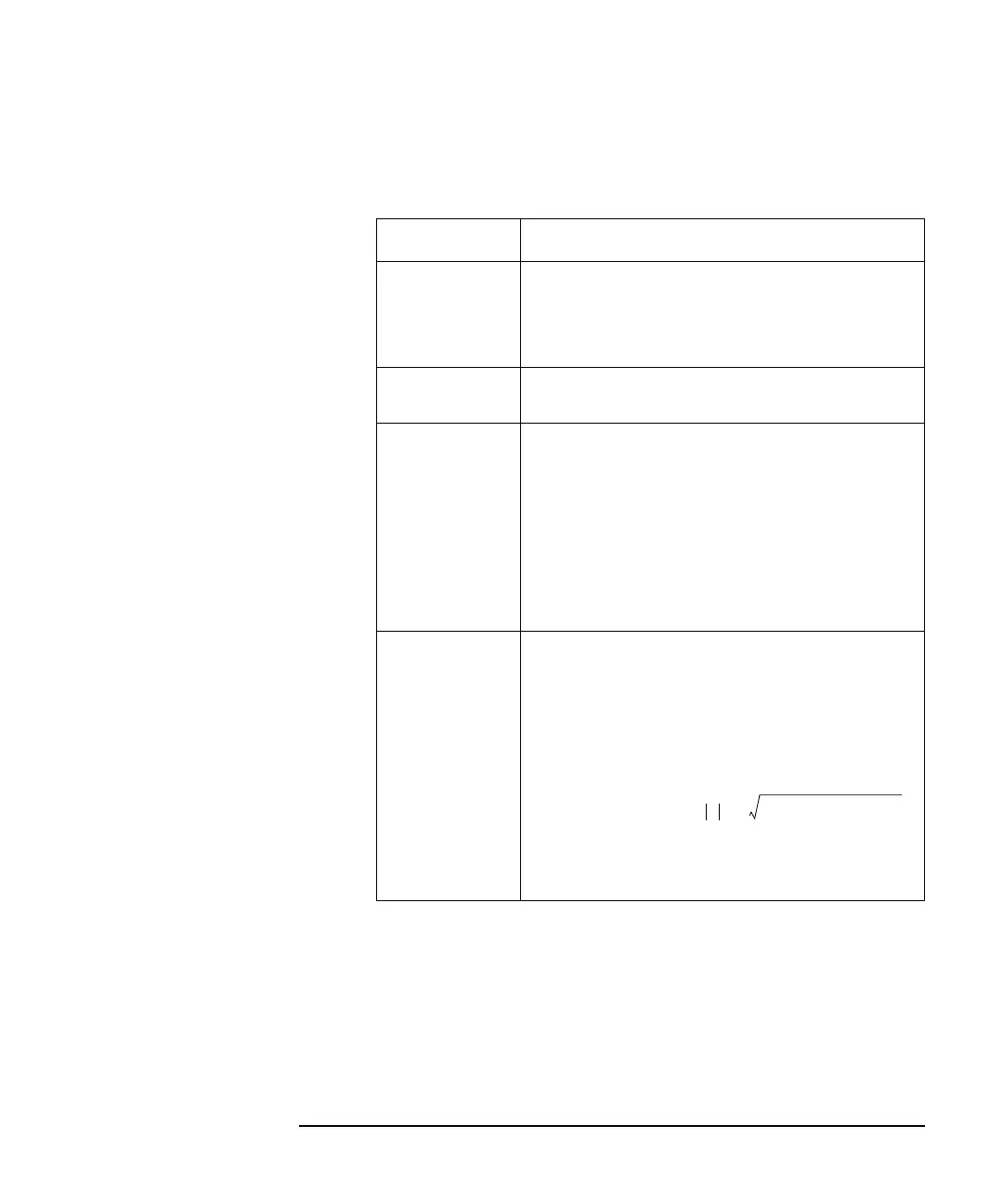
Standing Wave
Ratio (SWR)
Any two waves traveling in opposite directions (the
incident and reflected for example) cause a “standing
wave” to be formed on the transmission line. SWR is
defined as the maximum voltage over the minimum
voltage of the standing wave. SWR can also be
mathematically derived from the reflection coefficient
(ρ) with the following formula:
Impedance
Magnitude
The magnitude of the complex impedance at each
measurement point. See “How to Display
Impedance” on page 74 for information on making
impedance measurements.
ImpedanceMagnitude Z Z
2
real
Z
2
imaginary
+==
 Loading...
Loading...