MODULE POWER REQUIREMENTS
SIZING THE MODULAR POWER SYSTEM
I-E96-508C B - 9
QS(N+1) = if using N+1 redundancy, add 1 to the value of
QS(N)
NOTE:
The tables in Appendix D contain calculated values of Q1,
Q2, Q3 and QF for various load combinations. These tables enable
you to size the modular power system without doing the sizing cal-
culations.
System Calculation Example Using IEPDS01 and IEPDF01, or IEPDS02 and IEPDF02 Power
Modules
Assume that the current requirements for a set of modules
residing in a system cabinet has been calculated.
Additionally, the current requirements for 24 VDC I/O power
was:
A = 26.5 amps (5 VDC cabinet requirement)
B = 12 amps (24 VDC associated I/O requirement)
C = 0.9 amps (+15 VDC cabinet requirement)
D = 0.4 amps (-15 VDC cabinet requirement)
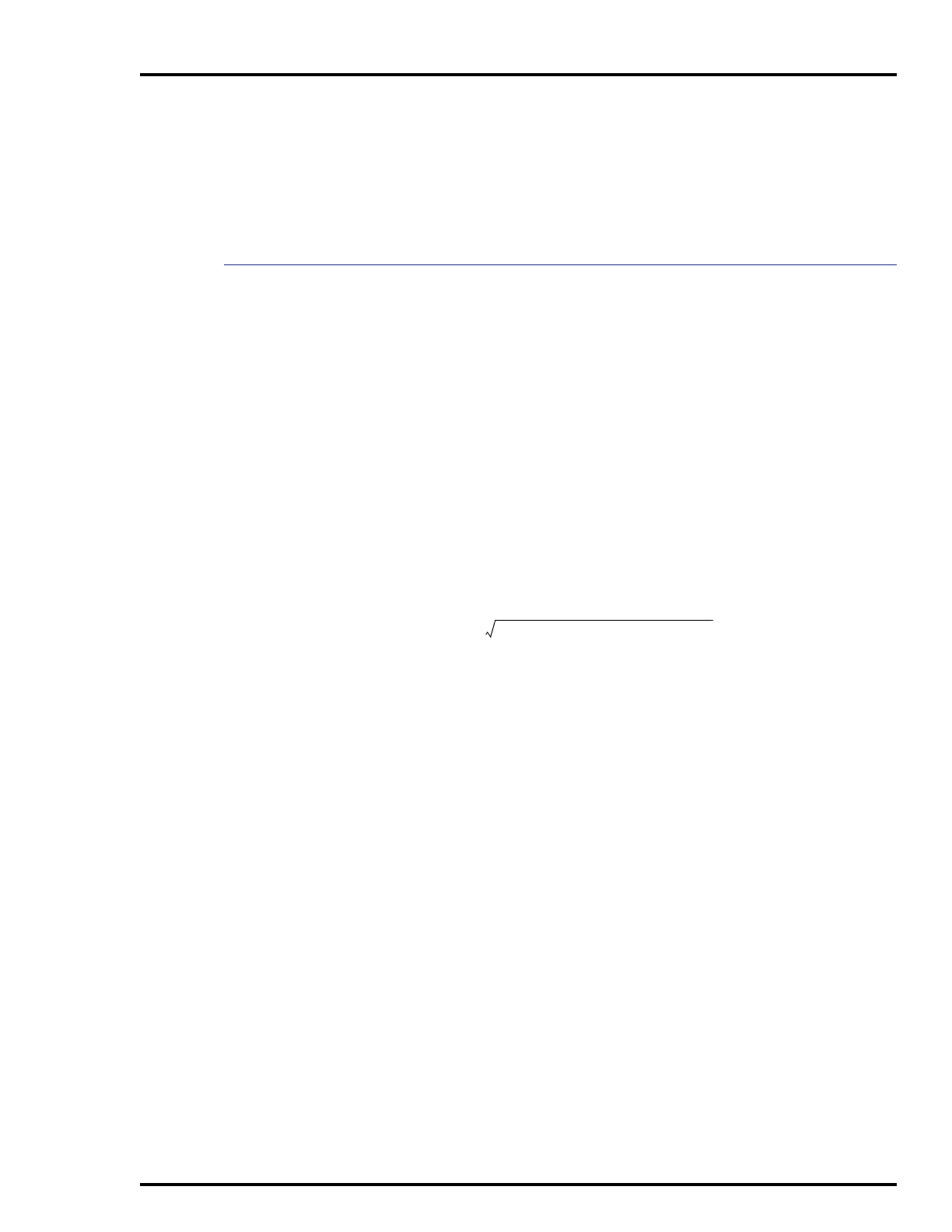
Substitute these values into the equation and solve for Q.
Q1 =
Q1 = 2.76
Q2 = 0.9/0.5
Q2 = 1.8
Q3 = 0.4/0.5
Q3 = 0.8
QS = Largest of Q1, Q2 and Q3
QS = 2.76
Round the value of QS to the next highest integer. This is the
number of PDS power modules required for system.
QS(N) = 3 PDS modules
Calculate the value of QF
QF = 12 x[5/(20 - 26.5/3)] - 3
QF = 2.37
Round the value of QF to the next highest integer. This is the
number of PDF power modules required to power associated
I/O current requirements.
QF(N) = 3 PDF modules
26.5 12×()80 26.5
2
1600⁄+⁄ 26.5 40⁄
+
 Loading...
Loading...