Broadcom Gigabit Ethernet Teaming ServicesNetXtreme User Guide
Broadcom
®
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 123
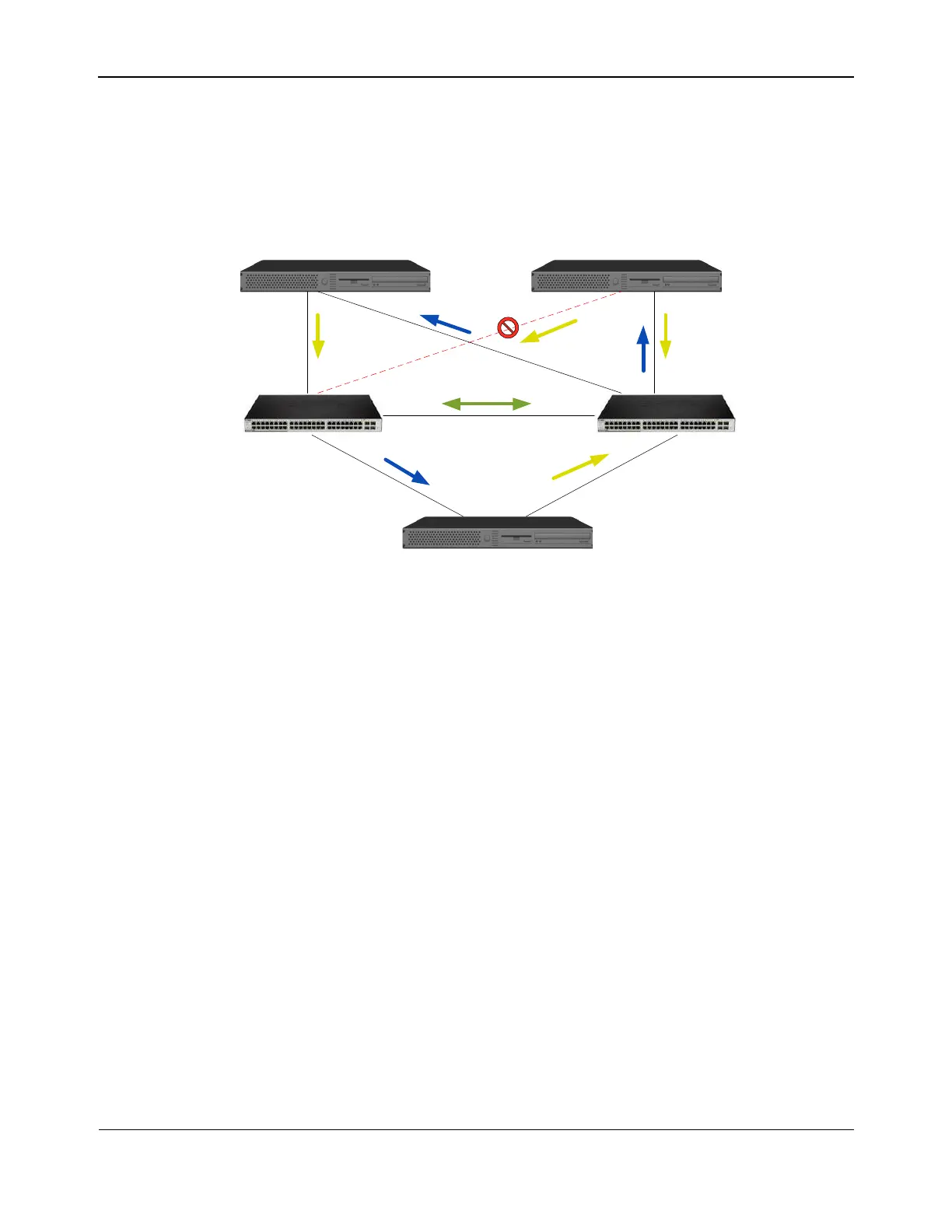
Figure 7 represents a failover event in which the cable is unplugged on the Top Switch port 4. This is a
successful failover with all stations pinging each other without loss of connectivity.
Figure 7: Failover Event
Spanning Tree Algorithm
• Topology Change Notice (TCN)
• Port Fast/Edge Port
In Ethernet networks, only one active path may exist between any two bridges or switches. Multiple active paths
between switches can cause loops in the network. When loops occur, some switches recognize stations on both
sides of the switch. This situation causes the forwarding algorithm to malfunction allowing duplicate frames to
be forwarded. Spanning tree algorithms provide path redundancy by defining a tree that spans all of the switches
in an extended network and then forces certain redundant data paths into a standby (blocked) state. At regular
intervals, the switches in the network send and receive spanning tree packets that they use to identify the path.
If one network segment becomes unreachable, or if spanning tree costs change, the spanning tree algorithm
reconfigures the spanning tree topology and re-establishes the link by activating the standby path. Spanning tree
operation is transparent to end stations, which do not detect whether they are connected to a single LAN
segment or a switched LAN of multiple segments.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol designed to run on bridges and switches. The specification
for STP is defined in IEEE 802.1d. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not run into a loop situation
when you have redundant paths in your network. STP detects/disables network loops and provides backup links
between switches or bridges. It allows the device to interact with other STP compliant devices in your network
to ensure that only one path exists between any two stations on the network.
Blue
SLB Team
192.168.1.101
Gray
SLB Team
192.168.1.102
ARP Table
100 = 49:C9
102 = 5E:CA
ARP Table
100 = 49:C9
101 = 82:82
Red
SLB Team
192.168.1.100
Top Switch
CAM Table:
Eth 1: 82:83
Eth2: 49:C9
Eth 4: 5E:C9
Eth 24: 82:82
Eth 24:49:C8
Eth 24: 5E:CA
Eth 24: A2:A12*
Bottom Switch
CAM Table:
Eth 1: 82:83
Eth2: 49:C8
Eth 4: 5E:CA
Eth 24: 82:83
Eth 24: 49:C9
Eth 24: 5E:C9
Eth 24: B0:30
ARP Table
101 = 82:82
102 = 5E:CA
82:82 (P) 5E:C9 5E:CA (P)
4
2
49:C9(P) 49:C8
1
2
4
1
82:83
24 24
*Bottom Switch Port 24
MAC Address
*Top Switch Port 24 MAC
Address

 Loading...
Loading...