16
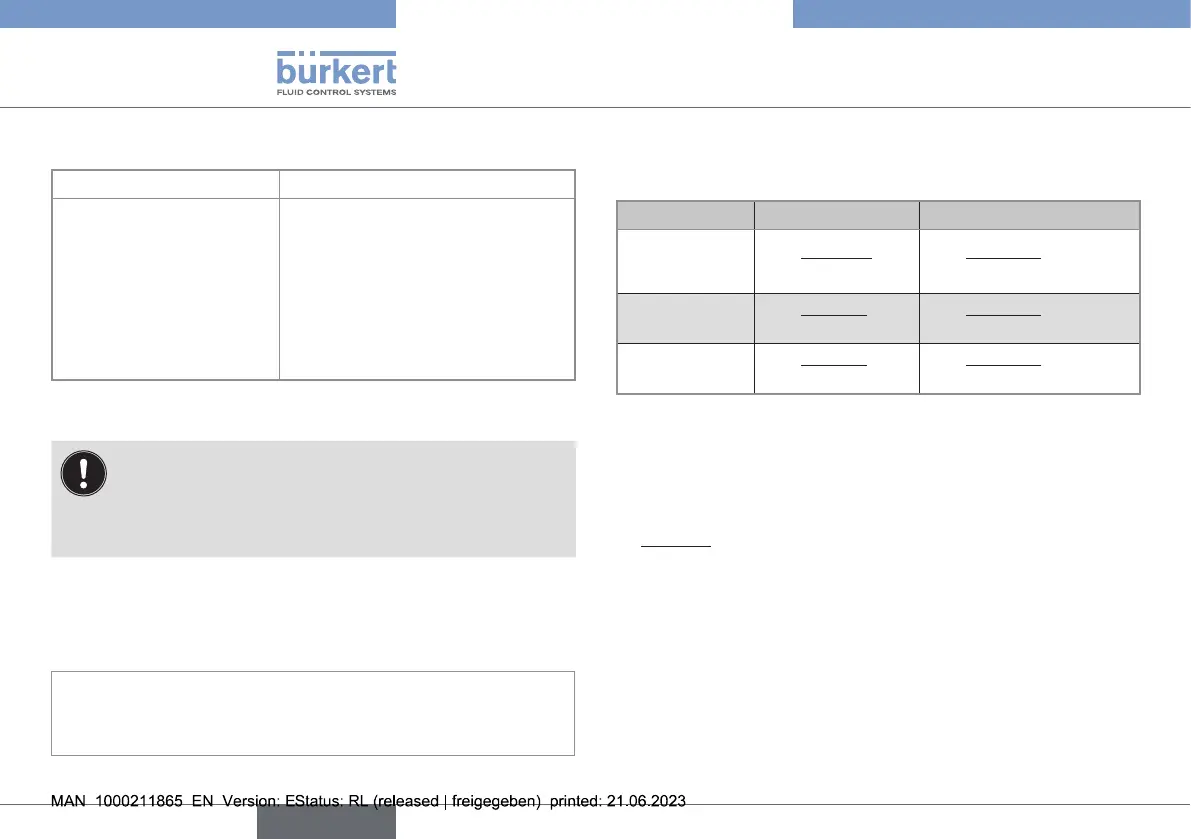
Technical data
The following formulae are used to calculate the K1 and K2
factors needed to convert the current or frequency into a ow
rate:
Full scale K-factor K
1
K-factor K
2
10 m/s
K
1
=
100
K
fitting
K
2
=
20
3*K
fitting
5 m/s
K
1
=
200
K
fitting
K
2
=
40
3*K
fitting
2 m/s
K
1
=
500
K
fitting
K
2
=
100
3*K
fitting
where K
fitting
=K-factor of the S020 tting used
Example:
If the full scale of the device is set to 5m/s, the value of the
current output will be:
I=40 Q + 4
3*K
tting
with I in mA, K
tting
in pulse/litre and Q in l/s.
6.7. Electrical connections data
Type of connection Through 2 M20x1.5 cable glands
▶ Cable type
▶ Cross section
▶ Diameter of each cable:
- if only one cable is
used per cable gland
- if two cables are
used per cable gland
▶ shielded
▶ 0.5...1.5mm
2
- 6...12mm
- 4mm, with the supplied
multi-way seal
6.8. K-factors
The S020 tting with weld end connections is available
in two versions: a version for the measuring devices with
a G2" nut and a version for the measuring devices with a
clamp connection.
Use the K-factor of the tting used.
The device measures the ow velocity (in m/s) of the uid and
converts it into a current (in mA) and a frequency rating (in Hz).
The current I or the frequency f are proportional to the ow rate
Q(l/s), the proportionality factor is called the "K-factor":
f = K
1
*Q
I = K
2
*Q + 4
with K
1
and K
2
in pulse/litre
english
Type 8041
 Loading...
Loading...