For example, add a zone called outside_zone.
e) Click the IPv4 and/or IPv6 tab.
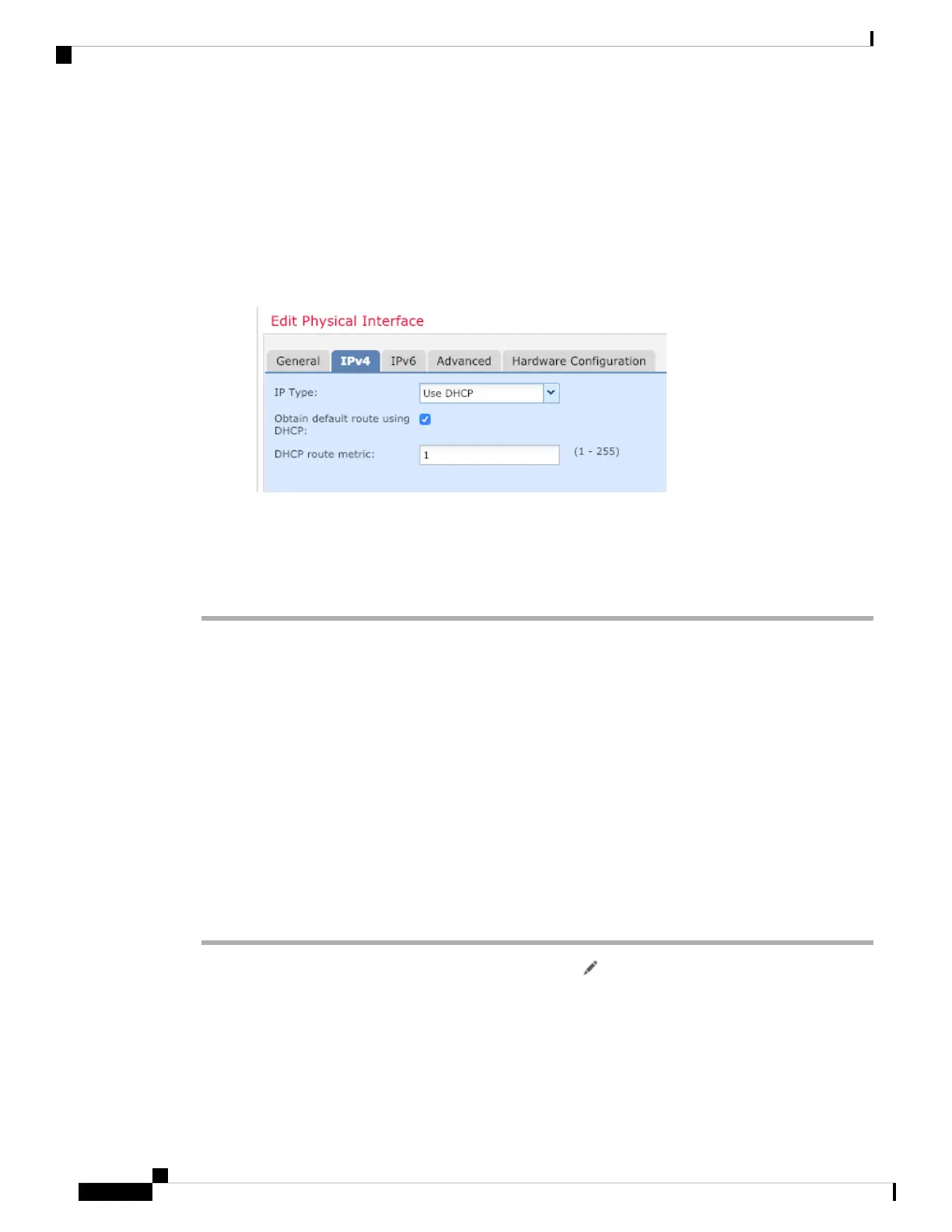
• IPv4—Choose Use DHCP, and configure the following optional parameters:
• Obtain default route using DHCP—Obtains the default route from the DHCP server.
• DHCP route metric—Assigns an administrative distance to the learned route, between 1 and
255. The default administrative distance for the learned routes is 1.
• IPv6—Check the Autoconfiguration check box for stateless autoconfiguration.
f) Click OK.
Step 7 Click Save.
Configure Interfaces (6.4)
Enable the threat defense interfaces, assign them to security zones, and set the IP addresses. Typically, you
must configure at least a minimum of two interfaces to have a system that passes meaningful traffic. Normally,
you would have an outside interface that faces the upstream router or internet, and one or more inside interfaces
for your organization’s networks. Some of these interfaces might be “demilitarized zones” (DMZs), where
you place publically-accessible assets such as your web server.
A typical edge-routing situation is to obtain the outside interface address through DHCP from your ISP, while
you define static addresses on the inside interfaces.
The following example configures a routed mode inside interface with a static address and a routed mode
outside interface using DHCP.
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Devices > Device Management, and click the Edit ( ) for the firewall.
Step 2 Click Interfaces.
Cisco Firepower 1010 Getting Started Guide
32
Threat Defense Deployment with the Management Center
Configure Interfaces (6.4)
 Loading...
Loading...
















