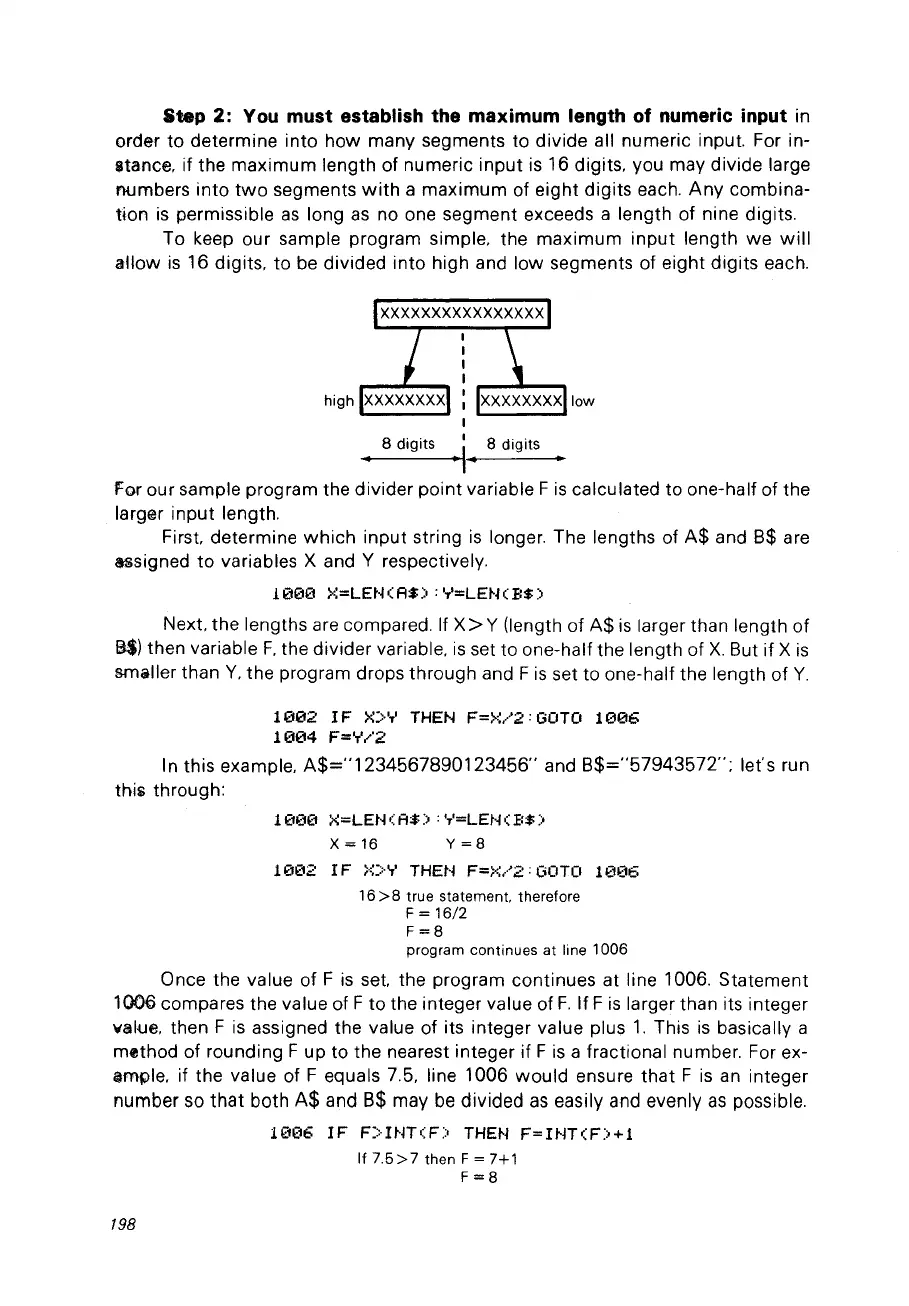
Step 2: Vou must establish the maximum length of numeric input in
order to determine into how many segments to divide ail numeric input. For in-
$tance, if the maximum length of numeric
input
is
16 digits,
Vou
may divide large
numbers into
two
segments
with
a maximum of eight digits each.
Any
combina-
tion
is
permissible
as
long
as
no one segment exceeds a length of nine digits.
To keep our sample program simple, the maximum input length
we
will
allow
is
16 digits, to be divided into high and low segments of eight digits each.
1
1
1
:~.....I
......
.....,
high 1
'-----'IL.-----'
8 digits
Il
8 digits
..
.'..
.
For our sample program the divider point variable F
is
calculated ta one-haIf of the
larger input length.
First
determine
which
input string
is
longer. The lengths of
A$
and B$ are
assigned to variables X and Y respectively.
1000
X=LEN(A$):Y=LEN(B$)
Next. the lengths are compared. If
X>
y (Iength
of
A$
is
larger than length
of
BS)
then variable
F.
the divider variable.
is
set to one-half the length of
X.
But if X
is
sm_11er
than
Y.
the program drops through and
Fis
set ta one-haIf the length
of
Y.
1002
IF
X>Y
THEN
F=X/2:GOTO
1006
1004
F=Y
....
'2
ln this example,
A$="1234567890123456"
and
B$="57943572";
le1's
run
this through:
1000
X=LEN(A$):Y=LEN(B$)
X=16
Y=8
1002
1F
~':::::''r'
THEN
F=>::",'2:
GOTO
1006
16>
8 true statement. therelore
F =
16/2
F=8
program continues at line 1006
Once the value of F
is
set. the program continues at line 1006. Statement
1006 compares the value of F ta the integer value of
F.
If
Fis
larger than its integer
value, then F
is
assigned the value of its integer value plus
1.
This
is
basically a
method of rounding F up to the nearest integer
if
F
is
a fractional number. For ex-
ample. if the value of F equals 7.5, line 1006
would
ensure that F
is
an integer
number so
that
both
A$
and B$ may
be
divided
as
easily and evenly
as
possible.
1006
IF
F>INT(F)
THEN
F=INT(F)+l
117.5>7
then F = 7+1
F=8
198
 Loading...
Loading...