Menu 3
Parameter
structure
Keypad and
display
Parameter x.00
Parameter
description format
Advanced parameter
descriptions
Serial comms
protocol
Electronic
nameplate
Performance
64 Digitax ST Advanced User Guide
www.controltechniques.com Issue Number: 1
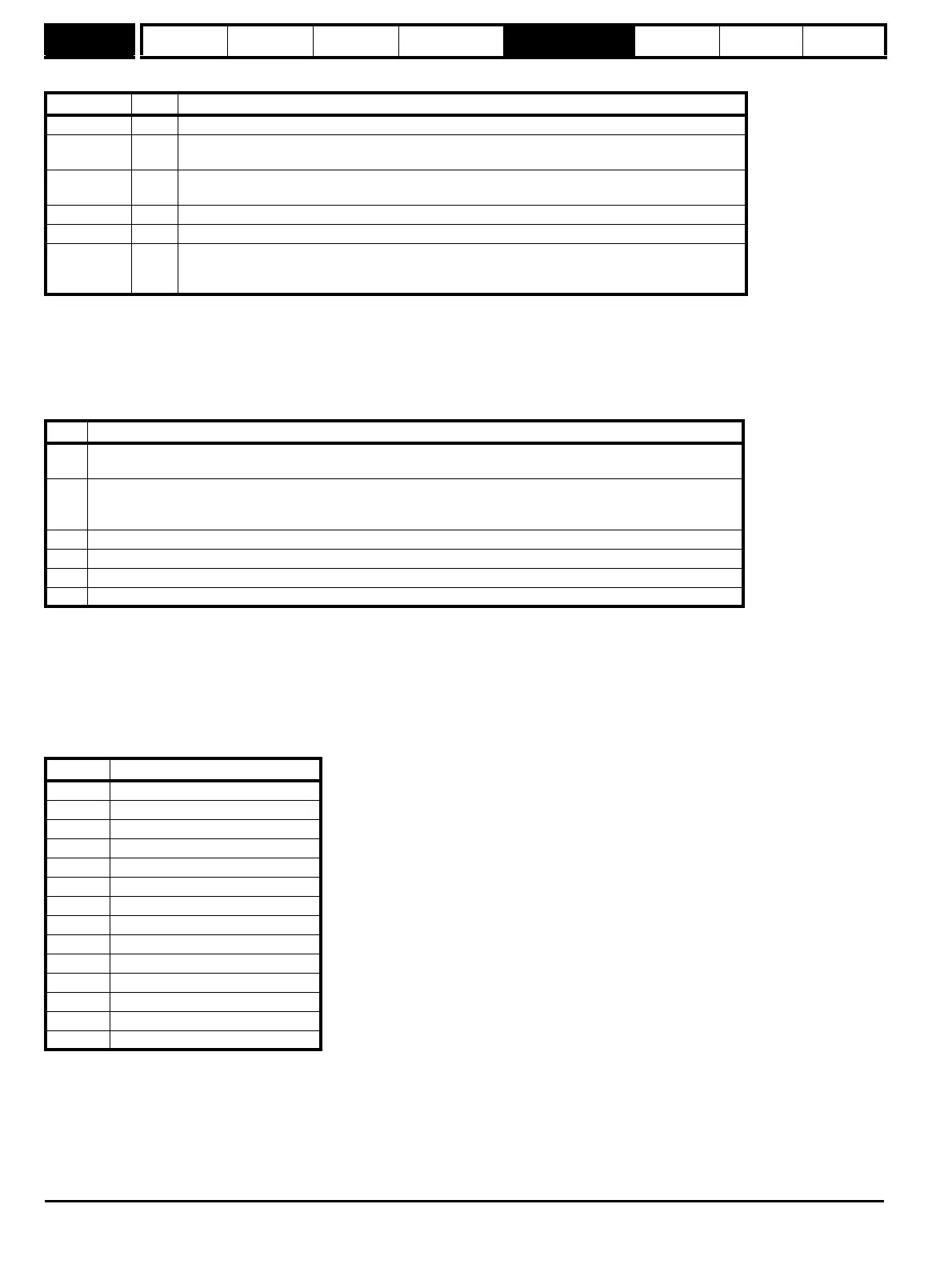
Bits 13-15 of the registers are used to indicate the following:
Data should be written to the transmit register (Pr 90.22) when the register has been reset to zero by the drive. The data will be transferred to the
comms buffer and the transmit register will be cleared.
Data can be read from the receive register (Pr 90.23) at any time. If there is receive data in the buffer bit 15 will be set. Once the data has been read
the register should be cleared and the drive will then transfer more data.
The actual encoder comms buffer is 16 bytes long and any messages that exceed this length (including the checksum added for Hiperface) will cause
an error. The status flags are defined as follows:
SC.Hiper type encoders
The Stegmann Hiperface comms protocol is an asynchronous byte based system. Up to 15 bytes of data can be written to the buffer. The first byte
should be the encoder address. The checksum will be calculated by the drive and added to the end of the message before the message is transmitted
to the encoder. The drive checks the checksum of the received message. If successfully received, the receive message can be read via the receive
register (Pr 90.23) including the address and the checksum received from the encoder. It should be noted that the encoder must be set up for 9600
baud, 1 start bit, 1 stop bit and even parity (default set-up) for the encoder comms to operate with the drive. Also the data block security should not be
enabled in the encoder if the drive encoder nameplate system is to operate correctly.
The following commands are supported:
Example of a Hiperface transfer: read position
Disable drive encoder position check by setting Pr 90.21 to one. This should be set back to zero at the end of the transfer if encoder position checking
is required.
Transfer the "read position" message to the encoder comms buffer by writing the sequence of words shown in the table below to Pr 90.22. A check
should be carried out before each word is written to ensure that the parameter is zero (i.e. the drive has taken any previous data).
Register Bit Function
Transmit 15 Must be set for the drive to transfer the LS byte to the comms buffer.
Transmit 14
The LS byte is the last byte of the message and this byte should be put in the comms buffer and be
transferred to the encoder.
Transmit 13
The LS byte is the first byte of the message. (If this is used the buffer pointer is reset to the start of
the buffer.)
Receive 15 Indicates data from the last transfer can be read from the receive buffer.
Receive 14 The byte in the LS byte is the last byte of the receive message
Receive 13
There is no data in the receive buffer and the LS byte is the comms system status. If there was an
error in the received message this will always be set and one of the status error bits will be set until
the comms is used again by this system or by the drive.
Bit Meaning
0
The number of bytes put into the transmit buffer is not consistent with the expected message length.
(Hiperface only)
1
The number of bytes written to the transmit buffer, or the expected length of the store data transmit message, or the
expected length of a read data message have exceed the length of the buffer.
(Hiperface only)
2 The command code is not supported.
3 The encoder has signalled an error.
4 There was an error in the checksum/CRC of the received message.
5 A timeout occurred.
Code Command
0x42 Read position
0x43 Set position
0x44 Read analog value
0x46 Read counter
0x47 Increment counter
0x49 Clear counter
0x4a Read data (maximum of 10 bytes)
0x4b Store data (maximum of 9 bytes)
0x4c Data field status
0x4d Create a data field
0x4e Available memory
0x50 Read encoder status
0x52 Read type
0x53 Reset encoder
 Loading...
Loading...