DAZZLER
TM
system manual Part I : installation & operation 3.3
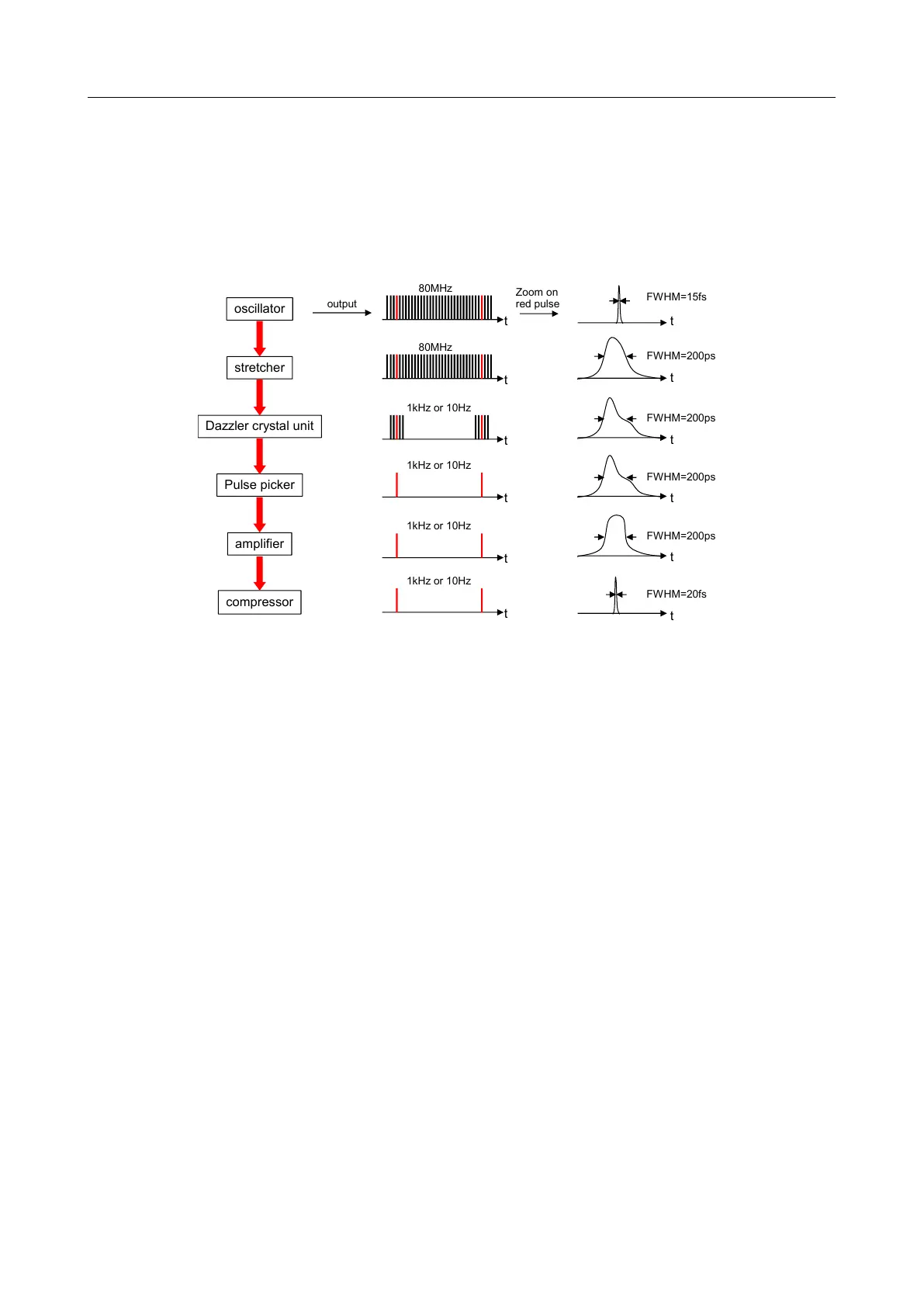
3.2.1 Ultrafast CPA laser controlled by a Dazzler
The Dazzler can be used to shape the spectral amplitude and/or the spectral phase of an optical
pulse in an ultrafast CPA laser. The crystal unit is generally inserted between the stretcher and
the amplifier (regen or multipass) because of its damage threshold (100MW/cm
2
). Figure 3.1
below sketches this setup.
oscillator
stretcher
Dazzler crystal unit
Pulse picker
amplifier
compressor
FWHM=15fs
FWHM=200ps
FWHM=200ps
FWHM=200ps
FWHM=200ps
FWHM=20fs
output
Zoom on
red pulse
t
t
t
t
t
t
80MHz
t
80MHz
t
1kHz or 10Hz
t
1kHz or 10Hz
t
1kHz or 10Hz
t
1kHz or 10Hz
t
Figure 3.1: Setup of an Ultrafast CPA Laser with a Dazzler
The amplitude shaping enables to avoid gain narrowing and get a smooth spectral shape. In
most of the cases, the spectral phase shaping is used to flatten the phase over the whole spectrum
to obtain perfectly compressed pulses after the compressor. More complex pulse shaping can
also be achieved such as multiple pulses or optimized pulse shape for a specific experiment.
3.2.2 Dazzler after an optical parametric amplifier
The Dazzler can be used as a pulse shaper at the output of an OPA. An example of setup is
shown on the Figure 3.2.
The Dazzler enables to control the output pulse shape, for example the generation of two or
more pulses separated in time. It is especially interesting in chemical or biochemical experiments
where a molecule can be excited in a specific energy state which is unaccessible without pulse
shaping. In the example of Figure 3.2, the Dazzler generates a sequence of shaped pulses
at 750nm. Dazzler systems for other center wavelengths are available (contact us for further
information at info@fastlite.com).
3.3 Optical Alignment
The input optical wave propagates through the crystal while interacting with the acoustic wave
(refer to chapter 2 for more details). Two different waves leave the crystal: the diffracted and
the transmitted (non-diffracted) waves as shown in Figure 3.3. The (P) plane corresponds to
V3.00 - 8
th
April 2019 (ContentsTable) (FiguresTable) 18/94
 Loading...
Loading...