60
Serial communication
The unit can communicate on a serial line using the Modbus communication protocol with RTU coding.
With the “Modbus Kit”, supplied as an accessory, the unit can be connected to an RS485 network and meet the requirements of any
master device connected to the network
Serial line settings
The serial line must be set in the following way :
• baud rate: 9600
• data bits : 8
• stop bits : 1
• parity : even
All the devices connected to the same serial line MUST use the same settings.
Device address
To communicate correctly, each device connected to the serial network must have a univocal address (“Modbus individual address”)
between 1 and 247. This address can be set by modifying the following parameters :
• family serial address H67
• device serial address H68
These parameters can assume a value between 0 and 14 and together define the address of the device :
Device address = H67 x 16 + H68
Example.
H67 = 1 Hex 01
H68 = 12 Hex 0C
Device address = 28 Hex 1C
Modbus commands
The Modbus commands implemented by the controller are :
• read parameters 3 (Hex 03 : Read Holding Registers)
• write parameters 16 (Hex 10 : Write Multiple Registers)
Table of addresses
All the available resources are stored in the controller as a WORD (2 bytes) and therefore require the reading or writing of an entire
Modbus register. According to the Modbus protocol, to identify a register of address X the address X-1 must appear in the message.
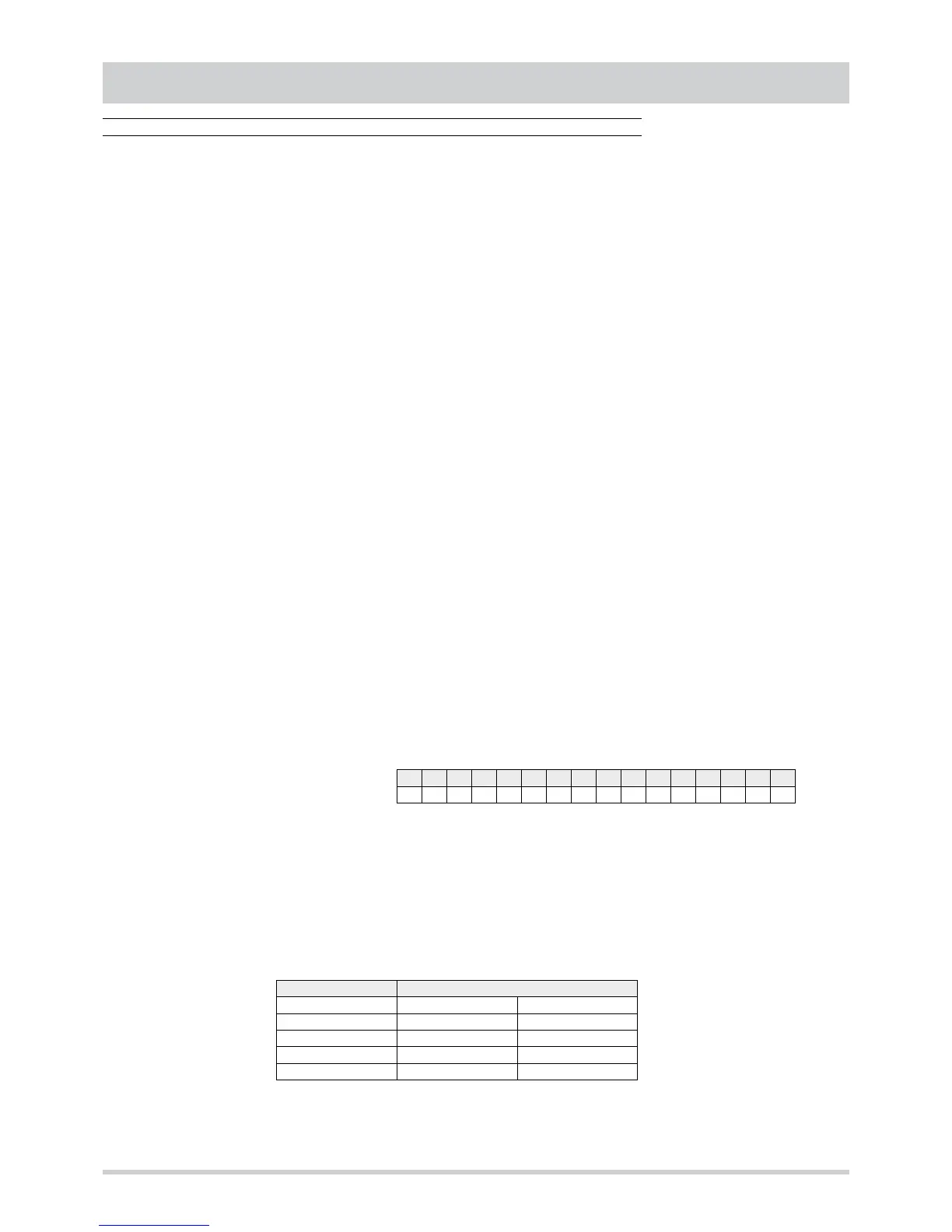
Some messages contain more than one piece of information : in this case the bits representing the value of the resource are identified
by the number of bits used (“Bit number”) and the least significant bit (“Lsb”). In writing such registers it is necessary to read the current
register value, modify the bits representing the relevant resource and rewrite the entire register.
Example.
Bit number = 4
Lsb = 7
Resource value = 3
Some resources can only be read (R) whereas other can also be written (RW).
To interpret the value written in the register it is necessary to consider the value of CPL, EXP and UM :
CPL : if the register represents a number with sign (CPL = Y) carry out the following conversion :
0 = register value < 32767 : resource value = register value
32768 = register value < 65535 : resource value = register value – 65536
EXP : indicates the exponent of the power of 10 to multiply by the register value to obtain the resource value.
MU : indicates the unit of measure of the resource
IMPORTANT. DO NOT modify any parameter not indicated in the tables provided or indicated as a read-only parameter (R), otherwise
the warranty will be invalidated.
CONTROL SYSTEM
EXP Multiplier
-2 10-2 0,01
-1 10-1 0,1
0 100 1
1 101 10
2 102 100
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0
 Loading...
Loading...











