3 CANopen access procedure
Festo – GDCP-CMMP-M3/-M0-C-CO-EN – 1510b – English 21
Every message sent on the CAN bus contains a type of address which is used to determine the bus
participant for which the message is meant. This number is designated the identifier. The lower the
identifier, the greater the priority of the message. Identifiers are established for the above-named com
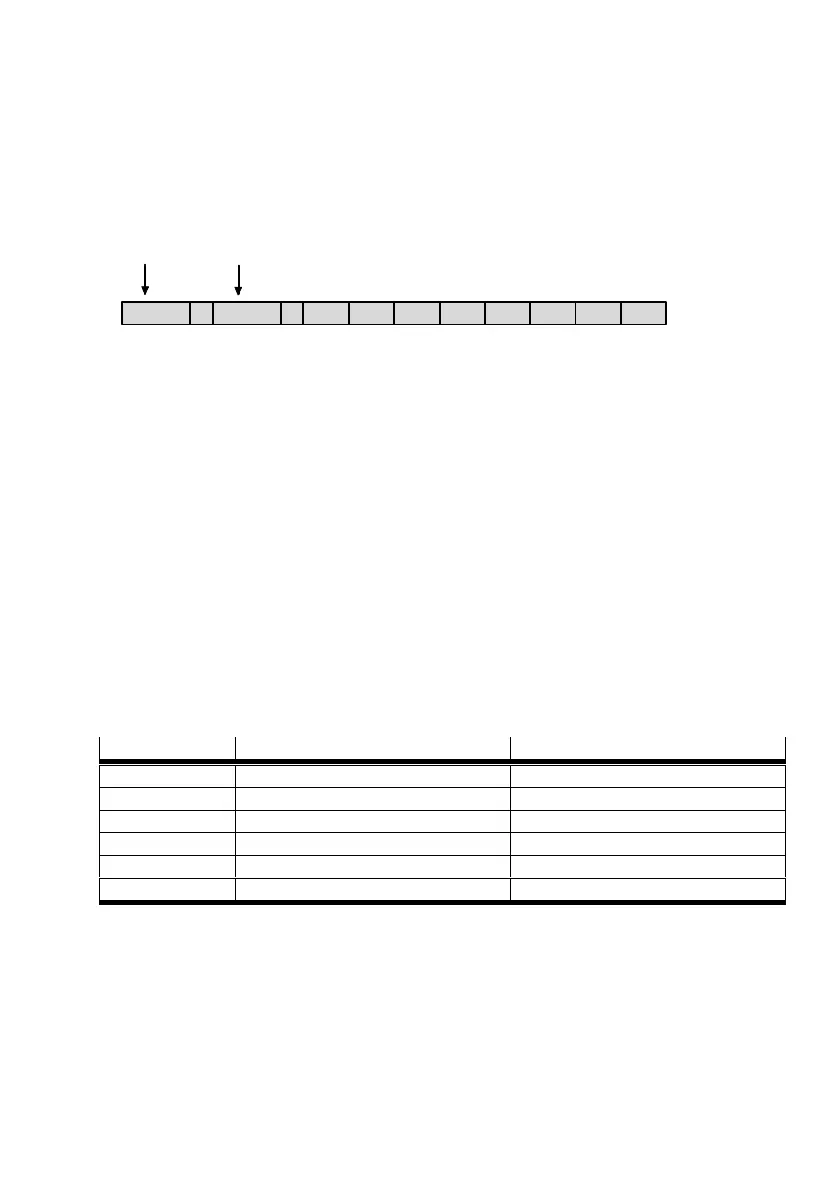
munication objects. The following sketch shows the basic design of a CANopen message:
601
h
Len D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7
Identifier
Data bytes 0… 7
Number of data bytes (here 8)
3.2 SDO Access
The Service Data Objects (SDO) permit access to the object directory of the motor controller. This
access is especially simple and clear. It is therefore recommended to build up the application at first
only with SDOs and only later to convert to the faster but also more complicated Process Data Objects
(PDOs).
SDO access always starts from the higher-order controller (Host). This either sends the motor control
ler a write command to modify a parameter in the object directory, or a read command to read out a
parameter. For each command, the host receives an answer that either contains the read-out value or –
in the case of a write command – serves as an acknowledgement.
For the motor controller to recognise that the command is meant for it, the host must send the
command with a specific identifier. This identifier is made up of the base 600
h
+ node number of the
applicable motor controller. The motor controller answers correspondingly with the identifier 580
h
+
node number.
The design of the commands or answers depends on the data type of the object to be read or written,
since either 1, 2 or 4 data bytes must be sent or received. The following data types are supported:
Data type Size and algebraic sign Range
UINT8 8 bit value without algebraic sign 0 … 255
INT8 8 bit value with algebraic sign -128 … 127
UINT16 16 bit value without algebraic sign 0 … 65535
INT16 16 bit value with algebraic sign -32768 … 32767
UINT32 32 bit value without algebraic sign 0 … (2
32
-1)
INT32 32 bit value with algebraic sign -(2
31
) … (2
32
-1)
Tab. 3.2 Supported data types

 Loading...
Loading...











