G(s) = 50 + 0.98s = .098 (s+51)
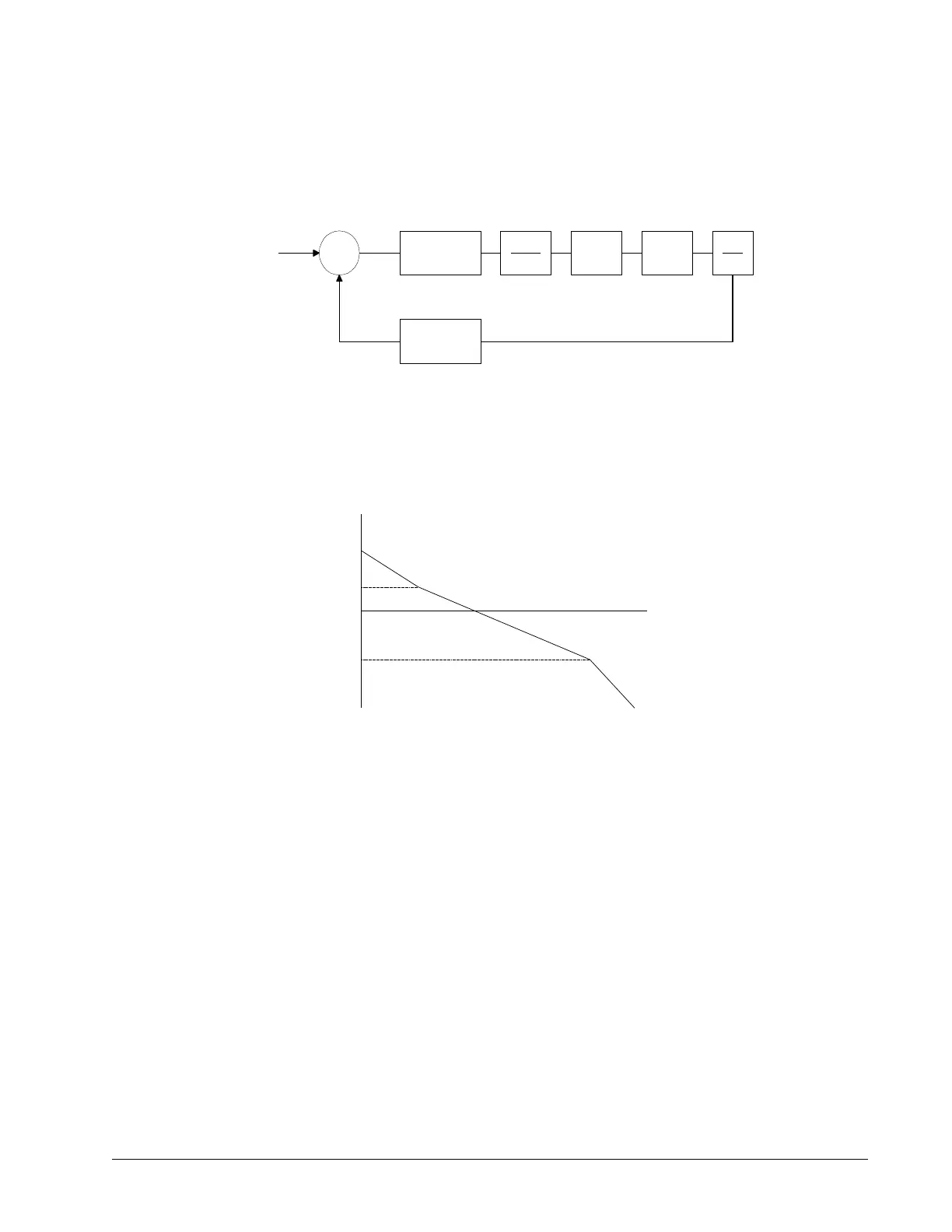
The system elements are shown in Figure 10.7.
Figure 10.7: Mathematical model of the control system
The open loop transfer function, A(s), is the product of all the elements in the loop.
A(s) = 390,000 (s+51)/[s
2
(s+2000)]
To analyze the system stability, determine the crossover frequency, ω
c
at which A(j ω
c
) equals one. This can be
done by the Bode plot of A(j ω
c
), as shown in Figure 10.8.
Figure 10.8: Bode plot of the open loop transfer function
For the given example, the crossover frequency was computed numerically resulting in 200 rad/s.
Next, we determine the phase of A(s) at the crossover frequency.
A(j200) = 390,000 (j200+51)/[(j200)
2
. (j200 + 2000)]
α = Arg[A(j200)] = tan
-1
(200/51)-180° -tan
-1
(200/2000)
α = 76° - 180° - 6° = -110°
Finally, the phase margin, PM, equals
PM = 180° + α = 70°
As long as PM is positive, the system is stable. However, for a well damped system, PM should be between 30° and
45°. The phase margin of 70° given above indicated over-damped response.
Next, we discuss the design of control systems.
Chapter 10 Theory of Operation ▫ 178 DMC-40x0 User Manual
50+0.980s
318
V
ENCODER
500
S
2
FILTER
2000
S+2000
0.0003 4
ZOH DAC
AMP
MOTOR
1
4
0.1
50 200 2000 W (rad/s)
Magnitude

 Loading...
Loading...