BZ Method - The BZ method forces the motor to zero electrical degrees by exciting phases A and B in a two
step initialization process . The location of the motor within it's magnetic cycle is known and sinusoidal
commutation is initialized.
Commands required: BA, BM, BZ
BX Method - The BX method uses a limited motion algorithm to determine the proper location of the motor
within the magnetic cycle. It is expected to move no greater than 10 degrees of the magnetic cycle. The last
stage of the BX command will lock the motor into the nearest 15 degree increment.
Commands required: BA, BM, BX
BI/BC Method – The motor initially boots up in a “pseudo-trapezoidal” mode. The BC function monitors the
status of the hall sensors and replaces the estimated commutation phase value with a more precise value upon
the first hall transition. The motor is then running in a sinusoidally commutated mode and the use of the halls
are no longer required.
Commands required: BA, BM, BI, BC
BZ and QH are used to aid in the wiring process and initial set-up for this method.
Note: These list the minimum required commands to provide commutation. There are many more
commutation configuration commands available not discussed here. See the Command Reference for details.
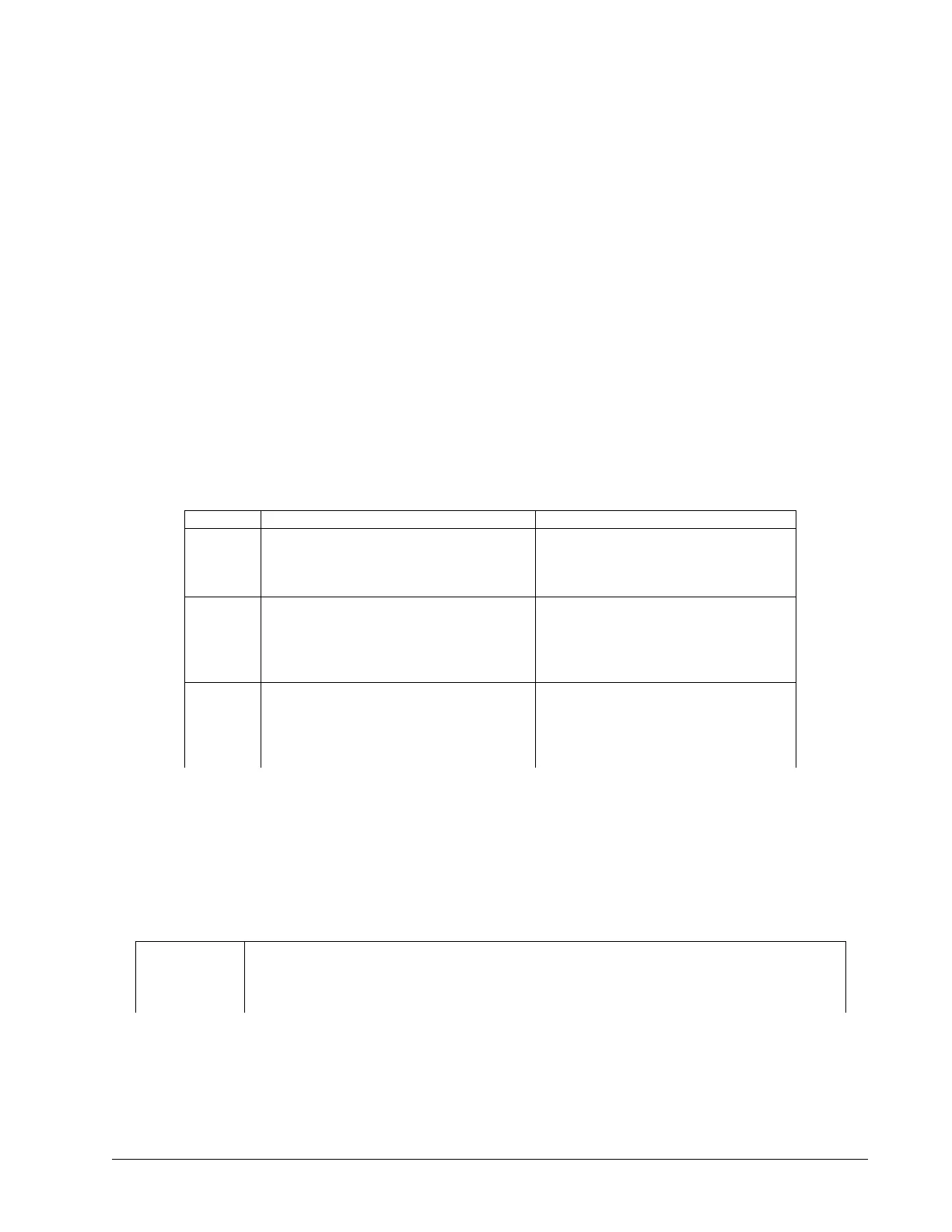
Method PRO CON
BZ
• Can be used with vertical or unbalanced loads
• Less sensitive to noise than BX
• Does not require halls
• Quick first-time set-up
• Can cause significant motor movement
• Will fail at hard stops
BX
• Provides the least amount of movement (If no
hall sensors are available)
• Does not require halls
• Quick first-time set-up
• Not recommended with vertical or
unbalanced loads
• Sensitive to noise on feedback lines
• Requires some movement
• Will fail at hard stops
BI/BC
1
• No unnecessary movement required
• Best option with a vertical or unbalanced load
• Requires halls
• Longer first-time set-up due to additional
wiring
• Can run away or stall if halls are not wired
properly
Table 2.14: Pros and cons of each commutation method
1
If your motor has halls, it is recommended to use the BI/BC method.
The following sections discuss how to wire and configure a motor for sinusoidal commutation using the different
commutation methods:
BZ/BX Method
WARNING
The BZ command must move the motor to find zero electrical degrees . This movement is
sudden and will cause the system to jerk. Larger applied voltages will cause more severe
motor jerk.
The BZ and BX method are wired in the same way. Both BZ and BX require encoder feedback to the controller
and the motor phases to the drive.
Chapter 2 Getting Started ▫ 27 DMC-40x0 User Manual

 Loading...
Loading...