Model G4000 (Mfg. Since 8/09)
-33-
Calculating Correct Spindle Speed
1. Use the table in Figure 43 to determine
the recommended cutting speed for the
workpiece material.
Note: Cutting speeds are expressed in SFM
(surface feet per minute) that the workpiece
moves against the cutter, which is different
from the spindle speed (RPM).
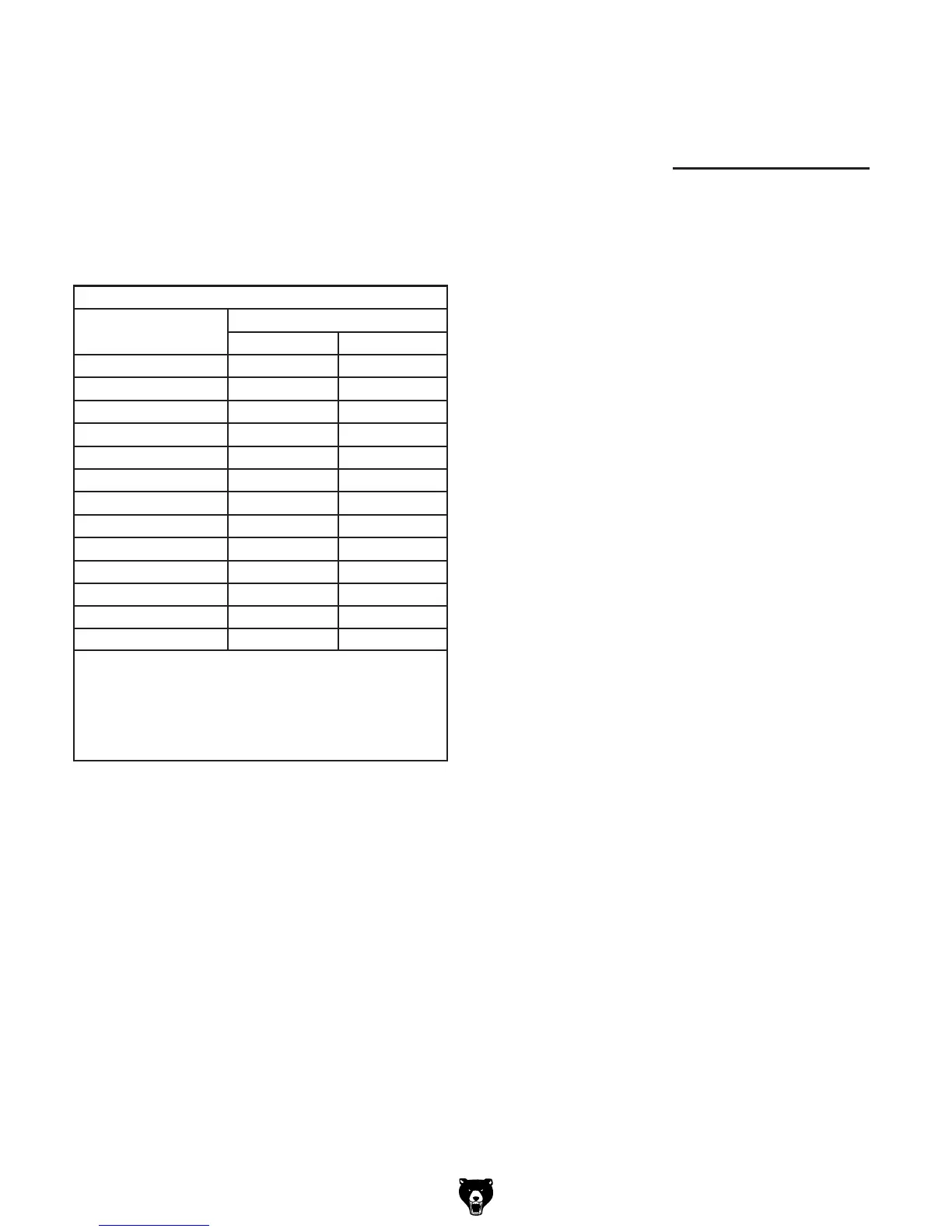
Recommended Cutting Speeds
Work Material
Magnesium
Aluminum
Brass & Bronze
Copper
Cast Iron (Soft)
Cast Iron (Hard)
Mild Steel
Cast Steel
Tool Steel
Alloy Steels (Hard)
Stainless Steel
Titanium
Hi Maganese Steel
Average Tool Speed (sfm)
Rough Cuts Finish Cuts
400
350
250
100
100
50
100
70
50
50
60
90
40
800
700
500
250
250
150
250
150
150
150
180
200
100
Note: These values are based on HSS cutting
tools. For carbide cutting tools, double the aver-
age speed. These values are a guideline only.
Refer to the MACHINERY’S HANDBOOK for
more detailed information.
Figure 43. Cutting speed table.
2. Determine the final diameter, in inches, for
the cut you intend to make.
Note: For this step, you will need to aver-
age out the diameters or work with the finish
diameter.
Example A:
You will finish cut
1
⁄2" diameter piece of
cast steel stock, using an HSS cutting
tool.
Step 1:
150 (SFM from chart) x 4 = 600
Step 2:
600 / .5" (Diameter of workpiece) = 1200
Result:
The correct spindle speed is 1200 RPM.
Example B:
You will rough turn a 1" diameter piece
of stainless steel, using a carbide cutting
tool.
Step 1:
60 (SFM from chart) x 2 (for carbide tool)
= 120
Step 2:
120 (Calculated SFM) x 4 = 480
Step 3:
480 / 1" (Diameter of workpiece) = 480
RPM
Result:
The correct spindle speed is 480 RPM.
3. Use the following formula to determine the
correct spindle speed (RPM) for your opera-
tion:
Diameter of Cut
Spindle Speed
=

 Loading...
Loading...