Rev. 1.60 62 August 20, 2019 Rev. 1.60 63 August 20, 2019
BS66F340/BS66F350/BS66F360/BS66F370
Touch A/D Flash MCU with LED Driver
BS66F340/BS66F350/BS66F360/BS66F370
Touch A/D Flash MCU with LED Driver
EEPROM Data Memory
These devices contain an area of internal EEPROM Data Memory. EEPROM, which stands for
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory, is by its nature a non-volatile form
of re-programmable memory, with data retention even when its power supply is removed. By
incorporating this kind of data memory, a whole new host of application possibilities are made
available to the designer. The availability of EEPROM storage allows information such as product
identification numbers, calibration values, specific user data, system setup data or other product
information to be stored directly within the product microcontroller. The process of reading and
writing data to the EEPROM memory has been reduced to a very trivial affair.
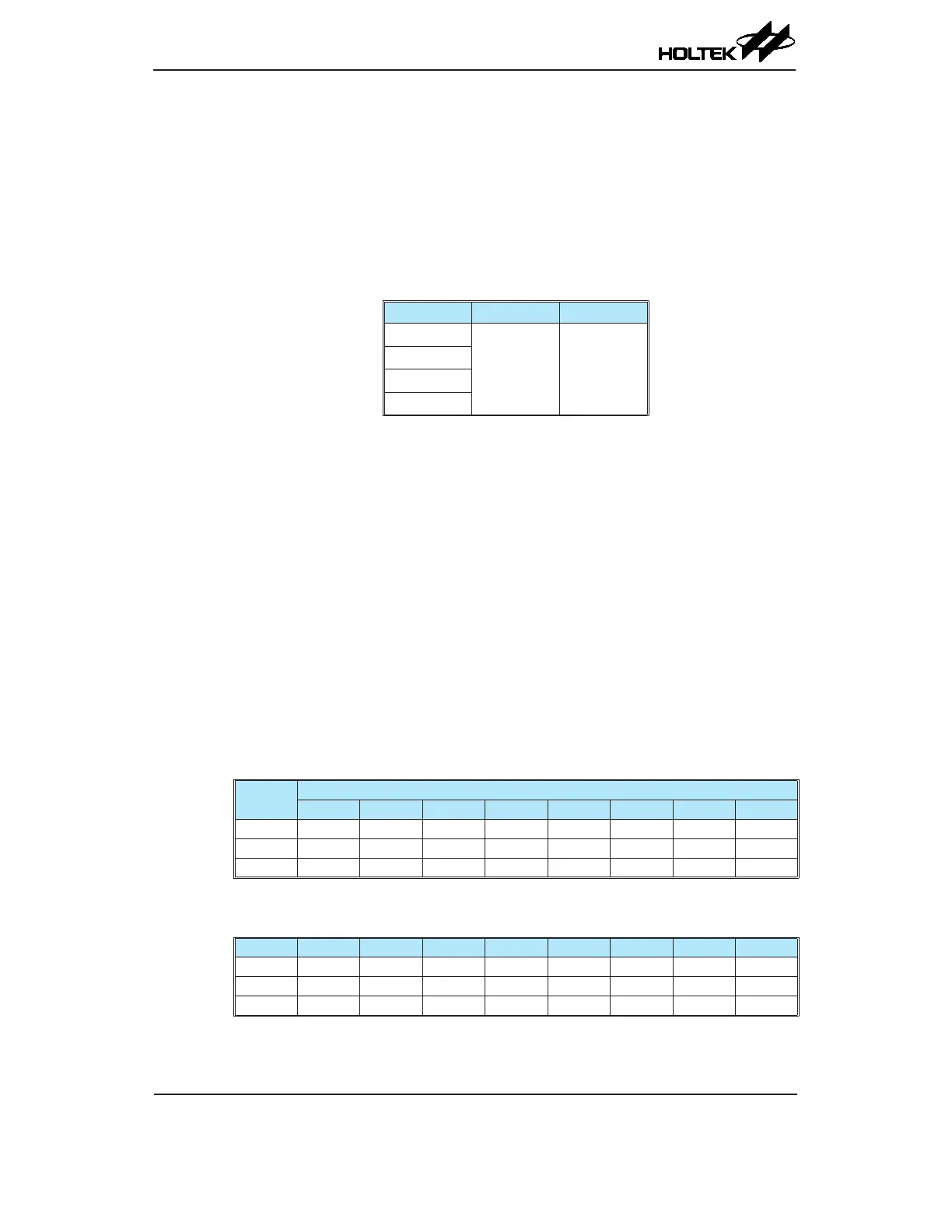
Device Capacity Address
BS66F340
128×8 00H ~ 7FH
BS66F350
BS66F360
BS66F370
EEPROM Data Memory Structure
The EEPROM Data Memory capacity is 128×8 bits for the series of devices. Unlike the Program
Memory and RAM Data Memory, the EEPROM Data Memory is not directly mapped into memory
space and is therefore not directly addressable in the same way as the other types of memory. Read
and Write operations to the EEPROM are carried out in single byte operations using an address and
data register in sector 0 and a single control register in sector 1.
EEPROM Registers
Three registers control the overall operation of the internal EEPROM Data Memory. These are the
address register, EEA, the data register, EED and a single control register, EEC. As both the EEA
and EED registers are located in sector 0, they can be directly accessed in the same was as any other
Special Function Register. The EEC register, however, being located in sector 1, can be read from
or written to indirectly using the MP1H/MP1L or MP2H/MP2L Memory Pointer pair and Indirect
Addressing Register, IAR1 or IAR2. Because the EEC control register is located at address 40H
in sector 1, the Memory Pointer low byte register, MP1L or MP2L, must rst be set to the value
40H and the Memory Pointer high byte register, MP1H or MP2H, set to the value, 01H, before any
operations on the EEC register are executed.
Register
Name
Bit
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
EEA — EEA6 EEA5 EEA4 EEA3 EEA2 EEA1 EEA0
EED D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
EEC — — — — WREN WR RDEN RD
EEPROM Registers List
• EEA Register
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — EEA6 EEA5 EEA4 EEA3 EEA2 EEA1 EEA0
R/W — R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
POR — 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 7 Unimplemented, read as "0"
Bit 6~0 EEA6~EEA0: Data EEPROM address bit 6 ~ bit0
 Loading...
Loading...