The key manager uses a key store to hold the certificates and keys (or pointers to
the certificates and keys) required for all encryption tasks. Refer to the appropriate
documentation for detailed information about the key manager and the key stores
it supports.
Two methods of encryption are available:
1. Application-managed encryption (AME)
2. Library-managed encryption (LME)
These methods differ in three ways:
v Where the encryption policy engine resides
v Where key management occurs for your encryption solution
v How the key manager is connected to the drive
Your operating environment determines which method is the best for you.
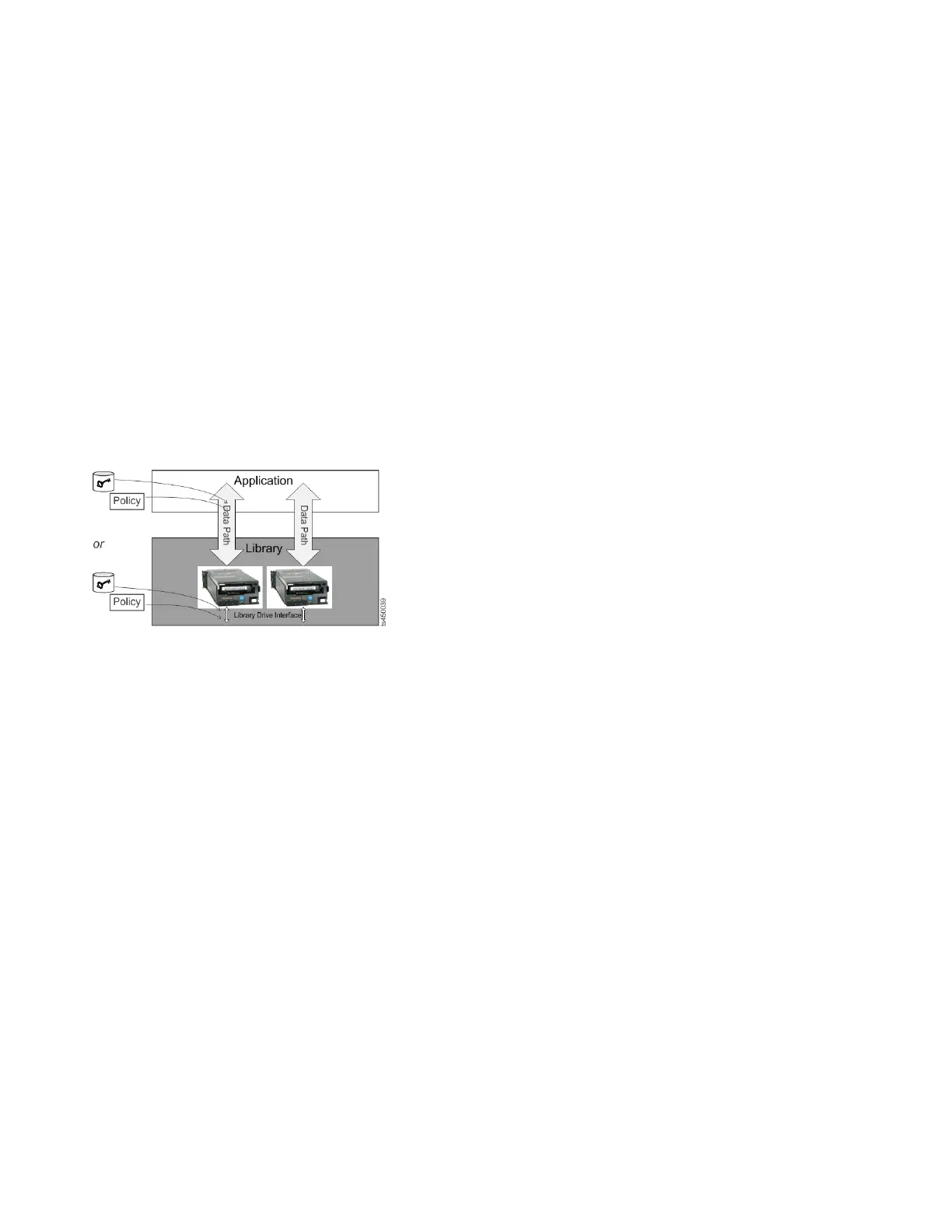
Key management and the encryption policy engine can be in any of the
environment layers shown in Figure 27
Application layer
Initiates data transfer for tape storage, for example Tivoli Storage Manager.
Library layer
The TS4500 tape library, which contains an internal interface to each tape
drive installed in the library.
Planning for application-managed encryption
Application-managed encryption (AME) is useful in operating environments that
run an application that is already capable of generating and managing encryption
policies and keys, such as Tivoli Storage Manager.
Figure 27. Possible locations for encryption policy engine and key management
112 IBM TS4500: Introduction and Planning Guide
 Loading...
Loading...











