Introduction to Digital Power Conversion
XMC4000/1000 Family
Converter Topologies
Application Guide 18 V1.0, 2015-01
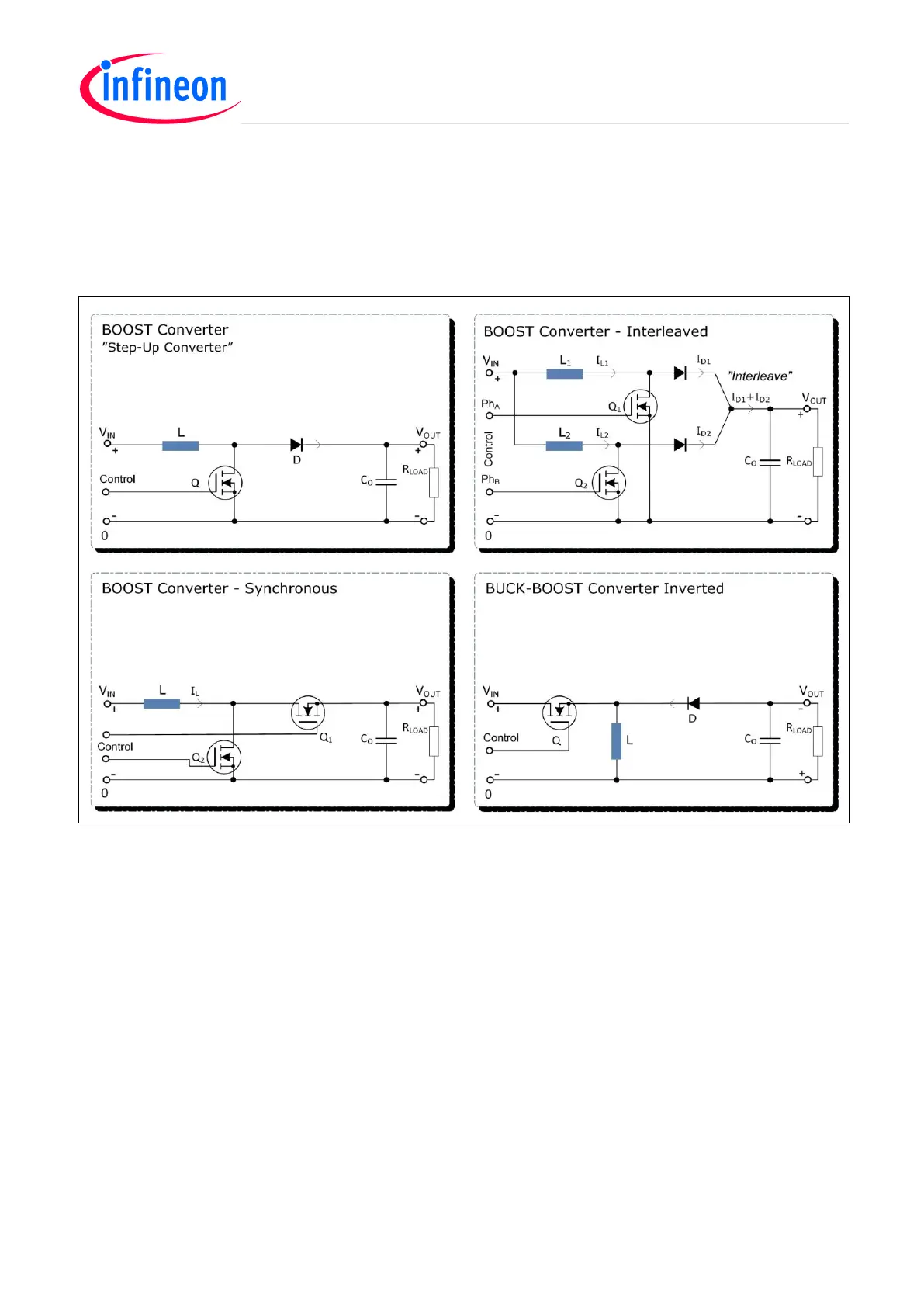
3.2 Boost
A Boost converter is non-isolating and can only generate a higher output average voltage than the
input supply voltage. It is therefore called a “Step-Up” converter.
There is one exception to note however. The Inverted Buck-Boost converter theoretically generates
an output voltage from 0 to minus infinity.
Figure 6 Boost
Interleaved Boost Converter
Similar to the Buck converter, i.e. the ripple will be reduced and smaller components can be used, by
having interleaved output currents from a multiphase Boost converter stage – here by a 2-phase
Boost converter that is controlled by fixed 180
o
phase-shifted PWM from an XMC CCU4/-8.
Synchronous Boost Converter
A synchronous Boost works similar to a synchronous Buck – however, this variant of improvement is
not often used, since reduced power conversion loss by replacing the rectifying diode D by an active
switch is not very significant in the high voltage range – where this topology more frequently appears.

 Loading...
Loading...