Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 105
Features
7 Features
7.1 Power-On Configuration Options
Several configuration options can be configured by hardware. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor 5300 Series sample its hardware configuration at reset, on the active-to-
inactive transition of RESET#. For specifics on these options, please refer to Table 7-1.
The sampled information configures the processor for subsequent operation. These
configuration options cannot be changed except by another reset. All resets reconfigure
the processor, for reset purposes, the processor does not distinguish between a “warm”
reset (PWRGOOD signal remains asserted) and a “power-on” reset.
Notes:
1. Asserting this signal during RESET# will select the corresponding option.
2. Address lands not identified in this table as configuration options should not be asserted during RESET#.
3. Requires de-assertion of PWRGOOD.
Disabling of any of the cores within the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300
Series must be handled by configuring the EXT_CONFIG Model Specific Register (MSR).
This MSR will allow for the disabling of a single core per die within the Quad-Core
Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series package. Additional details can be found in the
Conroe and Woodcrest Processor Family BIOS Writer’s Guide.
7.2 Clock Control and Low Power States
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series support the Extended HALT state (also
referred to as C1E) in addition to the HALT state and Stop-Grant state to reduce power
consumption by stopping the clock to internal sections of the processor, depending on
each particular state. See Figure 7-1 for a visual representation of the processor low
power states. The Extended HALT state is a lower power state than the HALT state or
Stop Grant state.
The Extended HALT state must be enabled via the BIOS for the processor to
remain within its specifications. Refer to the Conroe and Woodcrest Processor
Family BIOS Writer’s Guide. For processors that are already running at the lowest bus
to core frequency ratio for its nominal operating point, the processor will transition to
the HALT state instead of the Extended HALT state.
The Stop Grant state requires chipset and BIOS support on multiprocessor systems. In
a multiprocessor system, all the STPCLK# signals are bussed together, thus all
processors are affected in unison. When the STPCLK# signal is asserted, the processor
enters the Stop Grant state, issuing a Stop Grant Special Bus Cycle (SBC) for each
processor. The chipset needs to account for a variable number of processors asserting
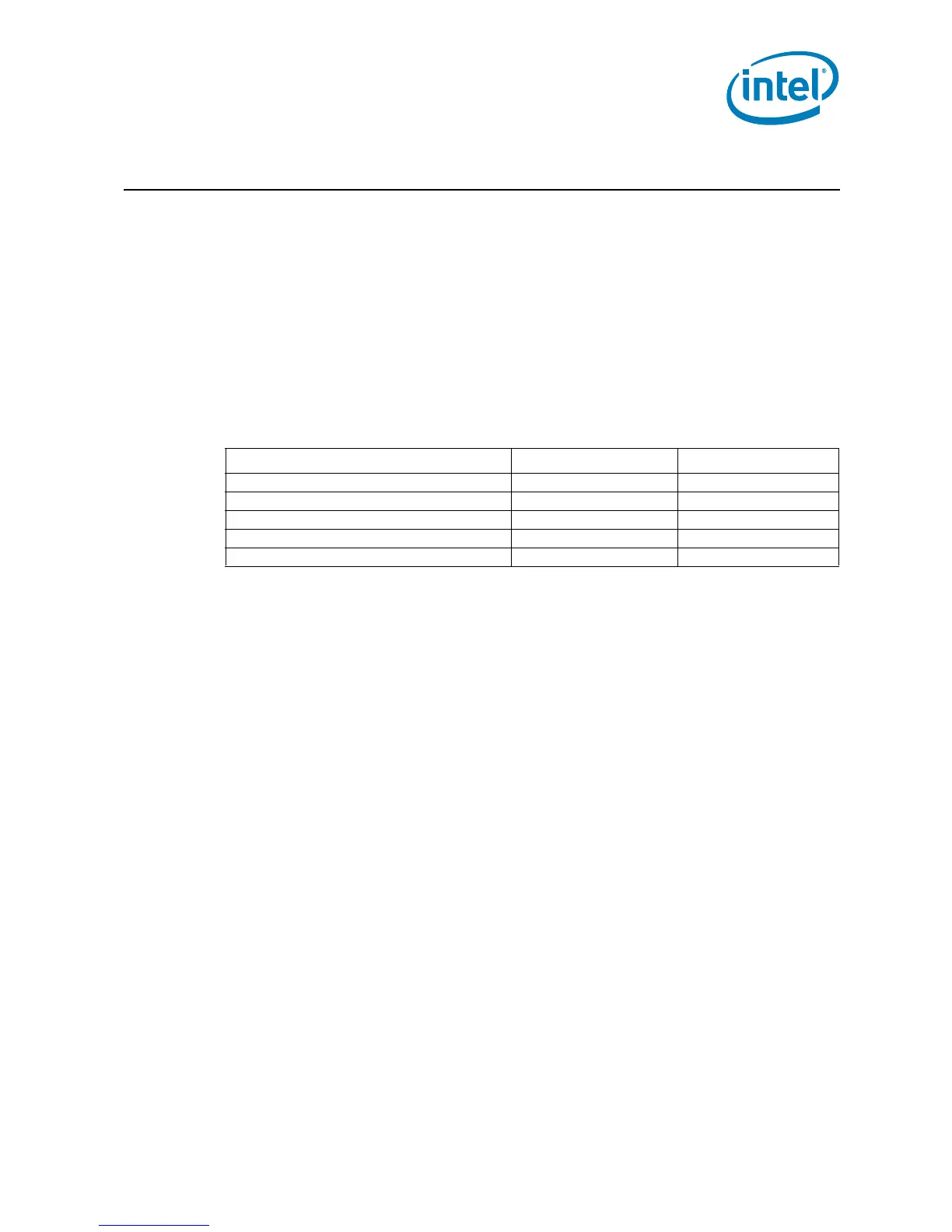
Table 7-1. Power-On Configuration Option Lands
Configuration Option Land Name Notes
Output tri state SMI# 1,2,3
Execute BIST (Built-In Self Test) A3# 1,2
Disable MCERR# observation A9# 1,2
Disable BINIT# observation A10# 1,2
Symmetric agent arbitration ID BR[1:0]# 1,2

 Loading...
Loading...











