44
Keyline S.p.A. NINJA Man. cod. B409286FG Copyright by Keyline - Italy
ITALIANO / ENGLISH
RICERCA CHIAVI KEY SEARCH
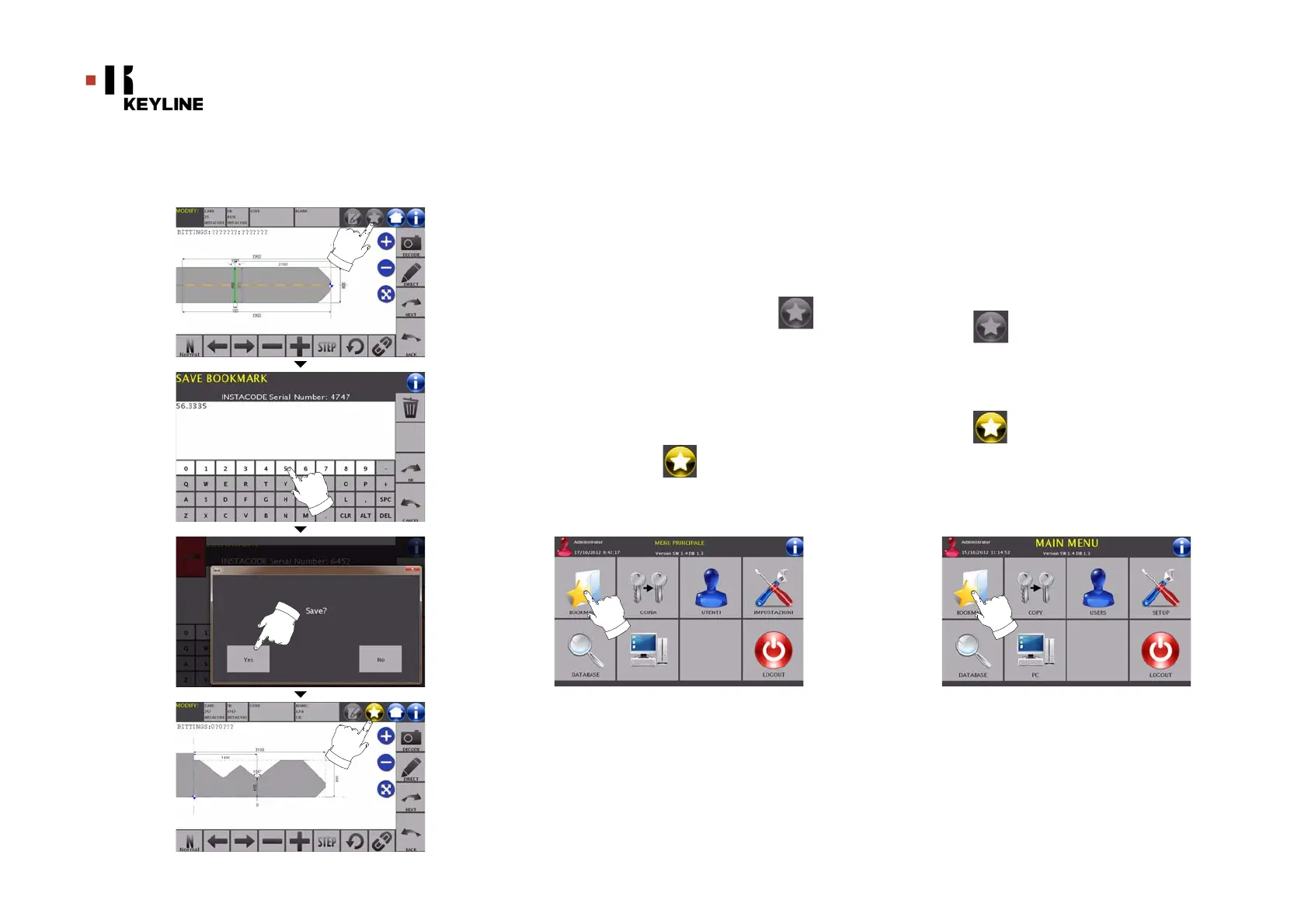
8.2.0 BOOKMARKS
Ogni volta che viene modificata una chiave, indipendentemente dal
database da cui provenga, è possibile memorizzarla in uno specifico
database di “chiavi preferite” assegnandogli un bookmark.
Come procedere:
• Per far ciò è sufficiente premere il pulsante dalla
pagina “MODIFICA” dopo aver apportato le modifiche
necessarie.
• Digitare il nome che si desidera dare alla bookmark e
premere “OK”.
• Confermare con “SI” la richiesta di salvataggio e ritornare
alla pagina “MODIFICA”.
La registrazione della chiave nel database BOOKMARKS viene segna-
lata dalla icona di colore giallo:
In seguito l’utente potrà ricercare il bookmark accedendo direttamen-
te nel menù “BOOKMARKS” del menù principale:
Nota: Questa funzione non è da confondere con il salvataggio di
una chiave in archivio. Infatti il salvataggio è relativo a
tutte le informazioni che caratterizzano la chiave
(cifratura, impostazioni di taglio, materiale, numero di
copie, ecc.) sia per chiavi ricavate da database (a codice)
che per chiavi lette. Un bookmark invece punta
direttamente a un ISN e cioè ad una scheda tecnica per il
taglio di una chiave (quindi la cifratura e gli altri dati non
vengono memorizzati).
8.2.0 BOOKMARKS
Every time a key is modified, irrespective of which database it
comes from, it is possible to save the changes in a specific "fa-
vourite keys" database, and to assign a bookmark to it.
How to proceed:
• Press the button from “MODIFY” page after making
the necessary changes..
• Type the name of the bookmark and press “OK”.
• Confirm that you want to save by pressing "YES" and go
back to the "MODIFY" page.
The yellow icon shows that the key has been saved in the
BOOKMARKS database.
Later, the user shall be able to look for the bookmark by accessing
the "BOOKMARKS" menu from the main menu:
Note: This function must not be confused with the saving of a key
in the archive. The saving concerns all the information that
characterise a key (bitting, cutting parameters, material,
number of copies, etc.) for both keys found in a database
(coded) and read keys. A bookmark, instead, leads directly
to a ISN, that is to say, a technical card for cutting a key
(and so the bitting and other data are not memorised).
 Loading...
Loading...