B-2April 2003 76-100016-002
PEGAsys™ LV
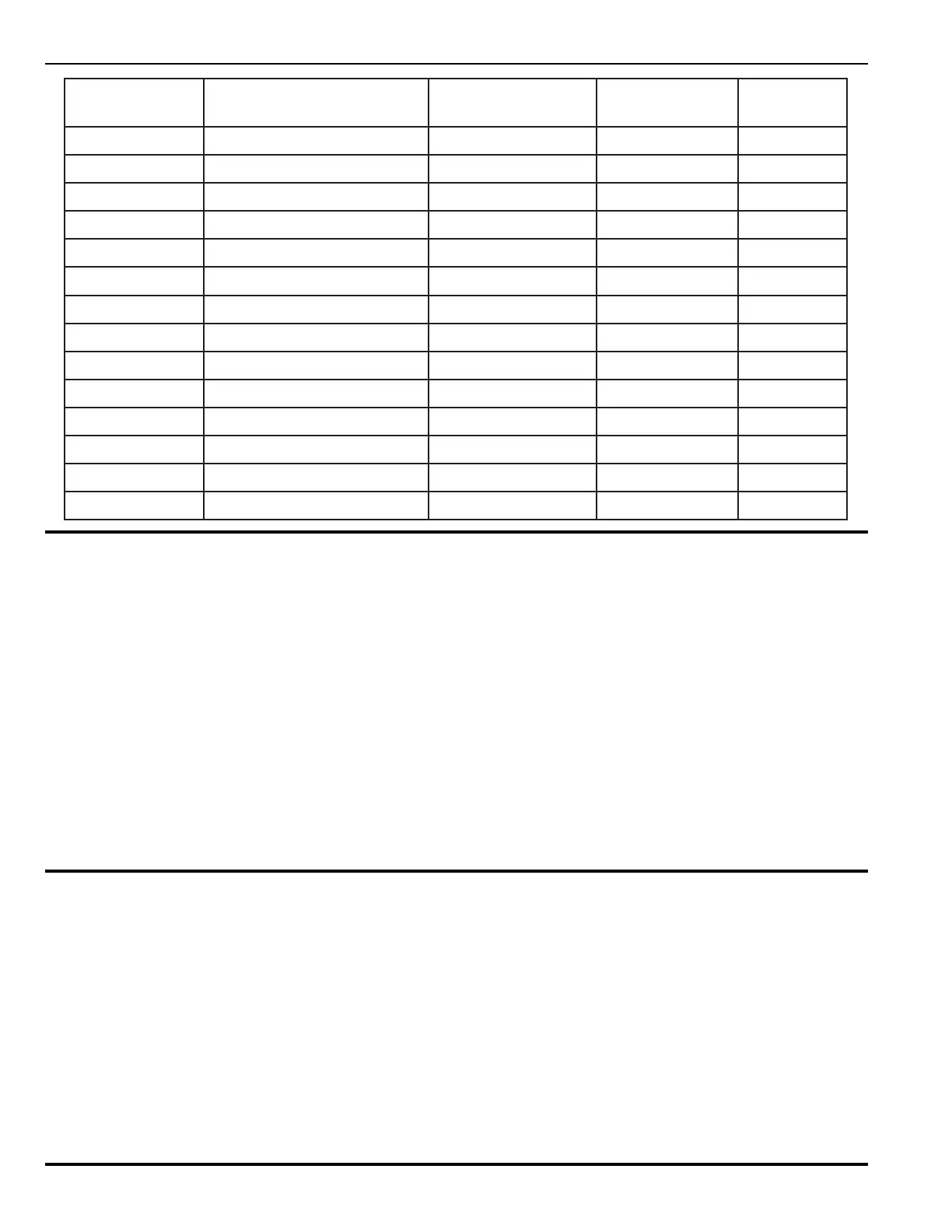
)GWA(eziSeriWrerutcafunaMrebmuNtraPgnitaR).tf/fp(paC
41.proCelbaC&eriWsaltAPT1-1-41-822LPF5.41
elbaCnameloC14189LPF0.02
elbaCnameloC02489RLPF0.52
noitaroproCnartmoC0424RLPF0.12
.oCelbaC&eriWnedleB0859RLPF0.72
.oCelbaC&eriWnedleBJU0216PLPF9.52
CCSBE204143PLPF0.02
smetsySelbaCsiseneG2504LPF0.91
smetsySelbaCsiseneG3344RLPF0.91
smetsySelbaCsiseneG3364PLPF0.02
21elbaCnameloC12189LPF0.72
elbaCnameloC00289RLPF0.92
smetsySelbaCsiseneG4504LPF0.12
smetsySelbaCsiseneG4344RLPF0.22
EXAMPLE NO. 1
Determine the recommended wire size for a daisy-chained, Class-B, Style-4 SLC with 160 RCUs and a total wire length of
7,500 feet. The total wire length is the sum of wiring for the positive and negative SLC legs, and is not the linear distance
from the control unit to the most-remote RCU.
Try #14 AWG wire.
The total SLC wiring resistance is:
7,500 ft. X 2.525 Ω/1,000 ft. = 18.9 Ω.
If we select Coleman Cable wire, P/N 98141 (from Recommended Wire Listing), the total SLC wiring capacitance is:
3,750 ft x 20 x 10
-12
farads/ft. = .075 x 10
-6
farads (or, 0.075 µF).
Coleman Cable wire, P/N 98141, is acceptable.
Note: Capacitance values correspond to a pair of wires as compared to resistance values that correspond to a single
conductor. The wire-pair length for this SLC is 3,750 feet, and this value is used for the SLC’s capacitance
calculation.
EXAMPLE NO. 2
Determine the proper wire size for a Class-A, Style-6 SLC with 100 RCUs and a total wire length 6,000 feet. The total wire
length is the sum of wiring for the positive and negative SLC legs for both the primary and redundant communications
circuits, and is not the linear distance from the control unit to the most-remote RCU.
Try #18 AWG wire first. The total SLC wiring resistance is using #18 AWG is:
6,000 ft. X 6.385 Ω/1,000 ft. = 38.3 Ω.
The total SLC wiring resistance (38.3 Ω) when using #18 AWG wire exceeds the maximum SLC wiring resistance of 26 Ω.
Use larger wire.
Try #16 AWG next. The total SLC wiring resistance using #16 AWG is:
6,000 ft. X 4.016 Ω/1,000 ft. = 24.1 Ω.
 Loading...
Loading...