MAINTENANCE MANUAL OF ENGINE
124
6.2 Structural principle of the alternator
Introductions for the alternator
The alternator is a three-phase alternator. Its prin-
ciple is to convert the mechanical energy into
electric energy through the rotating magnetic field.
Then, it delivers electric power to electric equip-
ments by means of direct current after being recti-
fied by the diode, and charges the battery simul-
taneously.
The alternator used by the tractor is a silicon rec-
tification alternator, which is composed of an al-
ternator and silicon rectifier, and is able to gener-
ate a three-phase alternating current.
Winding the stator coil: The electromotive force
produced by the three-phase winding, it should be
a symmetrical electromotive force, namely the
electromotive force at each phase is equal and
potential difference is 120° electrical degree.
Connection of the stator coil: It is connected by
star connection scheme or delta connection
scheme. The stator coil used in the alternator of
the tractor is connected by star connection
scheme.
1. Construction of the alternator-Rotor assem-
bly
Function: To build a magnetic field.
Composition: It is composed of two claw poles,
(rotor coil) excitation winding, shaft and slip
ring and etc.
Generation of a magnetic field: When the brush
transmits the direct current to two collector rings,
a direct current flows through the magnetic field
winding, and an axial magnetic flux is generated
to get one claw pole magnetized to pole N, and
the other claw pole magnetized to pole S, so that
six pairs of magnetic poles intersected are
formed. When the rotor rotates, a rotating mag-
netic field is formed.
For magnetic line distribution of the magnetic
field and excitation circuit, see the figure on
right hand.
2. Construction of the alternator-Stator as-
sembly
Function of the stator components: To produce a
three-phase alternating current.
Composition of the stator components: The
stator is composed of stator core and winding.
The stator core is superposed by silicon steel
sheets with grooved inner circle, and the cable
for the stator winding is placed in the groove of
the core. For the stator with a three-phase wind-
ing, the three-phase winding must be wound as
per requirements to obtain a three-phase elec-
tromotive force with same frequency, equal
magnitude and phase difference of 120 degree.
The stator winding has three phases, which is
connected by star connection scheme or delta
(big power) connection scheme.
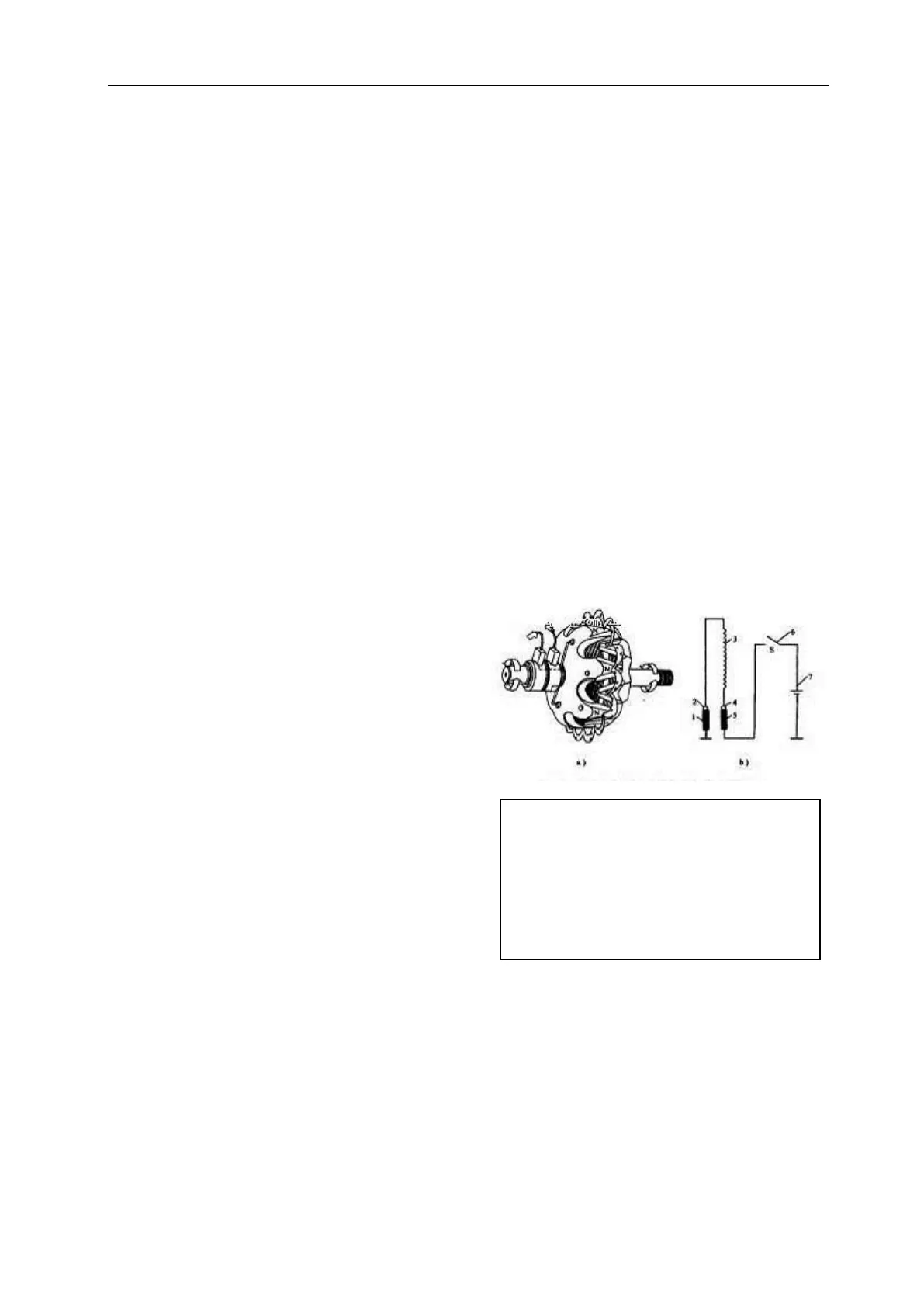
Magnetic line distribution of rotor field and
principle of magnetic field circuit
a. Magnetic line distribution of the magnetic
field.
b. Principle of magnetic field
1, 5 Brush; 2, 4 Slip ring; 3 Excitation wind-
ing; 6 Ignition switch(lock); 7 Battery

 Loading...
Loading...