85
H
3. Time Selectivity
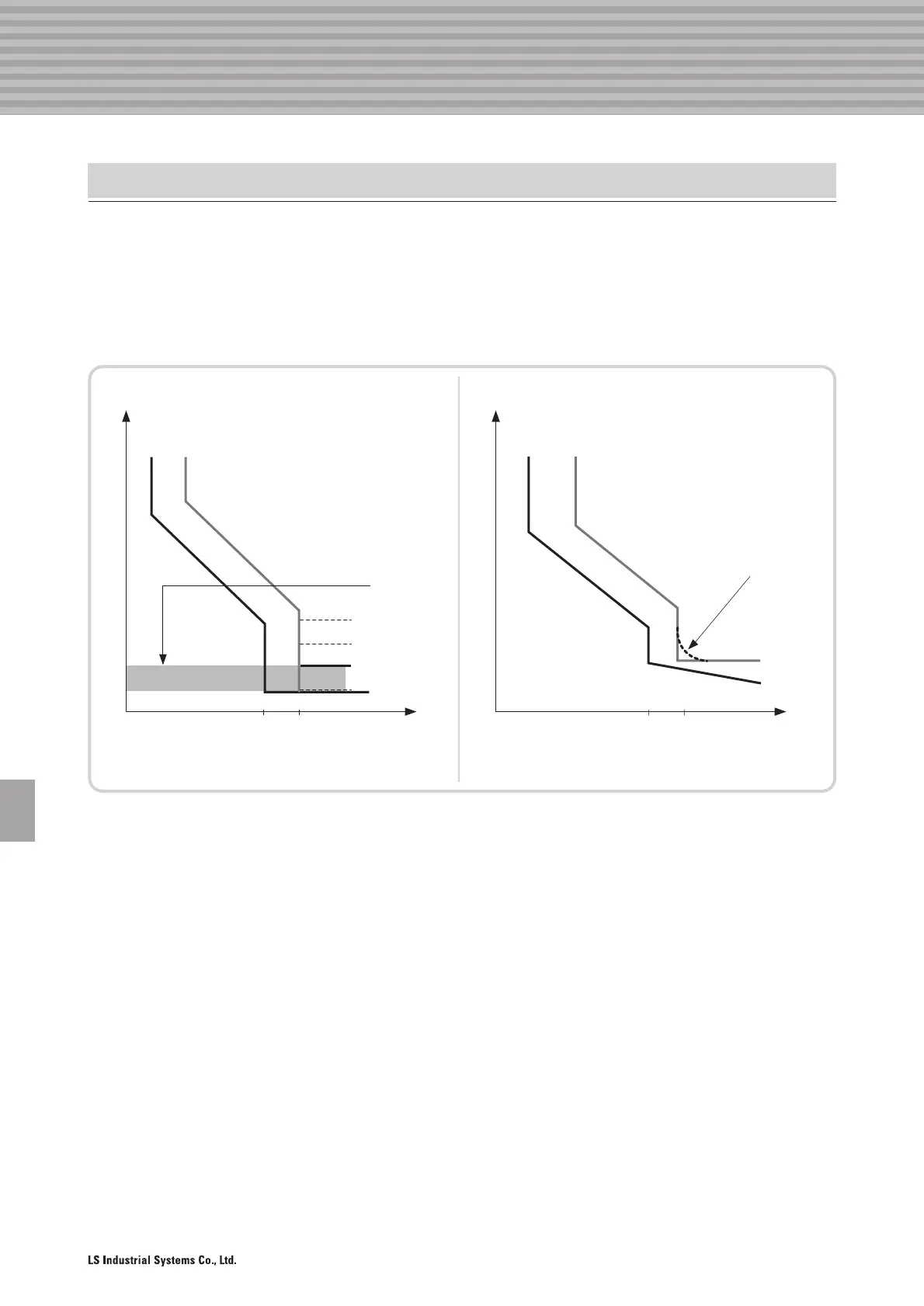
Time selectivity is achieved when upstream breaker has longer time delay than downstream breaker about the
same accident current. The optimum arrangement of this system can be organized with upstream breaker’s
electronic trip unit which can perform short time delay setting. Upstream breaker should be able to perform time
-delay function long enough for downstream breaker to eliminate the accident. Therefore upstream breaker can
withstand thermal and magnetic stress for the duration of operation time by downstream breaker. Below picture
3, time selectivity concept is illustrated.
Picture 4(a) illustrates time discrimination in general, picture 4(b) illustrates pseudo-time discrimination that extend
time discrimination by modifying its previous line from right angle to tilt between instantaneous and long time delay
areas. In general, ACB is designed with pseudo-time discrimination, and MCCB is equipped with general time
discrimination.
Using time discrimination to achieve selective protection between two breakers is limited to short time delay area
explained in picture 1. Because most of breakers operate at similar operation speed under instantaneous area.
Picture 4. Time Selectivity
(a) Time Selectivity (b) Pseudo-Time Selectivity
D1: Short Time Delay (Delay0~3)
Circuit Breaker
D2 : Current Limiting Circuit Breaker
D2 : I
ins2 as Instantaneous
Operation Current Breaker
Time Delay
from Delay1
Delay3
Delay2
Delay1
Delay0
Short / Inverse Time Delay
Characteristic
Inverse time characteristic
improve protective
coordination comparing to
definite time.
D
2 D1
t
I
ins2 I ins1 I
D
2 D1
t
I
ins2 I ins1 I
Protective Coordination
2. Selectivity Techniques

 Loading...
Loading...