8-4 Measurement
8.2.3 Doppler General Measurements
Doppler general measurements refer to general measurements on PW/CW-mode images. The
measurements listed below can be performed:
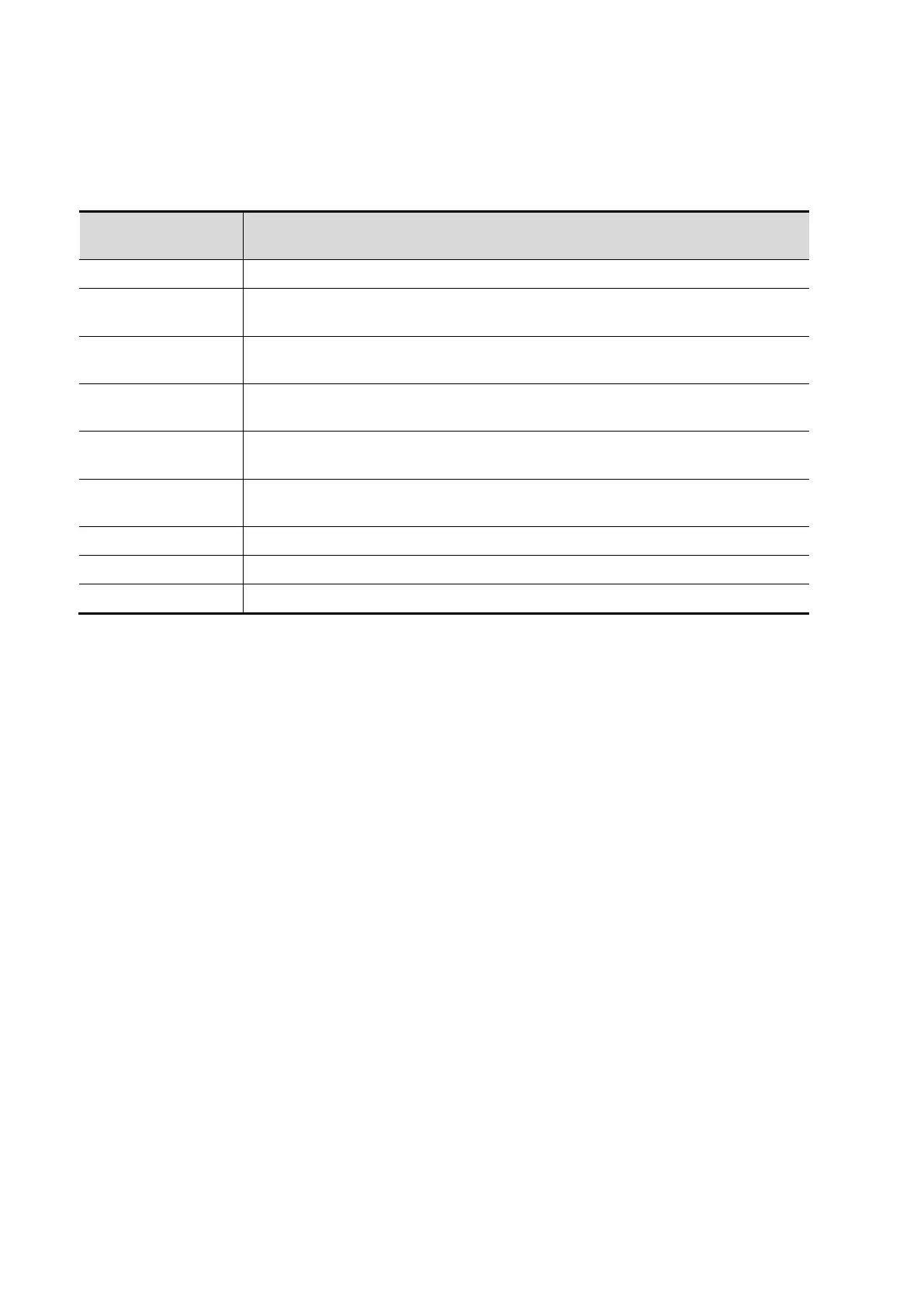
The time interval between any two points.
N intervals (n≤8) are measured to calculate a PW mode derived HR value in
Beats Per Minute (BPM).
On the Doppler mode image, velocity and PG (pressure gradient) of a point
on the Doppler spectrum waveform are measured.
Velocity and time interval between two points are measured to calculate
speed difference and acceleration.
On the PW mode image, one or several Doppler waveforms are traced to
obtain speed and PG, etc.
Velocity and PG between two peaks on the Doppler spectrum to calculate
RI (resistance index) and PS/ED (peak systolic/end diastolic).
Blood flow through some vascular cross section per unit time.
Measures D velocity and calculate ratio value for blood analysis.
Measures VTI values from the spectrum and then calculate ratio value.
8.3 Application Measurement
Abdomen measurements - Used for measurements of abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder,
pancreas and kidney, etc.) and large abdominal vessels.
OB measurements - Used for measurements of fetal growth indexes (including EFW) as well
as GA and EDD calculations. The fetus can be evaluated through growth graph analysis and
fetal biophysical profile.
Cardiac measurements – Used for left ventricle function measurements and measurements of
main artery and vein parameters, etc.
Gynecology measurements - Used for the uterus, ovary and follicles, etc.
Small Part measurements – Used for small parts such as thyroid.
Urology measurements - Used for prostate, seminal vesicle, renal, adrenal, micturated and
testicle volume.
Orthopedics measurements – Used for hip joint measurement.
Vascular measurements – Used for carotid, cerebral, upper and lower extremities vessels, etc.
EM measurements – Used for EM related full functional measurement.
 Loading...
Loading...