11.3 POWER CONSIDERATIONS
The average chip-junction temperature
l
T
J,
in
°c
can
be
obtained from:
TJ=
TA
+ (Poe8JA)
Where:
T A
==
Ambient T emperatu
re,
°c
8JA
==
Package Thermal Resistance, Junction-to-Ambient,
°C/W
PO==PINT+
PPORT
PINT
==
ICC
x VCC, Watts - Chip Internal Power
PPORT==
Port Power Oissipation, Watts - User Oetermined
(1
)
For most applications
PPORT~
PINT and can
be
neglected.
PPORT
may become significant if
the device
is
configured to drive Oarlington
bases
or sink
LEO
loads.
An appropriate relationship between
Po
and T J (if
PPORT
is
neglected)
is:
PO=K+(TJ+273°)
(2)
Solving equations 1 and 2 for K gives:
K=
Poe(TA + 273°C)
+8JAePo2
(3)
Where K
is
a constant pertaining
to
the particular part. K can
be
determined from equation 3 by
measuring Po (at equilibrium) for a known T
A Using this value
of
K the values
of
Po
and T J
can
be
obtained by solving equations
(1)
and
(2)
iteratively for any value
of
T A
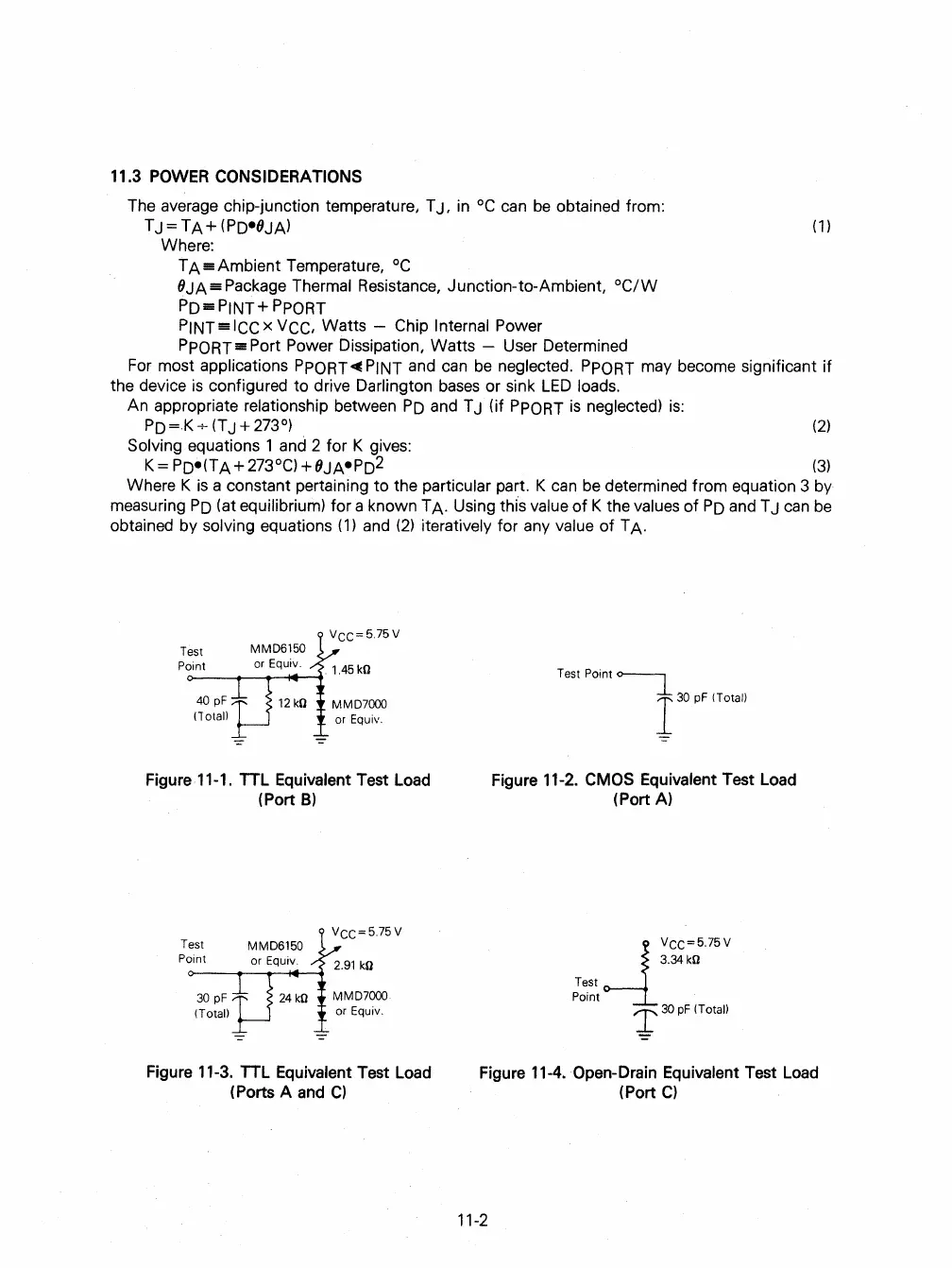
VCC=5.75V
Figure 11-1. TTL Equivalent Test Load
(Port
B)
Test
Point
30 pF
(Total)
VCC=5.75V
Figure 11-3. TTL Equivalent Test Load
(Ports A and
C)
TestPoint~
r
30
pF
ITo""
Figure 11-2. CMOS Equivalent Test Load
(Port A)
Test
Point
~
VCC=5'75V
3.34kO
l'
30
pF
(Total)
Figure 11-4. Open-Drain Equivalent Test Load
(Port
C)
11-2

 Loading...
Loading...