Video Grabber User Manual - v. 1.19 (FW 1.29)
4.1.3. NTP status
Video Grabber is synchronizing its internal clock using NTP protocol by connecting to NTP peers. The
choice between configured peers is done based on their time source quality
. Once configured the
synchronization “just works”. However for the rare cases when deep analysis of the NTP
synchronization process is required the Status page provides detailed information on the current NTP
operational parameters.
NTP status section of the Video Grabber’s Status page can be further divided into two subsections –
first contains a table listing all configured NTP peers along with their basic parameters, while the
second lists more detailed information related to the NTP peer that is currently used for clock
synchronization.
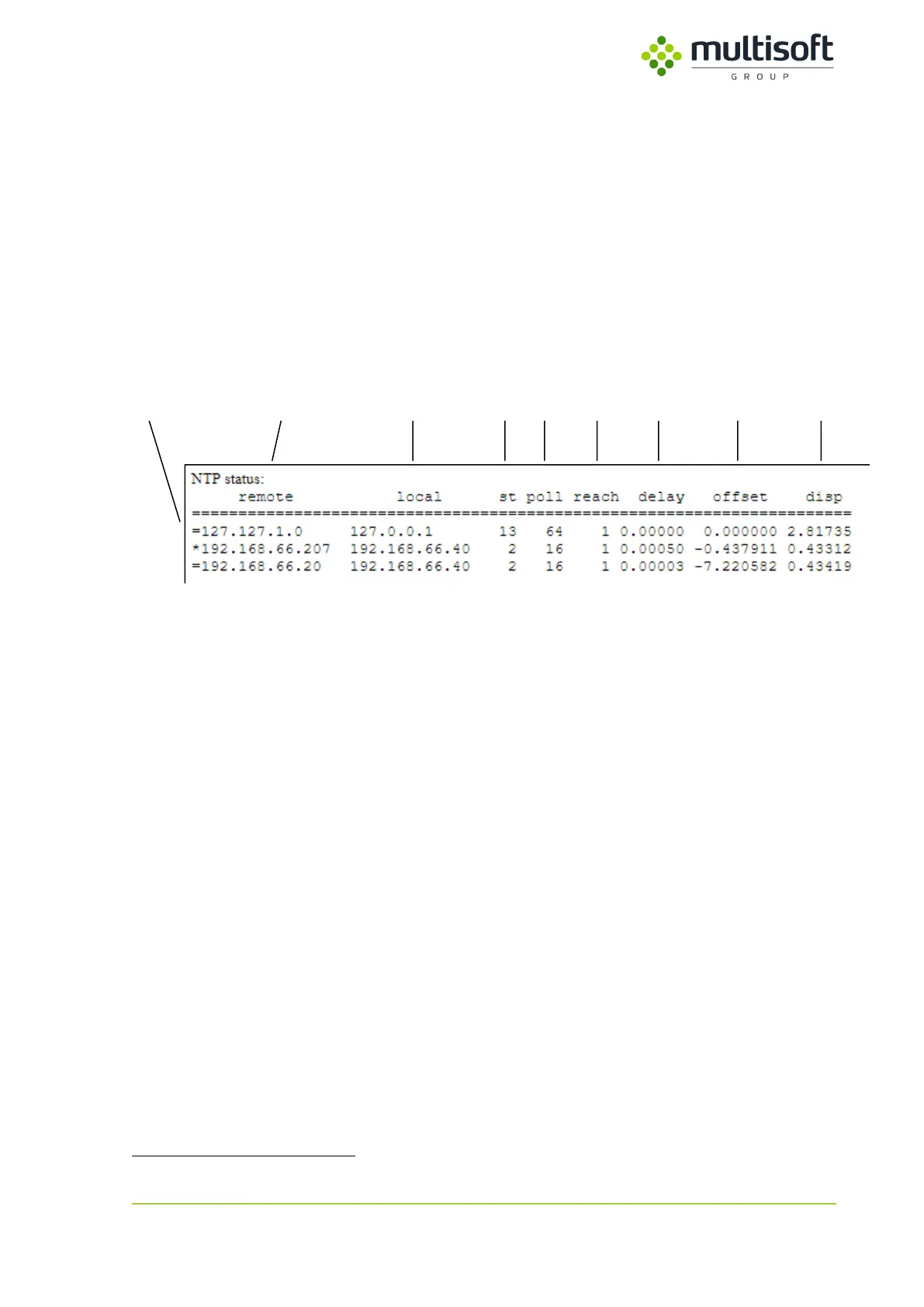
Figure 12: Table listing configured NTP peers
The table is a printout of standard NTP query program ntpdc. It lists all NTP peers that are configured
on the Video Grabber device along with their basic parameters and state:
1. Mode – single-character peer mode indicator. The list of possible modes is as follows:
a. * – server has been chosen and is used as a clock reference
b. = – server is being polled in client mode
c. + – server is in symmetric active mode
d. – – server is in symmetric passive mode
e. ^ – server is broadcasting to this address
f. ~ – server is sending broadcasts
2. remote – IP address of the time source
3. local – IP address used to connect to the time source
4. st – stratum number of the time source
5. poll – frequency (in seconds) at which the time source is polled for time
6. reach – octal bitmask of success or failure of last 8 queries (left-shifted). e.g.:
a. 377 – 11111111 – all 8 recent queries were successful
b. 317 – 11001111 – from 8 recent queries 5th and 6th failed
7. delay – roundtrip time of the queries to the reference time (in seconds)
8. offset – difference between the reference time and the system clock (in seconds)
9. disp – magnitude of jitter between several time queries (in seconds)
Consult NTP documentation (available e.g. on http://doc.ntp.org) for details on the algorithms used for time
synchronization.
 Loading...
Loading...