Synthesis Engine
Synthesis Engine
82 83
Automation and Rendering
Besides a few exceptions (oscillator phases, unison voices – only eective when play-
ing new notes), all parameters operate as smoothers within the synth engine and can
perform transitions from one value to another in a specified time (adjustable by the user).
This aects modulations, preset transitions and editing of parameters, each having their
individual times.
The whole control process of the synth engine is realized by a custom automation proto-
col, called TCD (time, curve, destination). Anything from a preset recall to performance is
transmitted, even instructions for envelope signals. There will be a separate document in
the future, explaining the basics and capabilities of TCD.
At the moment, adjustable parameters are only capable of handling monophonic values.
It is planned to change this in the future in order to be able to implement splitting, layer-
ing of sounds and modulation of selected voices.
5.3 Components of the Synthesis Engine
In this chapter, the individual components are described in further detail. Their func-
tionality is explained and methods for the creation and manipulation of signals are
contemplated. The goal here is to highlight the noticeable and audible eects of certain
mechanisms while avoiding the mathematical and physical foundations if possible. Con-
cludingly, profound knowledge of (digital) signal processing and acoustics is not required
– however, it surely can be helpful.
Envelopes
The primary purpose of the envelopes is to create modulation signals according to
played keys. Their most crucial applications are certainly the amplitudes (peak levels) of
the oscillators, which is predefined. So the amplitude of Oscillator A directly depends on
the signal of Envelope A, as the amplitude of Oscillator B directly depends on the signal
of Envelope B. Besides, there are other targets which can be influenced by the envelopes
according to modulation amount parameters. They are referred to in the following
sections.
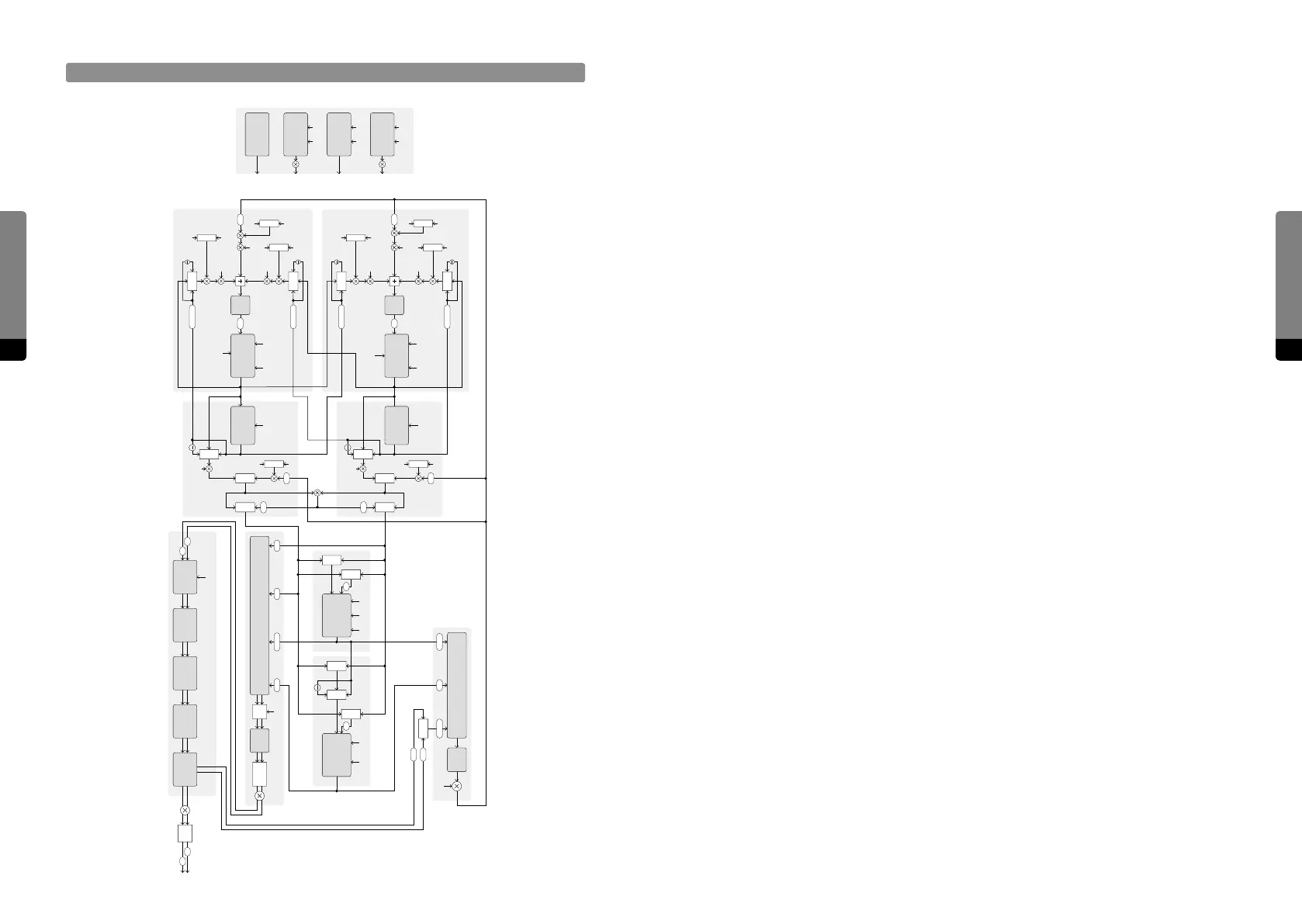
Signal Flow Detailed
Shaper A
PM
PM PM
PM
FB
Shaper A
Dry
EectsSVFComb
RM
RM
Comb SVFBA
Wet
Shaper B
Shaper B
L
R
L
R
FB
FB
FB
Env A
PM FB
Env A
Env B
KT
Env C
KTVel
KTVel
KTVel
1
PM Self
1
Env A
Env C
Gate
Env A
Env A
Gain
Env B
Gain
Env B
1
Env C
Env C KTGate
Gate
Key Pos
Env C KT
Gate
PM B
Env A
PM FB
Env C
1
PM A
1
Env C
KT
Env C
KT
Note On
Note On
Env B
1
PM Self
Env C
Gate
Master
Level
Level
Shaper
Shaper
Shaper
Shaper
RM
Comb
RM
Reverb
So
Clip
Pan Voice Mix
FB Mix
Mix
FB Mix
Mix
A
B
A
B
A
B
A
B
Shaper
Shaper
Chirp
Filter
Chirp
Filter
Envelope A
Envelope B
Envelope C
Gate
Shaper A
CabinetFlanger Echo Reverb
Gap
Filter
Feedback Mixer
Oscillator B
Oscillator A
Shaper B
Comb
Filter
State
Variable
Filter
Output Mixer
 Loading...
Loading...