CP TD1 Reference Manual V 1.44
96
7.4 Capacitance and DF Measurement on High-Voltage
Bushings
The dissipation factor test is the most effective known field test procedure for the
early detection of bushing contamination and deterioration. It also measures
alternating (AC) test current, which is directly proportional to bushing
capacitance.
Bushing dissipation factor and capacitance should be measured when a bushing
is first installed and also one year after installation. After these initial
measurements, bushing power or dissipation factor and capacitance should be
measured at regular intervals (3 to 5 years typically). The measured values
should be compared with previous tests and nameplate values.
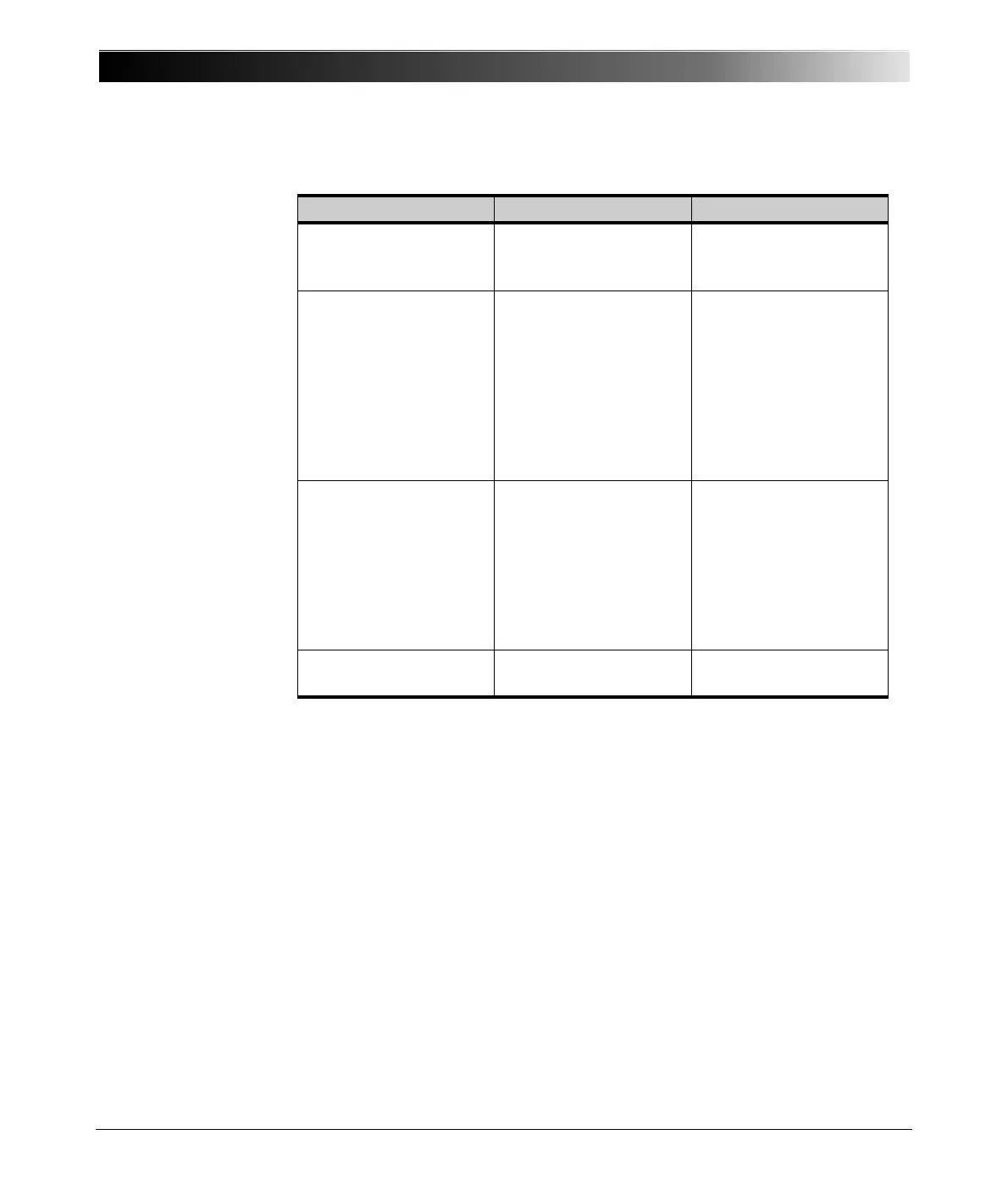
Lightning Cracked or broken
porcelain;
Complete failure
Visual inspection;
Test lightning arresters
Corona Internal breakdown;
Radio interference;
Treeing along surface of
paper or internal
surfaces
Power factor test;
Hot-collar test;
Hot wire test;
Radio-influence voltage
(RIV) test;
Thermographic
scanning;
Dissolved gas-in-oil
analysis (DGA)
Short-circuited
condenser sections
Increased capacitance;
Reduced voltage at
capacitance tap terminal;
Adds internal stress to
insulation
Power factor test;
Voltage test at
capacitance tap;
Capacitance test;
Thermographic
scanning;
Dissolved gas-in-oil
analysis (DGA)
Darkened oil Radio interference;
Poor test results
Power factor test;
Hot-collar test
Table 7-1 Bushing faults, part 1 [4.3]
Failure Possible results Methods of detection

 Loading...
Loading...