2-6SectionLamps
118
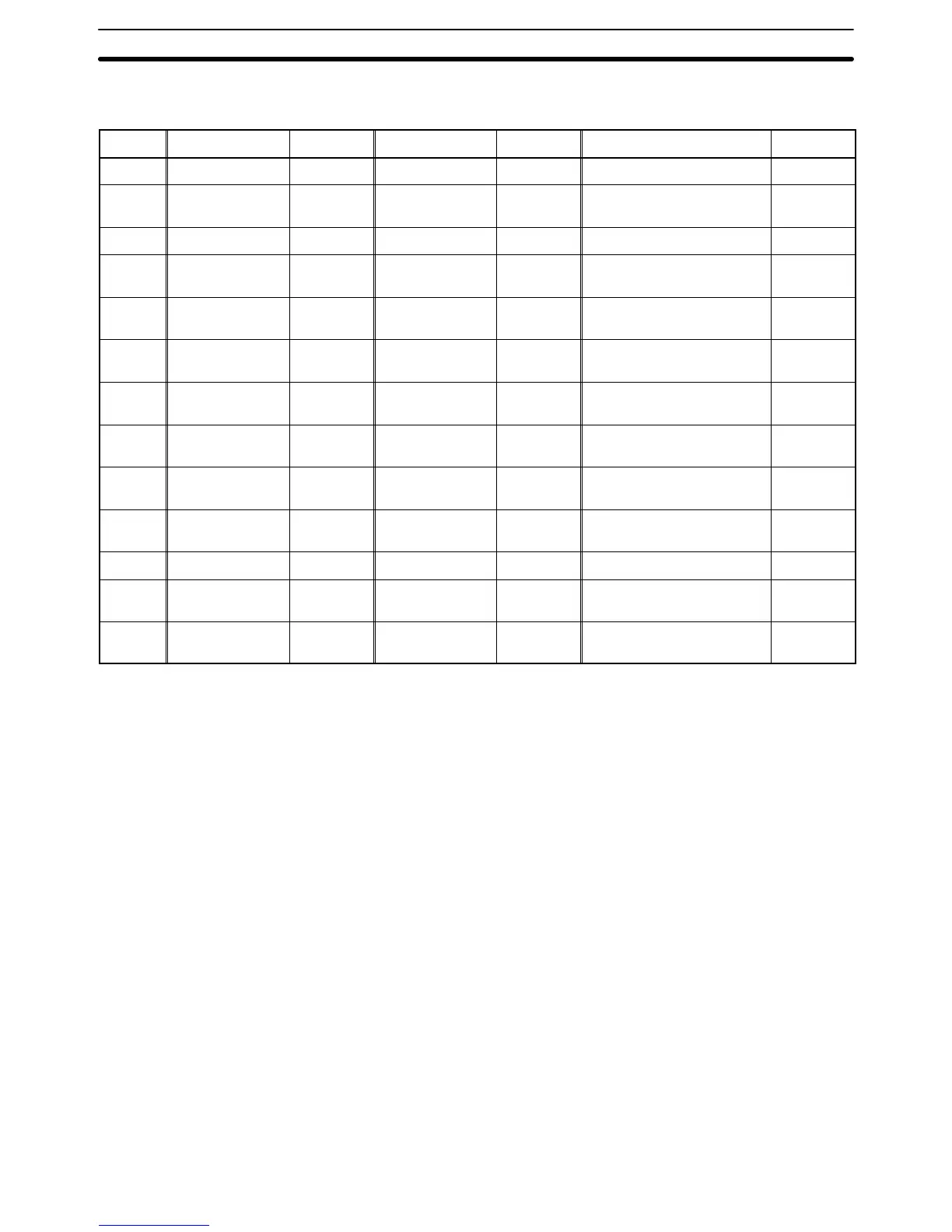
Allocated Bits
Bits can be allocated for lamp bits in the following host (PC) areas.
Symbol C-series PCs Allocation CV-series PCs Allocation CS/CJ-series PCs Allocation
None IR Area OK CIO Area OK CIO Area OK
H HR Area OK --- --- HR Area
Not for
Host Link
A AR Area OK Auxiliary Area No AR Area OK
L LR Area OK --- --- LR Area
*1
Not for
Host Link
T
TC Area,
Timer PVs
No
Timer Area,
Timer PVs
No
TC Area,
Timer PVs
No
TU --- --- --- ---
TC Area,
Timer Completion Flags
Not for
Host Link
C
TC Area,
Counter PVs
No
Counter Area,
Counter PVs
No
TC Area,
Counter PVs
No
CU --- --- --- ---
TC Area,
Counter Completion Flags
Not for
Host Link
W --- --- --- --- WR Area
Not for
Host Link
TK --- --- --- --- Task Flags
Not for
Host Link
D DM Area OK DM Area OK DM Area OK
E
EM Area
*2
,
current bank
OK
EM Area,
current bank
Not for
Host Link
EM Area,
current bank
Not for
Host Link
E0_ to
EC_
--- --- --- ---
EM Area,
EM banks 0 to C
Not for
Host Link
*1: LR 00000 to LR 00199 are converted to CIO 01000 to CIO 01199.
*2: The EM Area is supported only by the C200HX/HG/HE(-Z)E PCs.
The Auxiliary Area of the CVM1 and CV-series PCs is allocated to system func-
tions, and it cannot be used for purposes other than system use.
The range of each memory area differs according to the PC. Refer to Appendix D
PC Memory Maps on page 435.
When a DM Area or EM Area address is specified, add a bit number (00 to 15) to
the end of the word address.
Lamps read the contents of a bit at the host and execute processing in accor-
dance with the bit status.
However, the bit is only read in the following case:
When a lamp is used on the currently displayed screen
Lamps have no output function.
Lamps have no data processing function.
Relationship with Other Elements
• Touch switches (page 119) have the same display functions as normal (stan-
dard) lamps.
• Lamps overlap with other elements in accordance with the order in which they
were registered on the screen with the Support Tool. However, the way in
which they overlap can be changed with the Support Tool.
Input Functions
Output Functions
Processing Functions
 Loading...
Loading...