38
Section 3 BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF CLEAN SENSING SYSTEMS
ZN
System Manual
Section 3
Feedback Control
■ Feedback Methods
There are two feedback methods, "rapid feedback" and "constant feedback."
• Rapid feedback
When cleanliness has deteriorated, rapid feedback quickly increases the air volume
level to recover the cleanliness.
This feedback method is effective in environments with relatively lots of change.
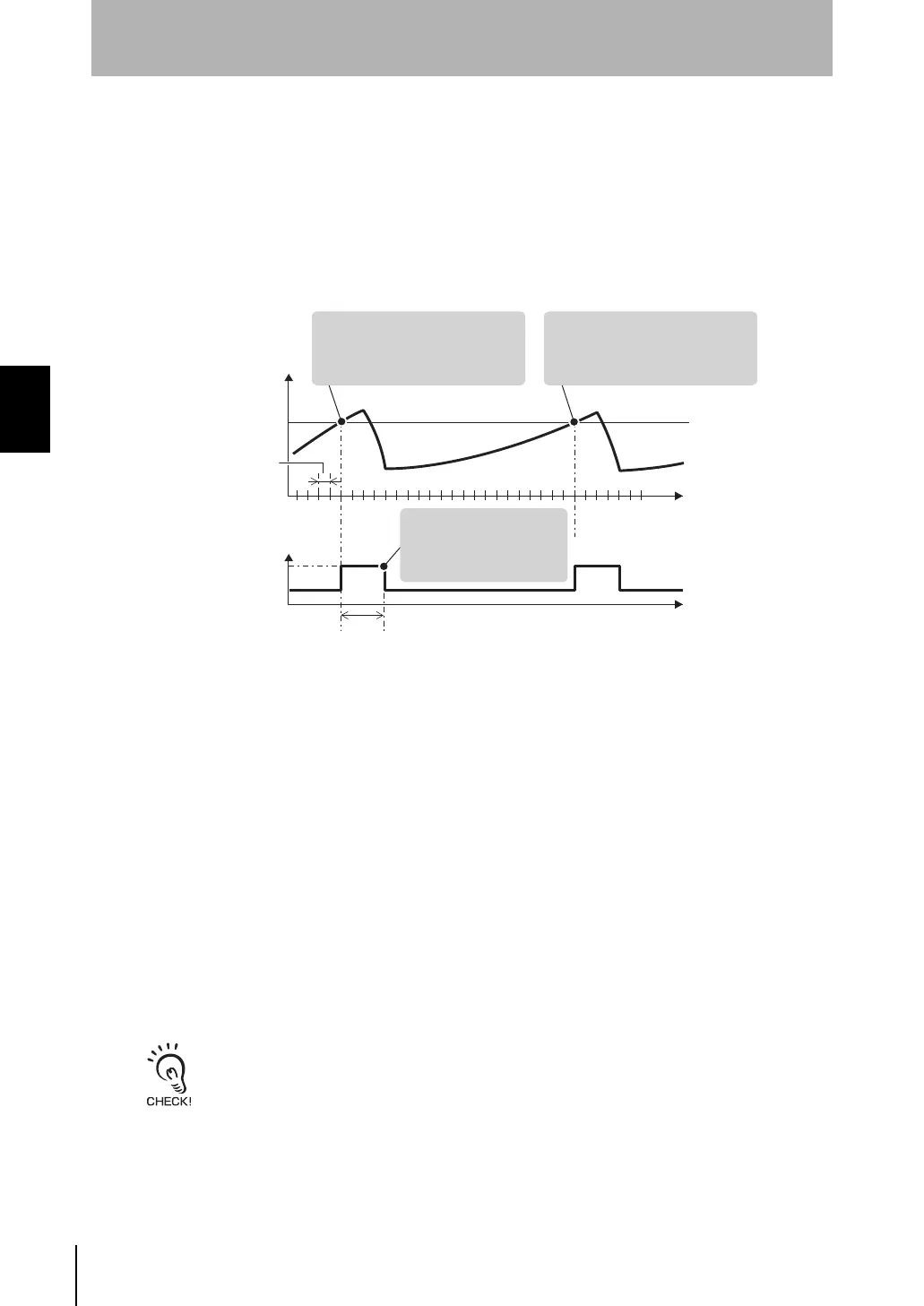
<Feedback Operation>
• When the high power time is set to a value other than "0":
The high power air volume level is switched to regardless of changes in the amount
of particles when the high power air volume level continues until the high power time
elapses.
• When the high power time is set to "0":
The high power air volume level continues until the amount of particles falls to a fixed
level or lower, and the low power air volume level is switched to.
• For the high power air volume level, set an air volume greater than the lower power air volume
level. Otherwise, feedback will not function properly.
• If the cleanliness is not restored after the high power time has elapsed, operation will continue at
the low power air volume level (i.e. the high power air volume level will not be switched to). When
this happens, either set a longer high power time or set the high power time to 0.
(2) When the high power
time elapses, the air
volume level returns
to low power.
(1) The air volume level is
changed to high power when
the cleanliness exceeds the
target cleanliness.
(3) The air volume level is
changed to high power when
the cleanliness exceeds the
target cleanliness again.
Amount of particles
Target cleanliness
High power air volume level
Low power air volume level
Feedback cycle
High power time
Time
Time
[Feedback Cycle]
• In a multi-clean sensing system:
The feedback cycle can be set on the Interface Unit.
• In a direct clean sensing system:
The feedback cycles equals the measurement time
of the Air Particle Sensor.
3basic.fm38ページ2007年6月28日 木曜日 午前9時18分

 Loading...
Loading...