44
Section 3 BASIC KNOWLEDGE OF CLEAN SENSING SYSTEMS
ZN
System Manual
Section 3
Clean Sensing
Clean Sensing
Principle of "Particle Count"
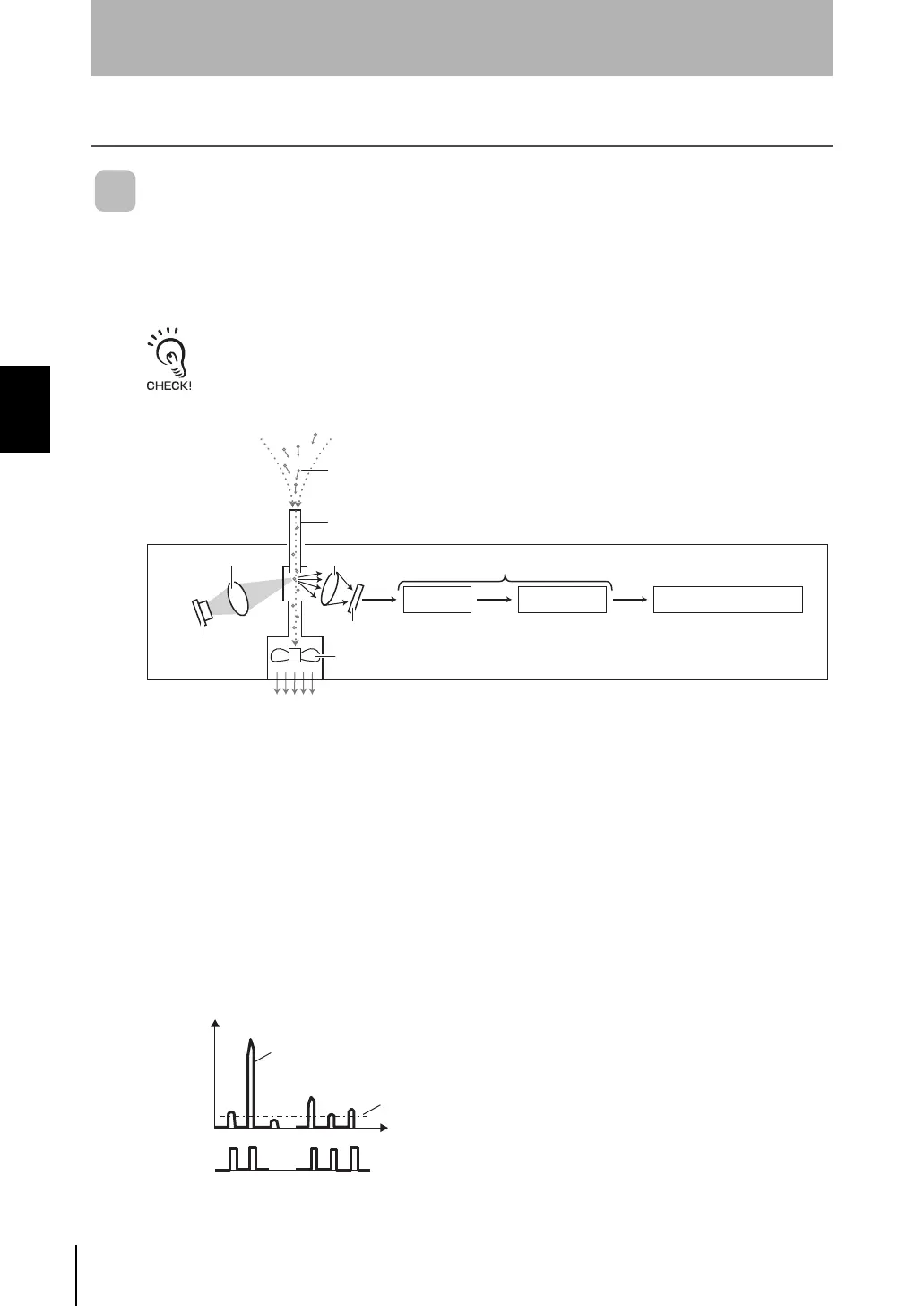
The ZN-PD series judges the cleanliness of target spaces by measuring the amount of particles
(dust or dirt) floating in the air. The amount of particles is measured using the "fan method" and
"scattered light method" mounted on the Air Particle Sensor (Sensor + Amplifier Unit).
The ZN-PD series adopts the "fan method" for sucking in air. Compared with the "pump method"
used on handy-type particle sensors, for example, this method has a service life that is about 10
times longer. This enables the amount of particles to be measured stably over a long period of time.
(1) Air inside the clean booth is sucked in from the suction inlet by the fan.
(2) The sucked in air is illuminated by a laser beam.
If the air contains particles, the light is scattered.
(3) Particles are detected by scattered light entering the light receiving lens, and the
amount of particles is measured.
The scattered light entering the light receiving lens is converted to electric signal by
the amplifier and comparator, and is sent to the signal processing circuit.
The amount of particles is measured based on the electrical signals that are sent to
this circuit.
■ Measurement of the Amount of Particles
The amount of particles is measured based on
the incident value. However, this incident value
increases the larger the particles become.
Thresholds are set for each of the target
particle diameters of 0.3 µm/0.5 µm/1.0 µm,
and the particle diameter is judged according
to the size of the incident value.
(1)
(2)
(3)
Particles
Suction inlet
Receiving lens
Light-receiving lens
Fan
Amplifier Comparator
Light source
Emission lens
Signal processing circuit
Received light signal
Threshold
Time
Comparator
output
Incident
value
Received light signal and comparator output
3basic.fm44ページ2007年6月28日 木曜日 午前9時18分

 Loading...
Loading...