Chapter 7 - Using the viewing options
Simulated BIO view
The Simulated BIO View simulates the retinal view as it would be seen via a Binocular Indirect
Ophthalmoscope.
The image is inverted and mirrored about the center of the image. This view allows you to target the
relevant areas during a BIO examination.
Recommended reading protocol
The Review application includes many functions that can help you review images. This recommended
protocol guides you through a typical protocol for reviewingindividual images.
You should follow this suggested protocol if you do not have one for your practice. The protocol is generic
and you should take any additional steps necessary to provide a comprehensive exam for each patient.
1. If the patient will be present during the image review, open an image of each eye in the 3D Wrap
view. You can use this when explaining details to the patient, see Using the 3D Wrap view on
page 46.
Caution
Using the 3D Wrap view for diagnostic purposes is not recommended.
2. Select the images and open them in an Image Stack window. In addition, open a previously reviewed
image if one is available, for example an image from the previous year.
3. Maximize the image window.
4. Evaluate the image for peripheral extent:
l
Zoom to at least 100%.
l
Pan around the image periphery and check that there is good peripheral coverage.
Increase the gamma if necessary.
5. Review the image for clinical information:
l
Switch to the Green Separation view.
l
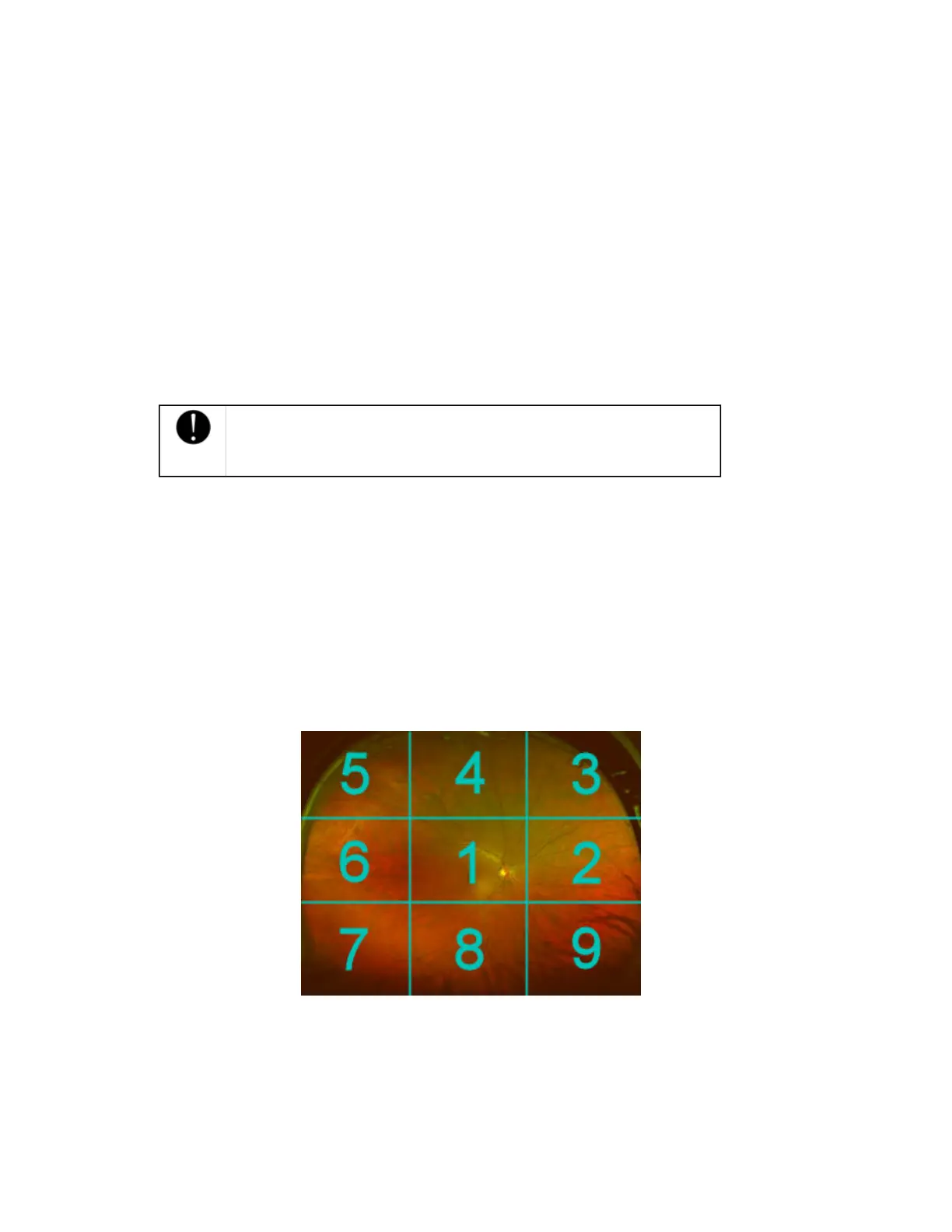
Pan around the image following the numbered sequence of the grading grid. Ensure all
areas have been reviewed. Adjust the image adjustment settings if required.
l
Mark any areas of interest with the relevant annotation, see Documenting your review on
page 51.
l
Switch to the Red Separation view and repeat for the deeper structures of the retina, from the
pigment epithelium through the choroid.
6. Review the full image and complete mark-ups:
l
Select the Composite Color view and review the entire image. Check for any areas that may
have been missed.
l
Check any markups that have been made and complete any annotations.
7. Compare the image with patient's previous images, if available:
44 of 100
 Loading...
Loading...