48 APPENDIX B: SENSOR INFORMATION
087-0065 REV B SCOTT SAFETY
Gas Interferences There are known gas interferences to a limited number of chemical compounds. Scott
Safety attempts to identify possible gas interferences to which gas sensors may be
exposed; however, not all chemical compounds that presently exist have been tested.
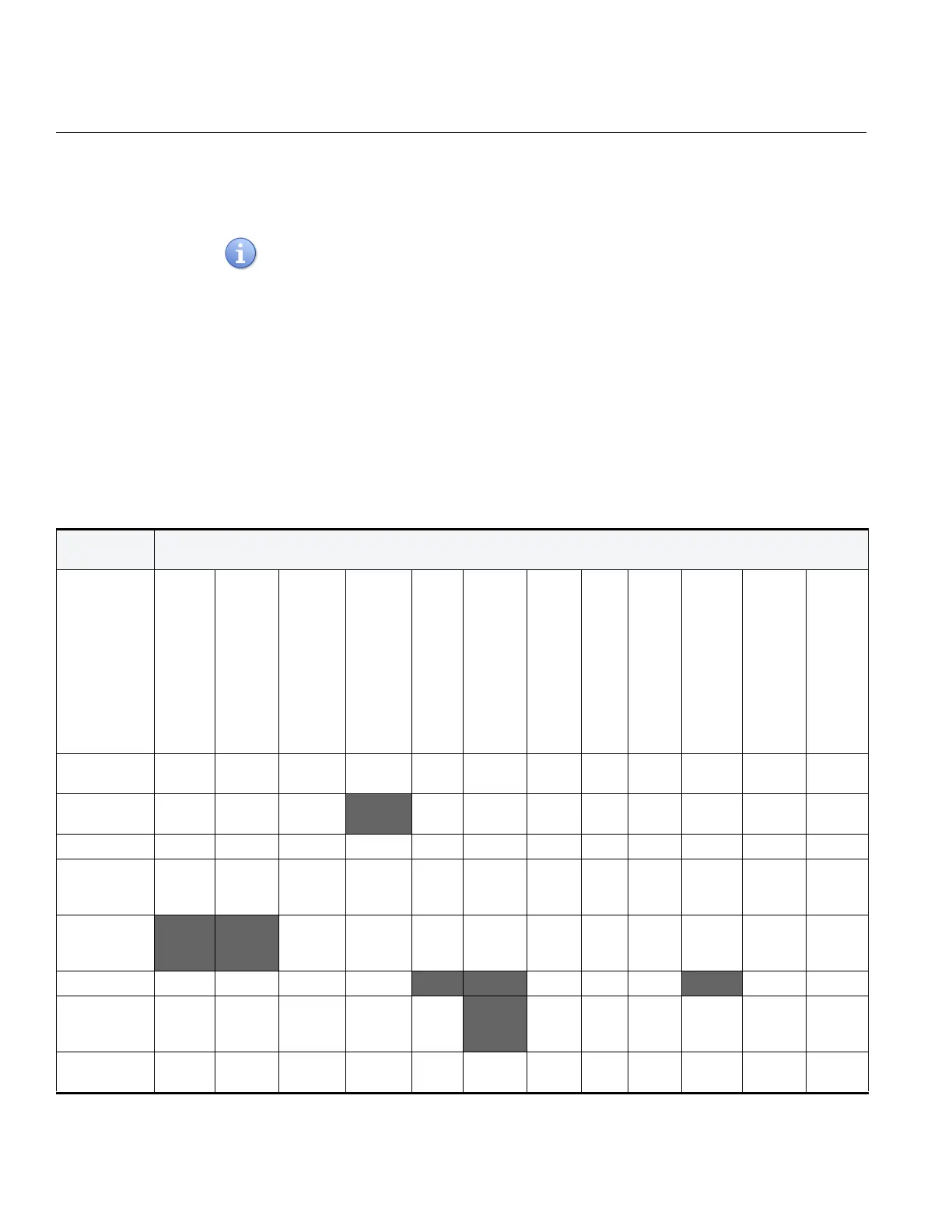
Table 21 provides known toxic gas interferences.
Table 21 does not show, nor should it be implied, that no additional interferences may
occur. These selectivity ratios are used as guides only. They are not to be used as
calibration factors. The gas species’ actual cross-sensitivities may vary from the
values shown.
Keys for Table 21.
• Zero – Indicates tested and confirmed no interferences
• Blank – Indicates not tested
• Neg – Indicates gas produces a negative signal
• Two values in a cell – Indicates initial peak and finish offset (unstable or transition
gas) and should not be used for cross calibration
Table 21 Gas Interferences
INTERFERE
NCE GAS: SENSOR TYPES (ALL VALUES IN PPM)
CO (Single)
CO (H
2
-resistant)
H
2
S (Single)
Ammonia (NH
3
)
Chlorine (Cl
2
)
Chlorine Dioxide (ClO
2
)
Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN)
Oxide (NO)
Nitric Dioxide (NO
2
)
Ozone (O
3
)
Phosphine (PH
3
)
Sulfur Dioxide (SO
2
)
Acetylene
(C
2
H
2
)
<3
Ammonia
(NH
3
)
0 <0.001 1 0
Arsine (AsH
3
) 0.7
Carbon
Dioxide
(CO
2
)
0 neg 0 0.005
Carbon
Monoxide
(CO)
1 1 <0.02 <0.01 0 0 <0.05 0 0 0 <0.003
Chlorine (Cl
2
)
0 <0.001 1 0.6 1 1.2 <‐0.4
Chlorine
Dioxide
(ClO
2
)
1 1.5
Diborane
(B
2
H
6
)
0.35
 Loading...
Loading...