Basics of program execution
5.1 Events and OBs
CPU 1516pro-2 PN (6ES7516-2PN00-0AB0)
Operating Instructions, 09/2016, A5E35873416-AA
47
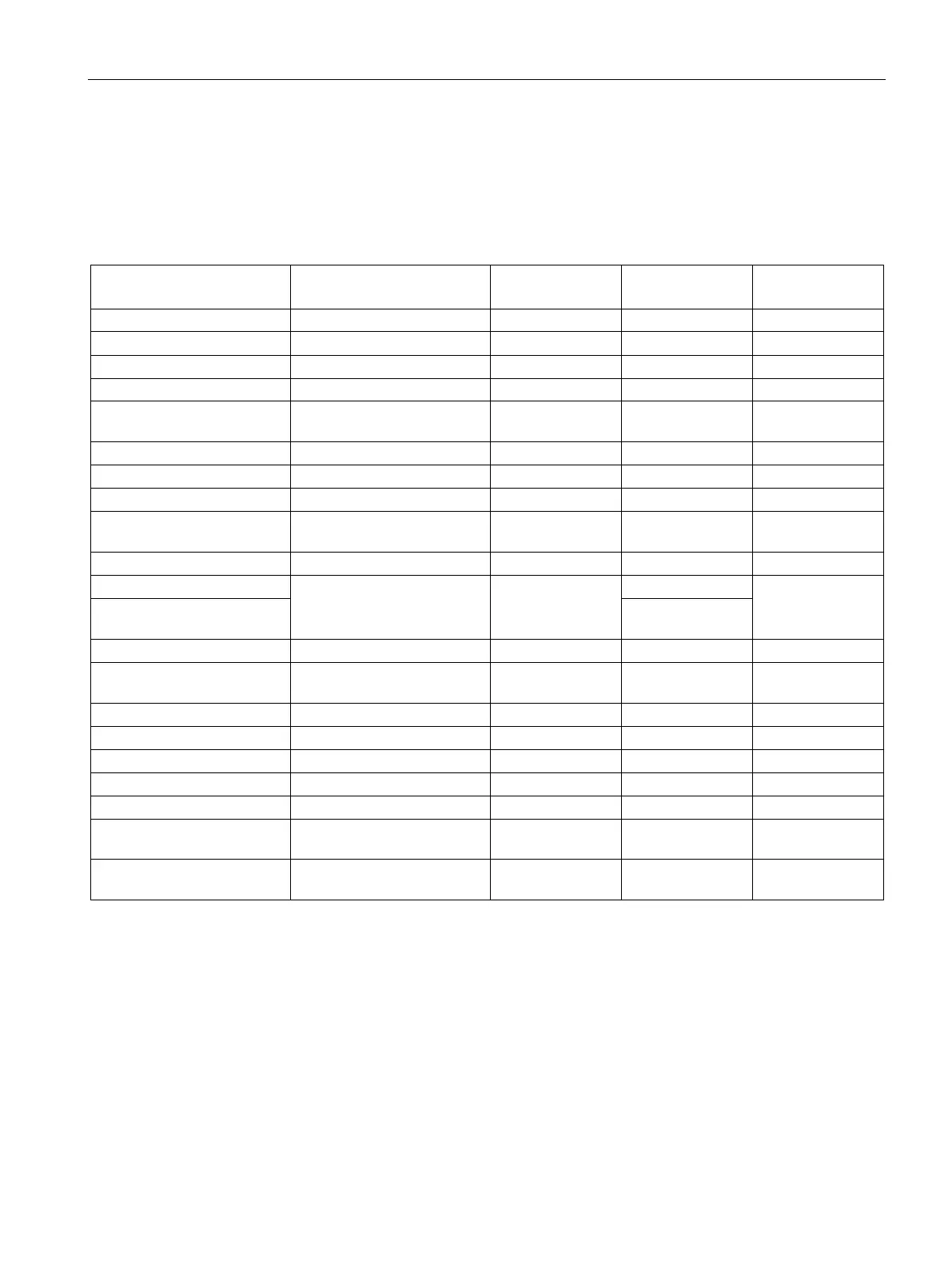
The table below provides an overview of the triggers, including the possible values for OB
priority, possible OB numbers, default system reaction and number of OBs.
Table 5- 1 Triggers
Possible priorities (default
priority)
Default system
reaction
1)
2)
Cyclic program
2)
1 1, ≥ 123 Ignore 0 to 100
2)
Time-delay interrupt
2)
2 to 24 (3) 20 to 23, ≥ 123 Not applicable 0 to 20
Cyclic interrupt
2)
2 to 24 (8 to 17, frequency
30 to 38, ≥ 123 Not applicable 0 to 20
2)
3)
Manufacturer-specific or
profile-specific interrupt
2 to 24 (4) 57 Ignore 0 or 1
Isochronous mode interrupt
4)
22 80
0 or 1
Maximum cycle time exceed-
STOP
Removal/insertion of mod-
2 to 26 (6) 83 Ignore 0 or 1
5)
5)
5)
MC interpolator
5)
16 to 26 (24) 92 Not applicable 0 or 1
Programming error (only for
2 to 26 (7) 121 STOP 0 or 1
I/O access error (only for
2 to 26 (7) 122 Ignore 0 or 1
If you have not configured the OB.
For these event sources, apart from the permanently assigned OB numbers (see column: possible OB numbers), you
can also assign OB numbers in STEP 7 from the range ≥ 123.
You can assign a maximum of one hardware interrupt OB to each I/O module in STEP 7.
The start information is displayed in the hardware interrupt OB in the TIA Portal the same as in S7-300/S7-400. You can
find additional information on the start information in the STEP 7 online help.
If the maximum cycle time has been exceeded twice within a cycle, the CPU always switches to STOP regardless of
whether you have configured OB 80.
You can find additional information about these event sources and the runtime behavior in the S7-1500 Motion Control
 Loading...
Loading...