Motor components, characteristics and options
4.2 Cooling
SIMOTICS M-1FE2 built-in motors
Hardware Installation Manual, 04/2020, A5E50074509B AA
69
Preventing cavitation
Motor damage caused by cavitation and abrasion
An excessive pressure drop at the motor can cause motor damage as the result of
cavitation and/or abrasion.
• Operate the motor so that the pressure drop at a converter or motor in continuous
operation does not exceed 0.2 MPa.
Connecting motors in series
For the following reasons, connecting motors in series can be recommended only
conditionally:
● The required flow rates of the motors must be approximately the same (< a factor of 2)
● An increase in the coolant temperature can result in derating the second or third motor if
the maximum coolant inlet temperature is exceeded
Coolant inlet temperature
Motor damage caused by condensation formation
Water condensation can cause motor damage.
• Select the coolant inlet temperature so that condensation does not form on the surface
of the motor. T
cooling
> T
ambient
- 5 K.
• Interrupt the supply of coolant for a longer motor standstill.
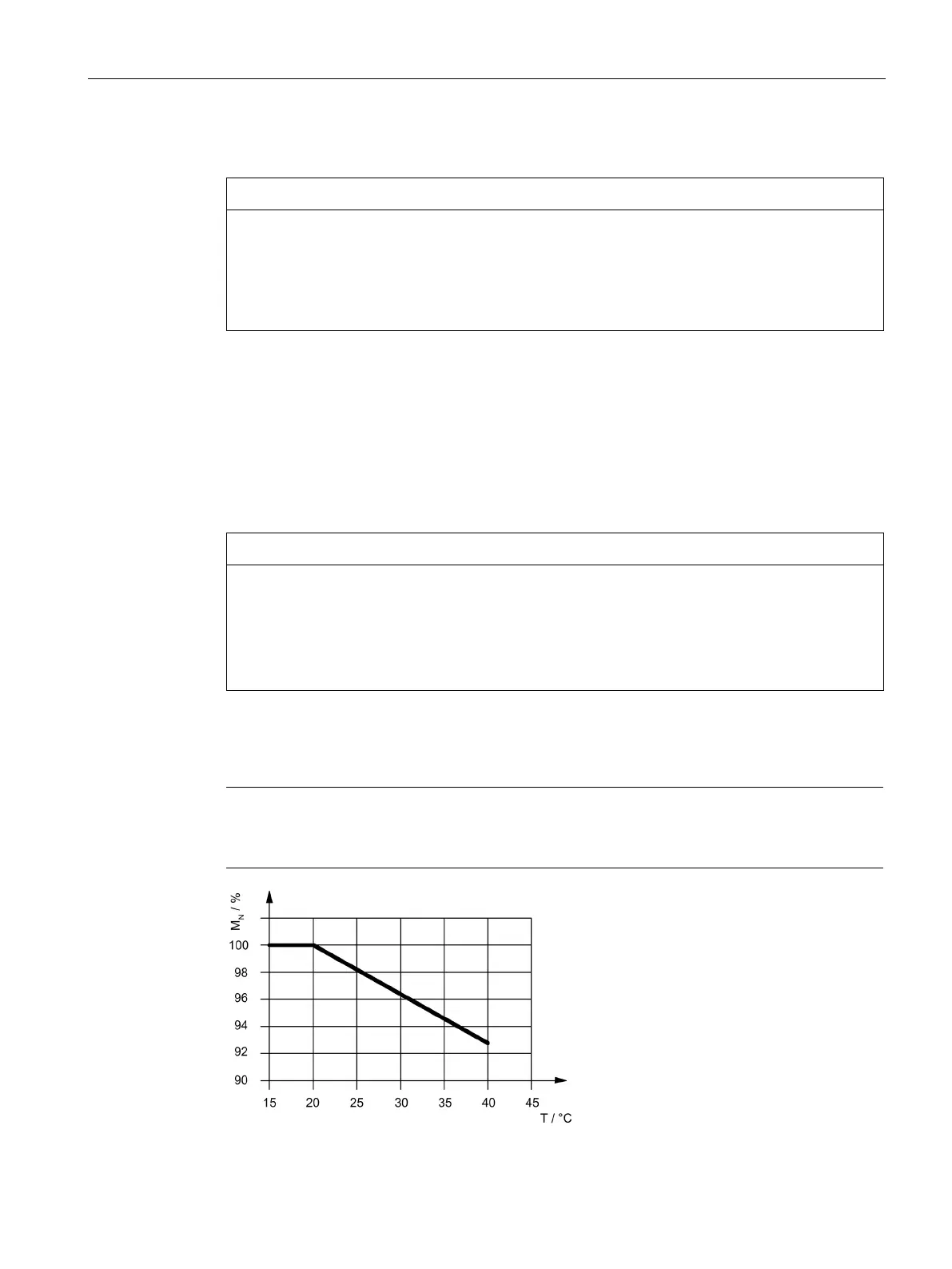
The motors are designed for full-load operation at maximum +20 °C coolant inlet
temperature.
Operation up to +40 °C coolant inlet temperature is possible with derating (reduced power).
Note
Derating
The spindle manufacturer
is responsible for the derating.
Figure 4-2 Effect of the cooling-medium intake temperature

 Loading...
Loading...