SC5 Signal Conversion Performance Measurements
62
Temperature coefficient
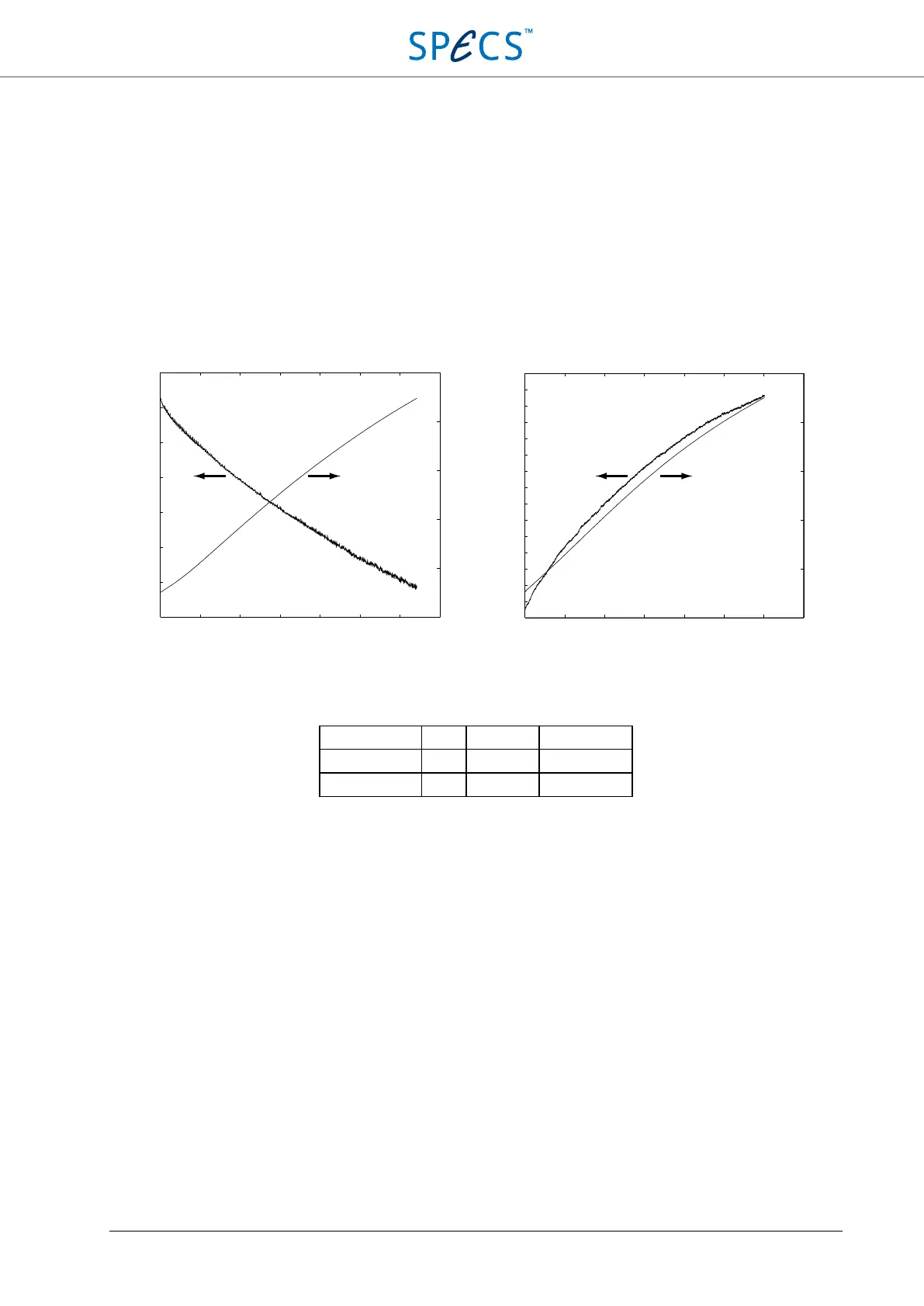
The temperature coefficient is determined by changing the environment temperature and recording both the output
voltage (AO1) and the internal temperature of the SC5. The measurement is performed for 0 V and 9.9 V output. For
negative voltages the temperature coefficient is negative, while for positive voltages it is positive.
Note: The temperature coefficient is determined with respect to the internal temperature of the instrument. The
internal temperature varies considerably less than the external temperature, meaning that the temperature coefficient
is smaller when based on the environment temperature.
Note: During normal operation, the SC5 reaches a typical operating temperature of 38 – 42 °C. The temperature
coefficient around the operating temperature is lower than the worst-case value given below.
Figure 42: Temperature dependence of the output voltage on the internal temperature of the SC5. The left plot is for 0 V
output voltage, the right plot for +9.9 V.
Output voltage ΔT ΔV Tc
0 V 20 °C < -55 µV < -2.75 µV/°C
9.9 V 20 °C < 1.42 mV < 71 µV/°C
Table 18: Temperature coefficient of the analog outputs.
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
Time [min]
Output voltage [μV]
Internal temperature [°C]
-180
-190
-200
-210
-220
-230
-240
-250
35
30
25
20
15
10
Internal temperature [°C]
35
30
25
20
15
10
Time [min]
Output voltage [mV - 9.9V]
6.5
6.4
6.3
6.2
6.1
6.0
5.9
5.8
5.7
5.6
5.5
5.4
5.3
5.2
5.1
5.0
Output range: ±10 V
Output voltage: +9.9 V
Output range: ±10 V
Output voltage: 0 V
 Loading...
Loading...