Core peripherals PM0214
242/262 PM0214 Rev 9
4.4.15 Memory management fault address register (MMFAR)
Address offset: 0x34
Reset value: undefined
Required privilege: Privileged
4.4.16 Bus fault address register (BFAR)
Address offset: 0x38
Reset value: undefined
Required privilege: Privileged
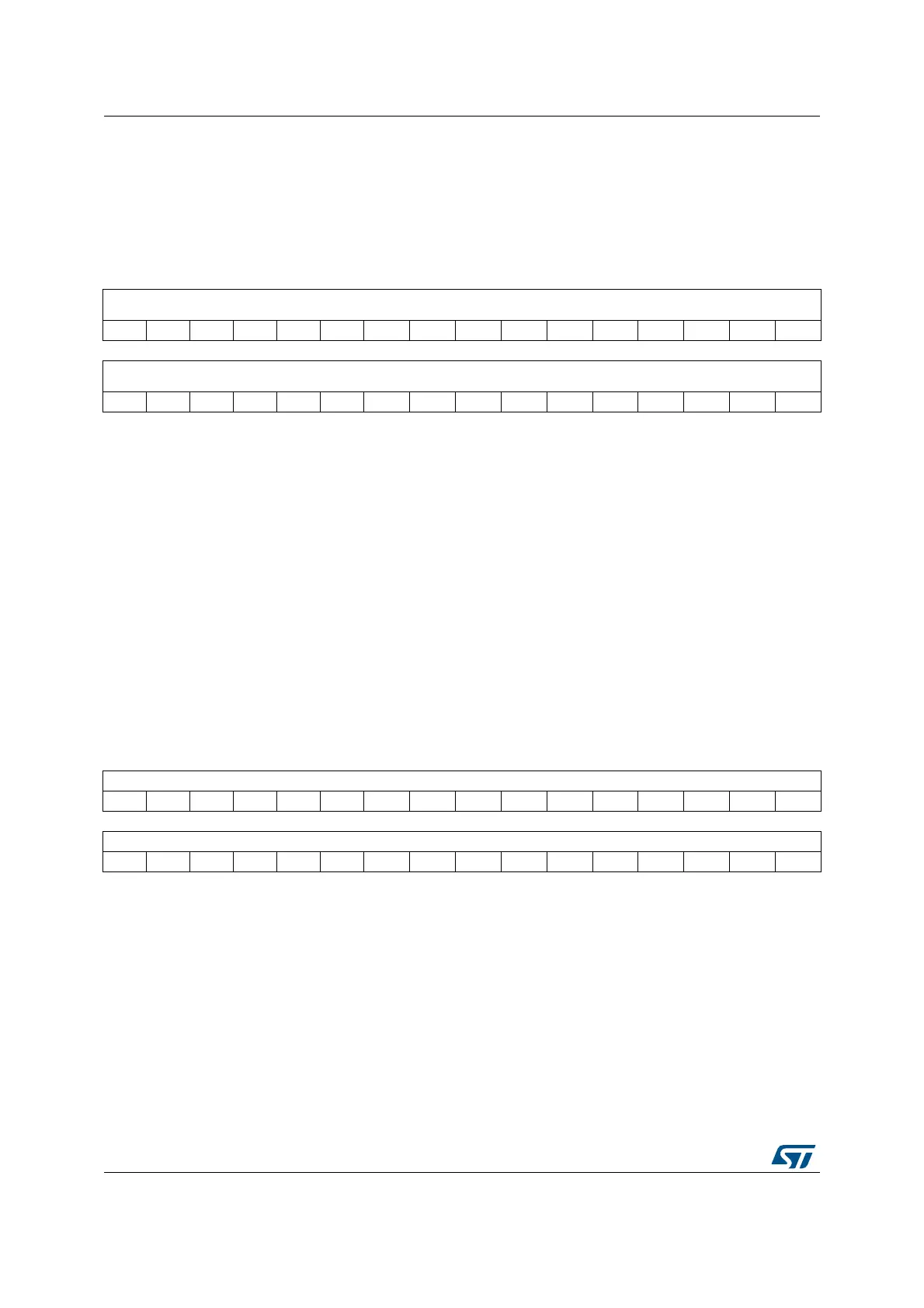
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
MMFAR[31:16]
rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw
1514131211109876543210
MMFAR[15:0]
rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw
Bits 31:0 MMFAR: Memory management fault address
When the MMARVALID bit of the MMFSR is set to 1, this field holds the address of the
location that generated the memory management fault.
When an unaligned access faults, the address is the actual address that faulted. Because a
single read or write instruction can be split into multiple aligned accesses, the fault address
can be any address in the range of the requested access size.
Flags in the MMFSR register indicate the cause of the fault, and whether the value in the
MMFAR is valid. See Configurable fault status register (CFSR; UFSR+BFSR+MMFSR) on
page 237.
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
BFAR[31:16]
rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw
1514131211109876543210
BFAR[15:0]
rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw
Bits 31:0 BFAR: Bus fault address
When the BFARVALID bit of the BFSR is set to 1, this field holds the address of the location
that generated the bus fault.
When an unaligned access faults the address in the BFAR is the one requested by the
instruction, even if it is not the address of the fault.
Flags in the BFSR register indicate the cause of the fault, and whether the value in the BFAR
is valid. See Configurable fault status register (CFSR; UFSR+BFSR+MMFSR) on page 237.

 Loading...
Loading...