CB3000 Client Bridge User Guide
1-8
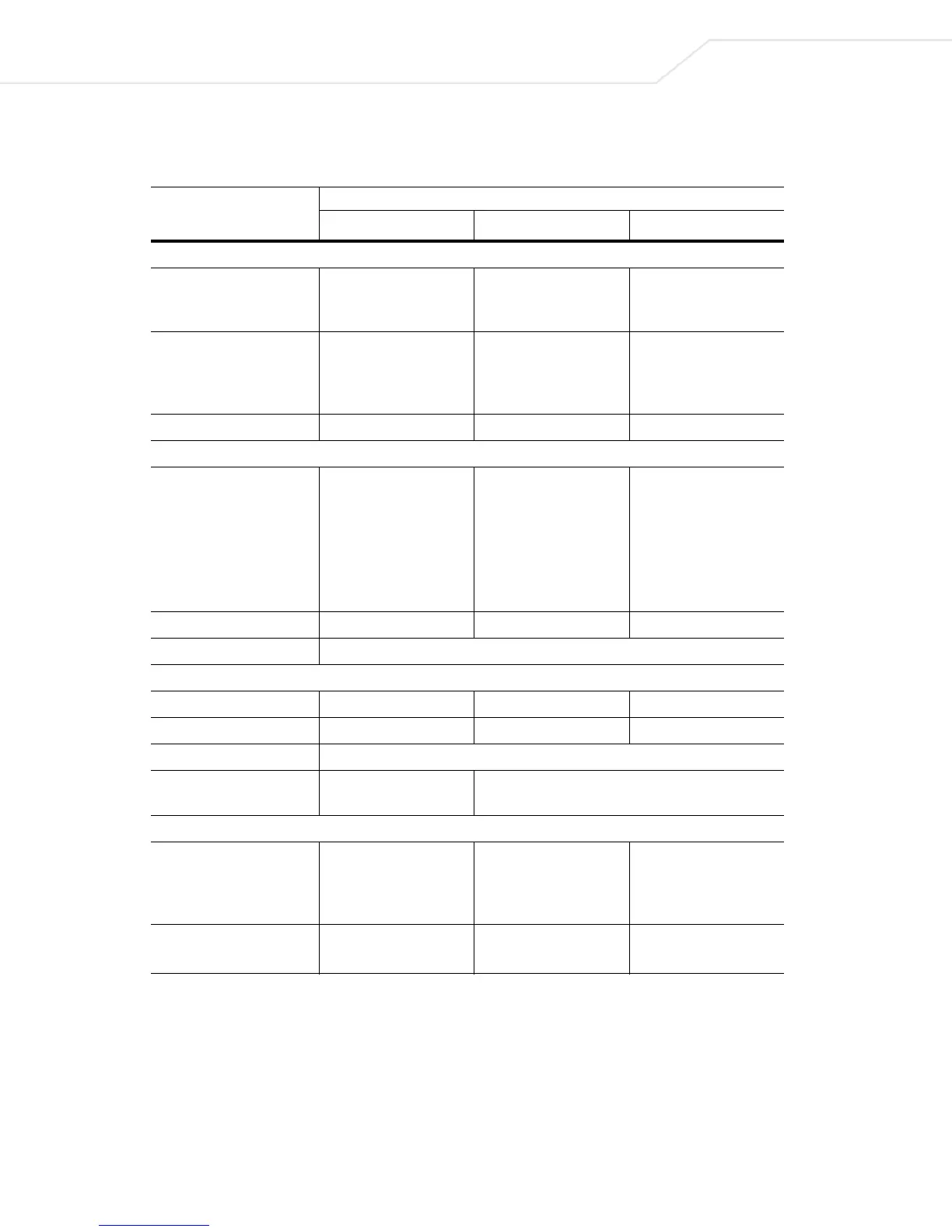
Table 1.1 summarizes the major differences between the protocols.
Table 1.1 Detailed Comparison of TLS-based EAP Methods
EAP Type
TLS (RFC 2716)
a
a.TLS is secure, but the requirement for client certificates is too big a hurdle for most institutions to deal
with.
TTLS (Internet draft)
b
b.TTLS, at least initially, is much more widely implemented than PEAP, and therefore has a slight
convenience advantage over the comparable PEAP method.
PEAP (Internet draft)
c
c. PEAP uses the TLS channel to protect a second EAP exchange. PEAP is backed by Microsoft.
Software
Supported Client Platforms Linux, Mac OS X,
Windows 95/98/ME,
Windows NT/2000/XP
Linux, Mac OS X,
Windows 95/98/ME,
Windows NT/2000/XP
Windows XP
Authentication Server
Implementations by
Cisco, Funk, HP,
FreeRADIUS (open
source), Meetinghouse,
Microsoft
Funk, Meetinghouse Cisco
Authentication Methods Client certificates Any Generic token card
Protocol Operations
Basic Protocol Structure Establish TLS session
and validate certificates
on both client and server
Two phases:
• Establish TLS
between client and
TTLS server
• Exchange attribute-
value pairs between
client and server
Two parts:
• Establish TLS
between client and
PEAP server
• Run EAP exchange
over TLS tunnel
Fast Session Reconnect No Yes Yes
WEP Integration Server can supply WEP key with external protocol (e.g. RADIUS extension)
PKI and Certificate Processing
Server Certificate Required Required Required
Client Certificate Required Optional Optional
Certificate Verification Through certificate chain or OCSP TLS extension (current Internet draft)
Effect of Private Key
Compromise
Re-issue all server and
client certificates
Re-issue certificates for servers (and clients if using
client certificates in first TLS exchange)
Client and User Authentication
Authentication Direction Mutual: Uses digital
certificates both ways
Mutual: Certificate for
server authentication,
and tunneled method for
client
Mutual: Certificate for
server, and protected
EAP method for client
Protection of User Identity
Exchange
No Yes; protected by TLS Yes; protected by TLS
 Loading...
Loading...