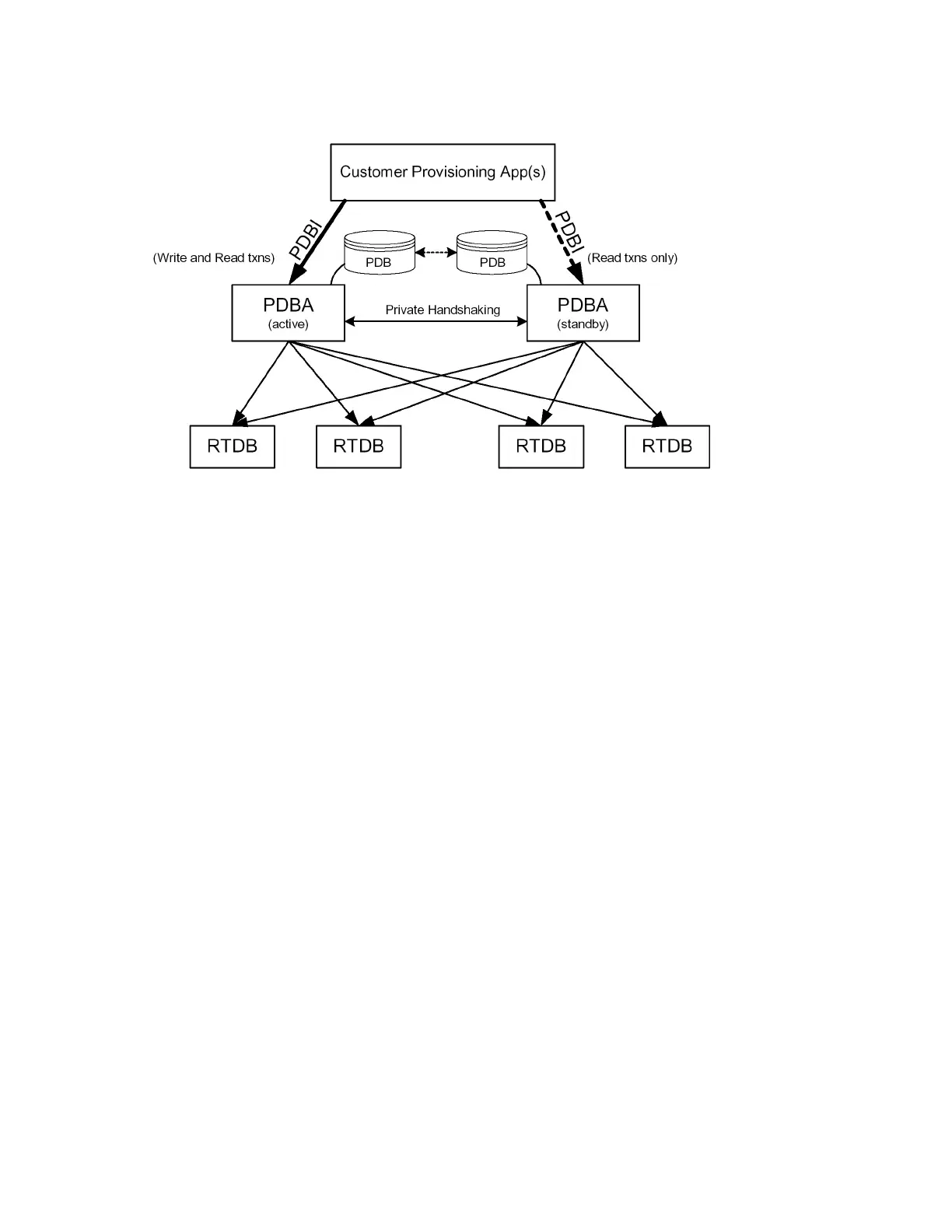
Figure 2: PDBI System Architecture
Updates that are sent to the active PDBA are also sent asynchronously to the standby PDBA after
being successfully committed into the active PDB. This methodology allows for provisioning to be
performed quickly from the PDBI client’s point of view because the client receives the success message
as soon as the update is committed to the active database. The client does not have to wait for the
update to be forwarded across their WAN and replicated on the standby database.
This design contains an inherent short delay between the time the active PDB receives the update and
when the standby PDB does. Because of this delay, clients only reading the database might be better
off reading from the standby PDBA. It should also be noted that both PDBA clients must be up for
the asynchronous replication to occur.
Note:
The active/standby status of the two PDBA processes can be switched through a PDBI command or
through the configuration user interface for the PDBA.
Also, the PDBA uses 5873 as its well-known listen port, although this value is modifiable through a
command line argument.
You can configure which PDBA forwards updates to an RTDB. Due to the asynchronous nature of the
PDBA replication, it is recommended that the RTDBs select the standby PDBA. This configuration
ensures that there are no problems with differing levels if the active PDBA is stopped while there are
many levels left to send to the standby PDBA. The RTDBs are guaranteed to always be on the PDBA
that has the lower level number.
System Overview and Terminology
Figure 3: MPS/EPAP System Configuration shows a block diagram of the MPS/EPAP platform. It also
shows a mated pair of EAGLE 5 ISSs. The EAGLE 5 ISSs are the large blocks at the bottom. The MPSs,
which are attached to the EAGLE 5 ISSs, are above the EAGLE 5 ISSs and contain EPAP A and EPAP
B.
An MPS system consists of two MPS servers and associated hardware, including a modem, CD-ROM,
etc. Each EAGLE 5 ISS in a mated pair has one MPS system attached. The two MPS systems are referred
22
910-6022-001 Revision A, March 2011
Functional DescriptionProvisioning Database Interface Manual
 Loading...
Loading...