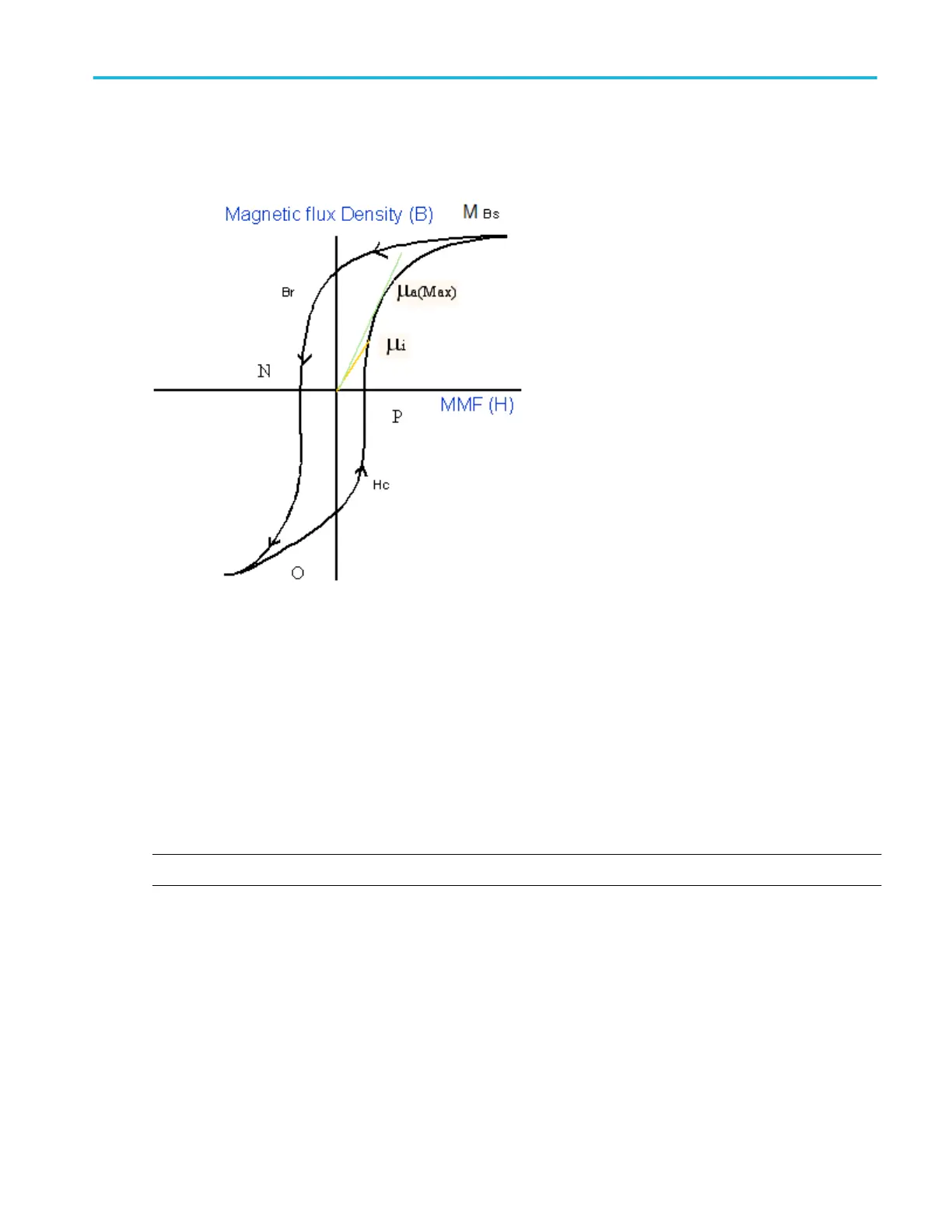
Magnetic Property algorithm. The following diagram shows a plot of Hysteresis in a typical magnetic material (magnetic field
strength (H) versus saturation flux density (B)).
Figure 12: BH Curve
B
s
is the Saturation Flux Density
B
r
is the Remanence Flux Density
H
c
is the Coercive Force (Hc)
U
i
is the Initial Permeability
U
a
is the Max Amplitude permeability
H is the magnetic field used to induce Magnetic Flux in the magnetic material
MMF is Magneto Motive Force, it is also known as Magnetic Field Strength
NOTE. The data waveform starts from the Max value of H, decreases, and then increases again (M-N-O-P).
Magnetic Field Strength (H)
The previous figure shows the hysteresis in a typical magnetic material. The magnetic field induces a magnetic flux in the DUT.
The units of measurement are Ampere per meter in SI unit, and Oersted in CGS unit.
Saturation Flux Density (B
s
)
The Saturation Flux Density represents maximum magnetic flux density that can be induced in the magnetic material regardless
of the magnitude of the externally applied field H. This is represented in the BH Curve were B value is considered, when H is
maximum.
B
s
= Max (Bk)
The Magnetic Field Intensity H is also calculated on the maximum flux density cycle Bk.
B
s
= Max (B)
Measurement algorithms
MSO54, MSO56, MSO58, MSO58LP, MSO64 Help 473

 Loading...
Loading...