LE910Cx Hardware Design Guide
1VV0301298 Rev.40 Page 59 of 149 2023-03-16
Not Subject to NDA
A protection diode must be inserted close to the power input to protect the
LE910Cx module from power polarity inversion. This can be the same diode as for
spike protection.
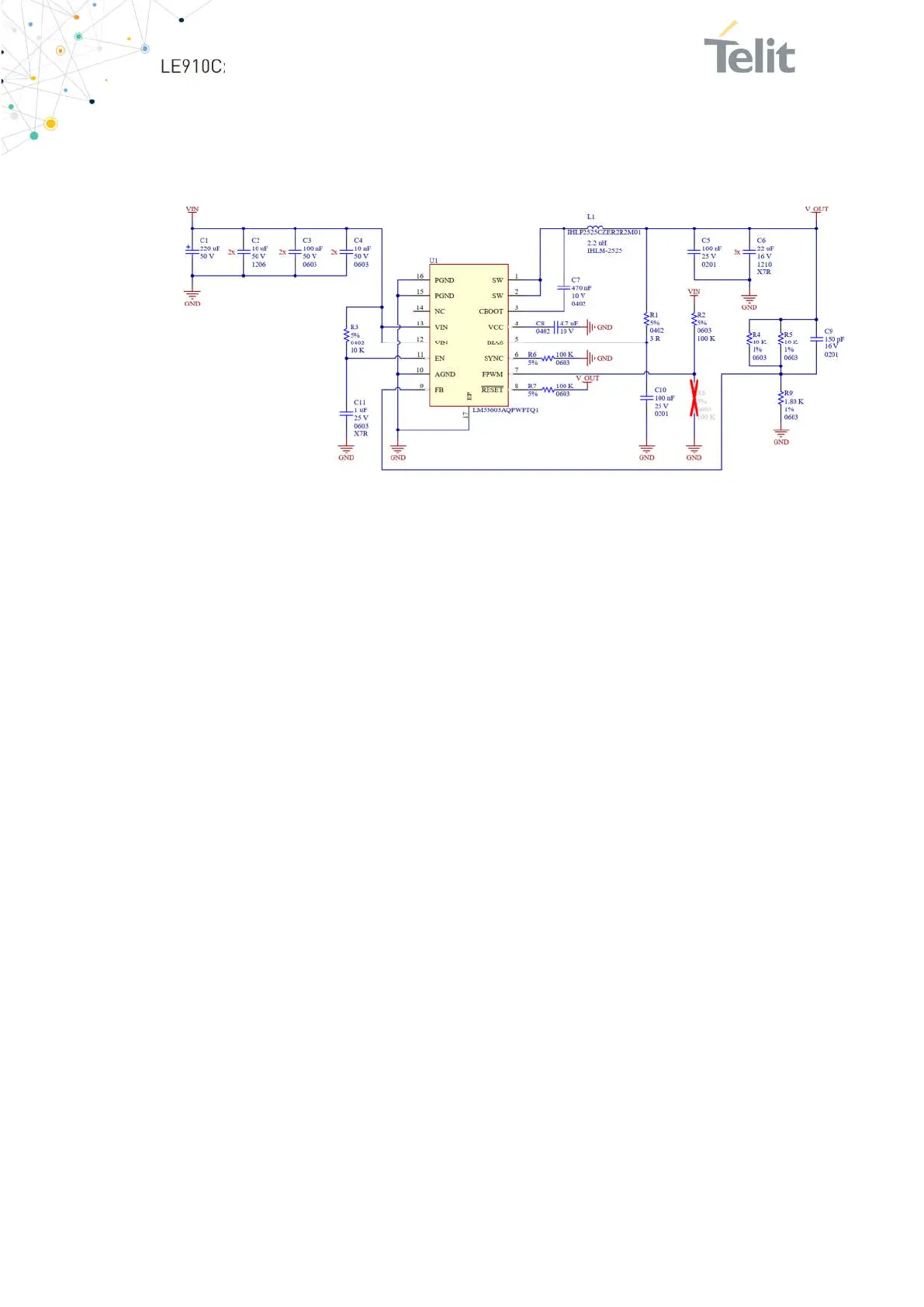
Figure 15: Example of Switching Regulator with 12V Input
6.3.1.3. Battery Source Power Supply – Design Guidelines
The desired nominal output for the power supply is 3.8V, and the maximum voltage
allowed is 4.2V. Hence, a single 3.7V Li-Ion cell battery type is suitable for
supplying the power to the LE910Cx module.
LiFePO
4
batteries with 3.2V nominal voltage range between 2.5V (0% charge) and
3.65V (100% charge), therefore they are not an optimal choice for direct powering
the modem. In case you are using a LiFePO4 battery, you can add a buck-boost
converter to supply the modem with constant 3.8V.
Primary Lithium batteries such as LiSOCl
2
batteries have 3.6V nominal voltage but
generally they have high internal resistance and the voltage drop during current
absorption peaks is high and can exceed the operating range of the modem,
especially when battery is partially depleted. Bobbin types are more affected by
this drop than spiral types. You should carefully evaluate the voltage drop during
modem operation and, in case, either add a DCDC converter to boost the voltage
inside the modem operating range or add capacitance to supply the current peaks.
Some LiSoCl
2
batteries come already paired with a hybrid layer capacitor to
support high current peaks without too much voltage drop.

 Loading...
Loading...