DRAW Instructions 8-19
8308DRAW.DOC TI-83 international English Bob Fedorisko Revised: 02/19/01 12:29 PM Printed: 02/19/01 1:49
PM Page 19 of 20
A graph database (
GDB
) contains the set of elements that
defines a particular graph. You can recreate the graph from
these elements. You can store up to 10
GDB
s in variables
GDB1 through GDB9, or GDB0 and recall them to recreate
graphs.
A
GDB
stores five elements of a graph.
•
Graphing mode
•
Window variables
•
Format settings
•
All functions in the
Y=
editor and the selection status of
each
•
Graph style for each
Y=
function
GDB
s do not contain drawn items or stat plot definitions.
To store a graph database, follow these steps.
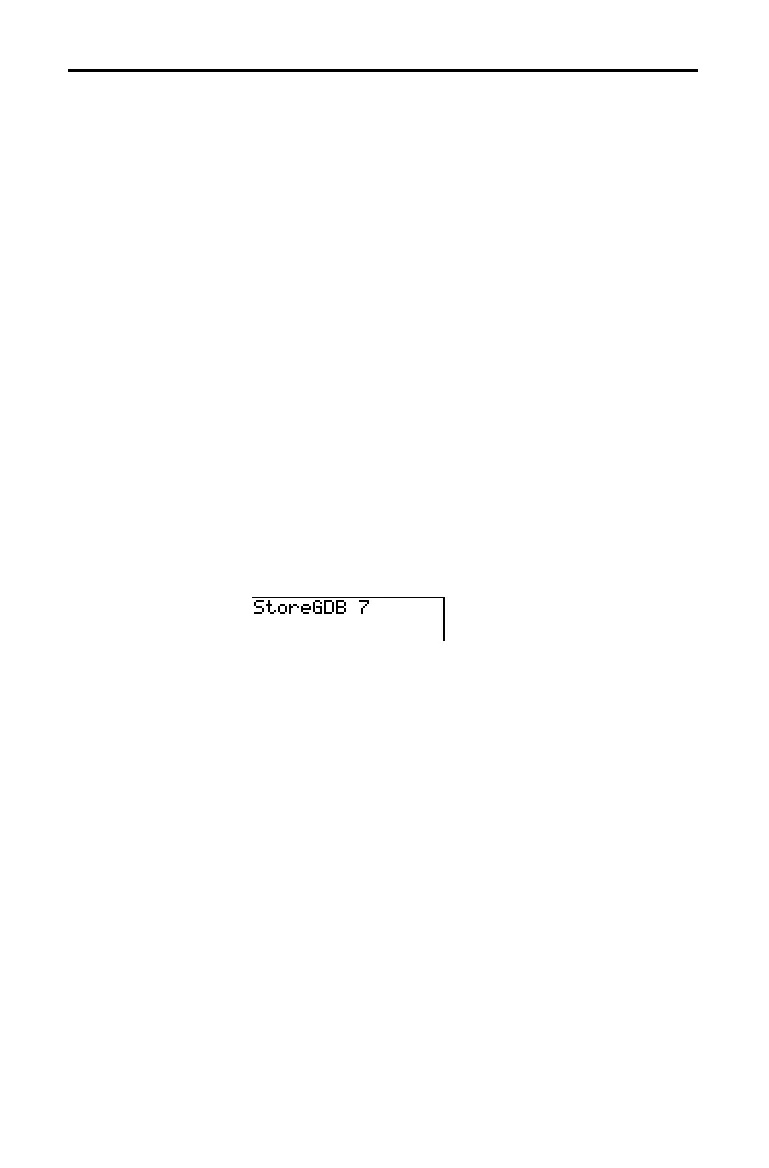
1. Select
3:StoreGDB from the
DRAW STO
menu. StoreGDB
is pasted to the current cursor location.
2. Enter the number (from
1 to 9, or 0) of the
GDB
variable
to which you want to store the graph database. For
example, if you enter
7, the TI
-
83 will store the
GDB
to
GDB7.
Note:
You also can select a variable from the
GDB
secondary
menu (
3
). The variable is pasted next to
StoreGDB
.
3. Press
Í
to store the current database to the
specified
GDB
variable.
Storing Graph Databases (GDBs)
What Is a Graph
Database?
Storing a Graph
Database

 Loading...
Loading...











