Appendix A: Functions and Instructions 813
log() CATALOG
log(
expression1
) ⇒
expression
log(
list1
) ⇒
list
Returns the base-10 logarithm of the argument.
For a list, returns the base-10 logs of the elements.
log(2.0)
¸ .301
...
If complex format mode is
REAL
:
log({ë 3,1.2,5})
¸
Error: Non-real result
If complex format mode is
RECTANGULAR
:
log({ë 3,1.2,5})
¸
{
ln(3)
ln(10)
+
p
ln(10)
øi .079...
ln(5)
ln(10)
}
log(
squareMatrix1
) ⇒
squareMatrix
Returns the matrix base-10 logarithm of
squareMatrix1
. This is
not
the same as calculating the
base-10 logarithm of each element. For information
about the calculation method, refer to
cos()
.
squareMatrix1
must be diagonalizable. The result
always contains floating-point numbers.
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular complex
format mode:
log([1,5,3;4,2,1;6,ë 2,1]) ¸
.795…+.753…øi .003…ì.647…øi …
.194…ì.315…øi .462…+.270øi …
ë.115…ì.904…øi .488…+.777…øi …
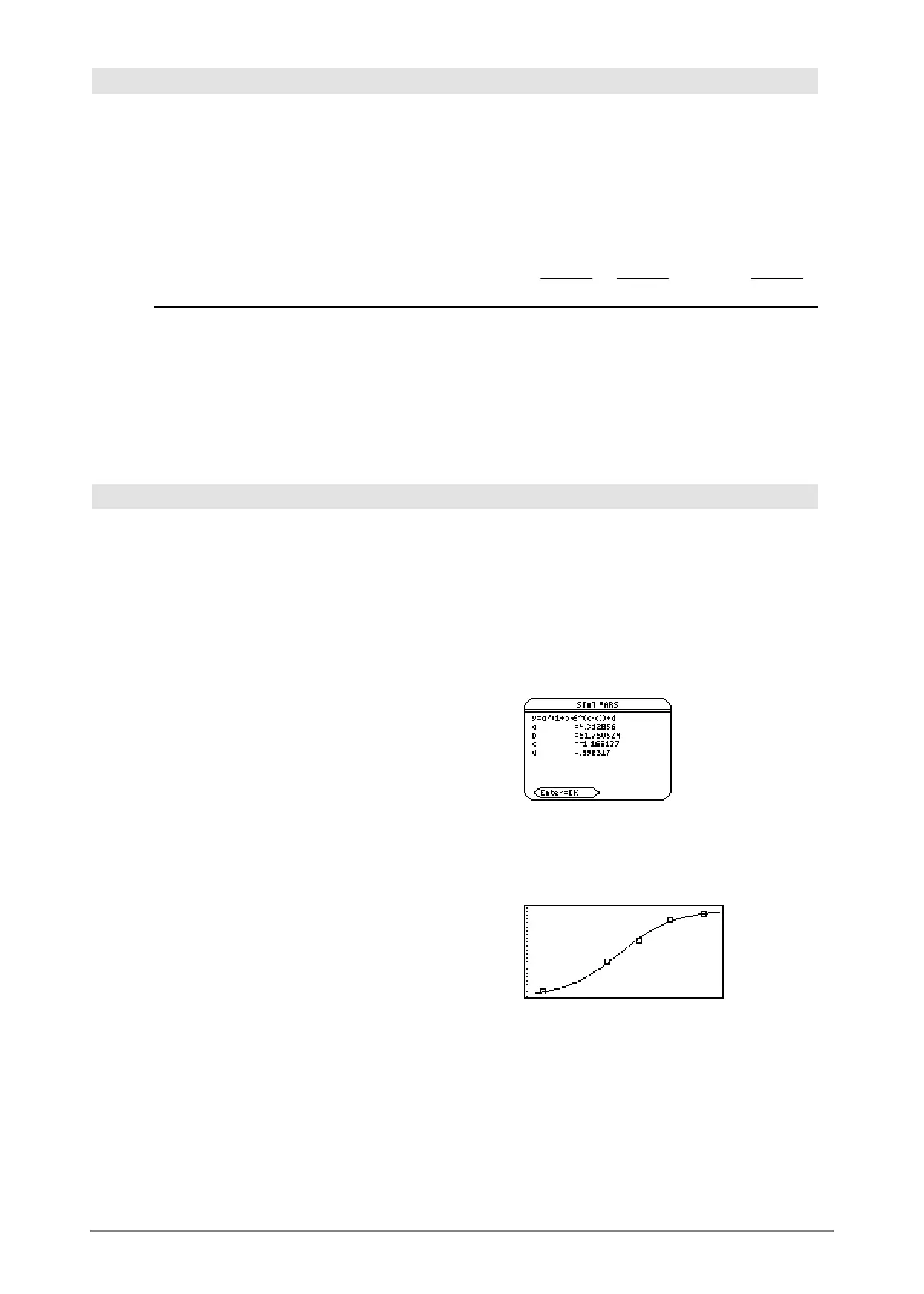
Logistic MATH/Statistics/Regressions menu
Logistic
list1
,
list2
[ , [
iterations
] , [
list3
] [,
list4
,
list5
] ]
Calculates the logistic regression and updates all
the system statistics variables.
All the lists must have equal dimensions except for
list5
.
list1
represents xlist.
list2
represents ylist.
list3
represents frequency.
list4
represents category codes.
list5
represents category include list.
iterations
specifies the maximum number of times a
solution will be attempted. If omitted, 64 is used.
Typically, larger values result in better accuracy but
longer execution times, and vice versa.
Note:
list1
through
list4
must be a variable name or
c1–c99 (columns in the last data variable shown in
the Data/Matrix Editor).
list5
does not have to be a
variable name and cannot be c1–c99.
In function graphing mode:
{1,2,3,4,5,6}! L1 ¸ {1 2 3 …}
{1,1.3,2.5,3.5,4.5,4.8}! L2
¸
{1 1.3 2.5 …}
Logistic L1,L2 ¸ Done
ShowStat ¸
¸
regeq(x)! y1(x) ¸ Done
NewPlot 1,1,L1,L2 ¸ Done
¥%
„ 9
 Loading...
Loading...











